An Insight On Use Case Modelling
This article will help readers in understanding Use Case Modelling. Through this concept, one can easily understand user-system interaction.
Table of Contents
Use Case Modelling is a widely approached mechanism across industries. It gives you an insight into the interaction between users and the system. It is an illustrative method to represent a process broken as per system functionality.
Use Case Modelling explains the inception of a process, its implicit and explicit dimensions. The term “Implicit” means mandatory steps carried out to accomplish a functionality. “Explicit” means steps taken up by you as per the choice of optional functions.
Use Case Modelling is widely used in industries such as IT, aviation, electronics, metal, automobiles and e-commerce etc. The increasing demand for process orientation has played a vital role in exploring Use Case Modelling.
Best-suited Data Science courses for you
Learn Data Science with these high-rated online courses
Actors
Almost all industries involve customers or the end-users, systems and their functions and administrators. You can categorize actors as given below:
1. User/s
The actors who are directly involved in order to execute a function are called Primary users. They can be human or systems.
You can generalize users as primary, secondary and various other types of users who have a provision to initiate the function. For example, SBI FAST (Funds Available At Shortest Time) has an app called SBI FAST downloaded by end-user such as registered “Corporates” for Cheque Management services and configured SBI back office team members in the system.
Thus, the primary users are corporates and the secondary users are the backend team members. This kind of user categorization is called user generalization. We also have “External Actors” and “Systems” such as infra support required to run the application. For example servers, hardware, SMSC gateway etc.



2. Secondary User
Those actors that support a specific functionality to function in the desired manner. It is a supportive system/s in close cohesion with the architecture layout as designed. These users are mainly responsible for maintaining the service 24 x 7.
3. External Users
All the hardware systems come under this tree.
Tools Used in Use Case Modelling
Below are the illustration tools used in Use Case Modelling:
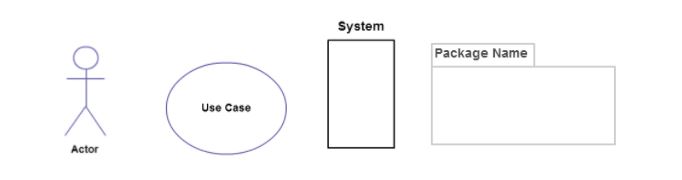
- Oval Shape: We use this shape to name the use case or functions that are supported in the system.
- Connectors: It is used to connect functionalities are admin.
- Include: Include is an implicit action required to run a functionality.For example the login should be successful to access internet banking facilities and it is an include function.
- Extend: It is the explicit function that is often referred as “Optional”. For example: – for a telecom subscriber post purchasing the primary offer, the purchase of Add On is secondary.
- System name: It represents the defined scope of a Use Case. However, it is an optional stencil used for huge representation and helpful in grouping.
- Package: It is used to represent group of use case based upon certain similarities.
Icons are represented as below: –
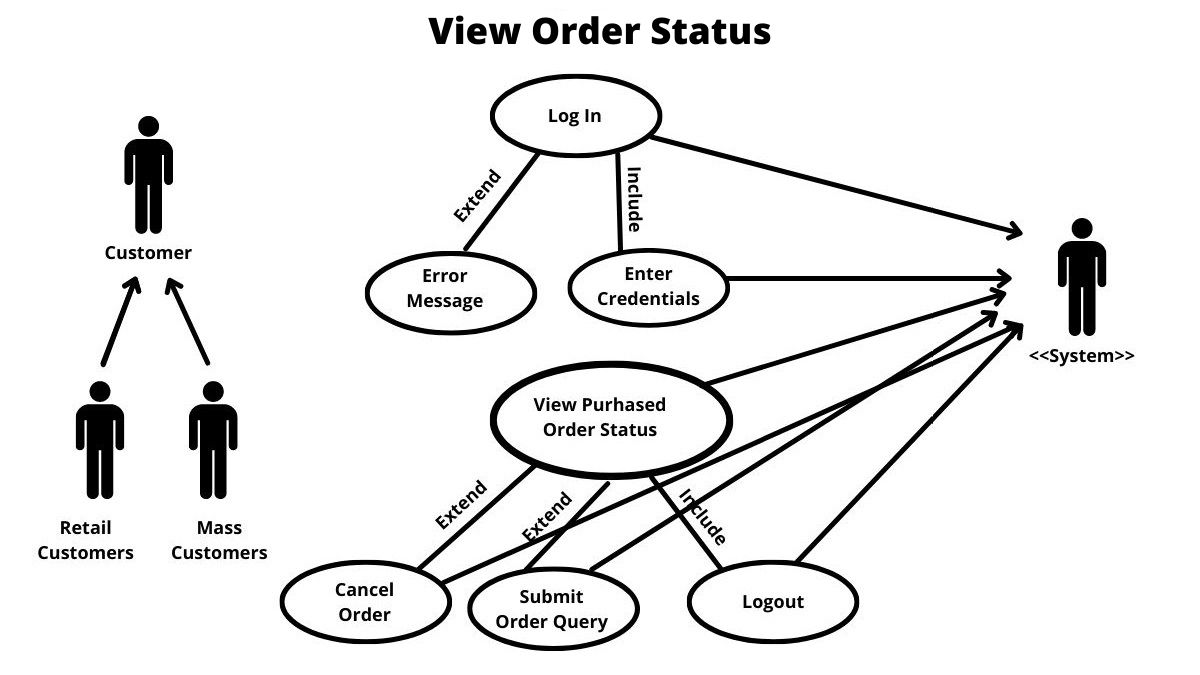
Use Case Model diagram on “View (Track) Order Status”-
In the above diagram, the subscriber is an actor who has a provision to track and manage orders through the “View Order Status” functionality post order submission.
The customer will log in as an implicit function. Login failure error message will get populated as part of the explicit function.
The customer can view purchased orders and can also perform explicit functions such as Cancel order or submit order query. The customer has an implicit function of log out or there will be auto log out by the system if no activity is found.
“Use Case Modelling” is a widely discussed topic and focuses on a breakdown approach of functionality. You can break complex functions with the help of “Use Case Modelling”.
Top Trending Articles:
Data Analyst Interview Questions | Data Science Interview Questions | Machine Learning Applications | Big Data vs Machine Learning | Data Scientist vs Data Analyst | How to Become a Data Analyst | Data Science vs. Big Data vs. Data Analytics | What is Data Science | What is a Data Scientist | What is Data Analyst
_______________
Recently completed any professional course/certification from the market? Tell us what you liked or disliked in the course for more curated content.
Click here to submit its review with Shiksha Online.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio