FTSE 100 Index: What is it and How To Trade in It?
FTSE 100 index is a share index that lists 100 companies on the London Stock Exchange by full market value. The FTSE group maintains this index.
- What is FTSE 100 index?
- FTSE Index Constituents
- Top FTSE 100 Index Constituents
- Returns on FTSE 100 Index Constituents
- Calculations
- Trading the FTSE 100
- Returns
What is FTSE 100 Index?
FTSE 100 index is a market-capitalization weighted index for the UK-listed blue chip companies. It is managed by the FTSE group. There are other popular indexes within the group including FTSE 250, FTSE 350 and FTSE All-share. All these indexes have index fund offerings in Vanguard FTSE 100, Vanguard FTSE 250, iShares 350 U.K. Equity Index Fund and the Vanguard FTSE UK All Share Index Unit Trust.
This market capitalization-weighted index replaced the price-weighted FT30 index. It is the performance benchmark for investors and is the most widely used US stock market indicator. Most investors in the FTSE 100 index explore opportunities for the big U.K. companies. A company must be listed on the London Stock Exchange in order to be included in this index. It must be denominated in Euro or sterling. It should also meet tests on nationality, free float and stock liquidity requirements.
FTSE Index at a Glance
| Parameters | Data |
| Constituent Quantity | 100 |
| Net MCap (GBPm) | 1,781,113 |
| Dividend Yield | 3.91% |
| Weight of the largest FTSE constituent | 9.22% |
| MCap of the Top 10 Holdings | 51.19% |
Best-suited Capital Markets courses for you
Learn Capital Markets with these high-rated online courses
Index Constituents
All FTSE 100 constituents are traded on the SETS trading system of the London Stock Exchange. These FTSE index constituents are reviewed every quarter during which some companies enter and exit the index. This impacts the share prices. The following companies are the part of FTSE 100 index:
| Company |
| 3i |
| Abrdn |
| Admiral Group |
| Airtel Africa |
| Anglo American plc |
| Antofagasta |
| Ashtead Group |
| Associated British Foods |
| AstraZeneca |
| Auto Trader Group |
| Avast |
| Aveva |
| Aviva |
| B&M |
| BAE Systems |
| Barclays |
| Barratt Developments |
| Berkeley Group Holdings |
| BP |
| British American Tobacco |
| British Land |
| BT Group |
| Bunzl |
| Burberry |
| Coca-Cola HBC |
| Compass Group |
| CRH plc |
| Croda International |
| DCC plc |
| Dechra Pharmaceuticals |
| Diageo |
| Electrocomponents |
| Entain |
| Evraz |
| Experian |
| Ferguson plc |
| Flutter Entertainment |
| Fresnillo |
| GlaxoSmithKline |
| Glencore |
| Halma |
| Hargreaves Lansdown |
| Hikma Pharmaceuticals |
| HSBC |
| IHG Hotels & Resorts |
| Imperial Brands |
| Informa |
| Intermediate Capital Group |
| International Airlines Group |
| Intertek |
| ITV plc |
| JD Sports |
| Kingfisher |
| Land Securities |
| Legal & General |
| Lloyds Banking Group |
| London Stock Exchange Group |
| M&G |
| Meggitt |
| Melrose Industries |
| Mondi |
| National Grid plc |
| NatWest Group |
| Next plc |
| Ocado Group |
| Pearson plc |
| Pershing Square Holdings |
| Persimmon plc |
| Phoenix Group |
| Polymetal International |
| Prudential plc |
| Reckitt |
| RELX |
| Rentokil Initial |
| Rightmove |
| Rio Tinto |
| Rolls-Royce Holdings |
| Royal Mail |
| Sage Group |
| Sainsbury’s |
| Schroders |
| Scottish Mortgage Investment Trust |
| Segro |
| Severn Trent |
| Shell |
| DS Smith |
| Smiths Group |
| Smith & Nephew |
| Smurfit Kappa |
| Spirax-Sarco Engineering |
| SSE plc |
| Standard Chartered |
| St. James’s Place plc |
| Taylor Wimpey |
| Tesco |
| Unilever |
| United Utilities |
| Vodafone Group |
| Whitbread |
| WPP plc |
Top 5 FTSE Constituents
As on September 2022, the following are the top 5 FTSE index constituents:
| Constituent | Sector |
| Shell SHEL | Oil, Gas and Coal |
| Aviva AV. | Insurance |
| Standard Chartered | Banking |
| Prudential | Banking |
| Diageo | Beverages |
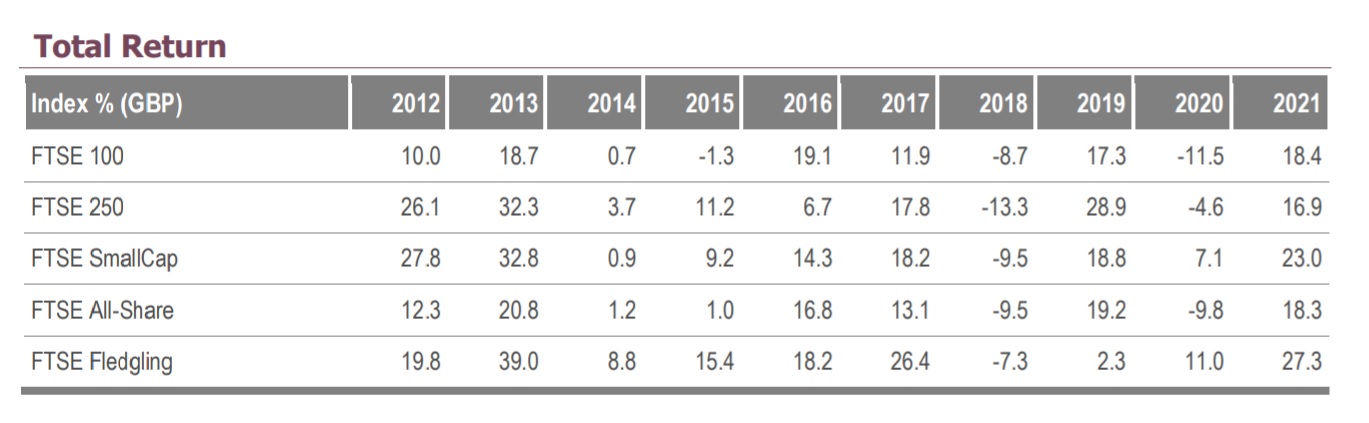
Returns on FTSE 100 Index Constituents
FTSE 100 Index Calculation
The FTSE 100 level is calculated through the total market capitalization of constituent companies and the index value. The total market capitalization and individual share prices of the indexed companies change throughout the trading day. As a result, the index value also changes.
When the FTSE 100 is either quoted up or down, it is measured against the close of the previous day’s market. It is calculated in real-time and is published every second when the market is open, it is continuously calculated on each trading day. The timing is from 8:00 a.m. (market opening) to 4:30 p.m. (LSE close). A decline in the index means that the value of the largest listed UK companies has decreased. When the index hits a new high, it indicates that the total worth of all indexed companies has increased.
Readjustments in the index constituents (companies in the FTSE 100) occur every quarter. Most of the time, this happens on the Wednesday following the first Friday of March, June, September, and December. Any change in the underlying index constituents and weighting comes from companies’ value taken at the closing of business. This happens the night before the review.
Weighting
Share prices are weighted through free-float capitalization in FTSE indices. Since the larger companies have more stock “floating”, they can make a significant difference to the index. The formula for these indices is:
Here, the free float adjustment factor indicates the percentage of issued shares that are available for trading. It is rounded up to the nearest multiple of 5%. The free-float capitalisation of the company is equal to the market capitalisation multiplied by the free-float adjustment factor. It does not include restricted stocks.



All About FTSE 100 Trading
Trading in FTSE 100 is possible with derivatives such as spread bets and CFDs. These allow price movements speculation without owning underlying assets. Both products are leveraged. You will get full exposure with a small deposit called margin. With leverage, there is a fair possibility of both losses and profits that can outweigh your deposit. The reason behind this possibility is that these are calculated on the position’s full size and not its margin. You can trade spread bets without the need of paying any tax. You can offset CFD losses against profits. With CFDs and spread bets, you gain access to cash indices and index futures.
How to buy a FTSE stock?
You do not have the option to directly invest in FTSE 100. Instead, you have the option to invest in an ETF or index fund. This tracks the stock performance in the FTSE 100 index.
Returns on FTSE
Returns depend on the factors impacting individual companies and industries on the index. This ultimately impacts the index price. Following are the annual returns since 1969:
| Year | Level of Closing | Change In Index (in points) | Change In Index (in %) |
| 1969 | 313.16 | _ | _ |
| 1970 | 289.61 | −23.55 | −7.52 |
| 1971 | 411.03 | 121.42 | 41.93 |
| 1972 | 463.72 | 52.69 | 12.82 |
| 1973 | 318.30 | −145.42 | −31.36 |
| 1974 | 142.17 | −176.13 | −55.33 |
| 1975 | 335.98 | 193.81 | 136.32 |
| 1976 | 322.98 | −13.00 | −3.87 |
| 1977 | 455.96 | 132.98 | 41.17 |
| 1978 | 468.06 | 12.10 | 2.65 |
| 1979 | 488.40 | 20.34 | 4.35 |
| 1980 | 620.60 | 132.20 | 27.07 |
| 1981 | 665.50 | 44.90 | 7.23 |
| 1982 | 812.37 | 146.87 | 22.07 |
| 1983 | 1,000.00 | 187.63 | 23.10 |
| 1984 | 1,232.20 | 232.20 | 23.22 |
| 1985 | 1,412.60 | 180.40 | 14.64 |
| 1986 | 1,679.00 | 266.40 | 18.86 |
| 1987 | 1,712.70 | 33.70 | 2.01 |
| 1988 | 1,793.10 | 80.40 | 4.69 |
| 1989 | 2,422.70 | 629.60 | 35.11 |
| 1990 | 2,143.50 | −279.20 | −11.52 |
| 1991 | 2,493.10 | 349.60 | 16.31 |
| 1992 | 2,846.50 | 353.40 | 14.18 |
| 1993 | 3,418.40 | 571.90 | 20.09 |
| 1994 | 3,065.50 | −352.90 | −10.32 |
| 1995 | 3,689.30 | 623.80 | 20.35 |
| 1996 | 4,118.50 | 429.20 | 11.63 |
| 1997 | 5,135.50 | 1,017.00 | 24.69 |
| 1998 | 5,882.60 | 747.10 | 14.55 |
| 1999 | 6,930.20 | 1,047.60 | 17.81 |
| 2000 | 6,222.46 | −707.74 | −10.21 |
| 2001 | 5,217.35 | −1,005.11 | −16.15 |
| 2002 | 3,940.36 | −1,276.99 | −24.48 |
| 2003 | 4,476.87 | 536.49 | 13.62 |
| 2004 | 4,814.30 | 337.57 | 7.54 |
| 2005 | 5,618.76 | 804.46 | 16.71 |
| 2006 | 6,220.81 | 602.05 | 10.71 |
| 2007 | 6,456.91 | 236.10 | 3.80 |
| 2008 | 4,434.17 | −2,022.74 | −31.33 |
| 2009 | 5,412.88 | 978.71 | 22.07 |
| 2010 | 5,899.94 | 487.06 | 9.00 |
| 2011 | 5,572.28 | −327.66 | −5.55 |
| 2012 | 5,897.81 | 325.53 | 5.84 |
| 2013 | 6,749.09 | 851.29 | 14.43 |
| 2014 | 6,566.09 | −183.00 | −2.71 |
| 2015 | 6,274.05 | −292.04 | −4.45 |
| 2016 | 7,142.83 | 868.78 | 13.85 |
| 2017 | 7,687.77 | 544.94 | 7.63 |
| 2018 | 6,728.13 | −959.64 | −12.48 |
| 2019 | 7,542.44 | 814.31 | 12.10 |
| 2020 | 6,460.52 | −1,081.92 | −14.34 |
| 2021 | 7,384.54 | 924.02 | 14.30 |

Jaya is a writer with an experience of over 5 years in content creation and marketing. Her writing style is versatile since she likes to write as per the requirement of the domain. She has worked on Technology, Fina... Read Full Bio