Top 46 CCNA Interview Questions and Answers
Are you preparing for a CCNA interview? Check out these common CCNA interview questions to help you ace your interview. From topics like VLANs and routing protocols to subnetting and network security, these questions will test your knowledge and readiness for a career in networking. Don’t miss this opportunity to boost your chances of success!
If you want to succeed in your next CCNA interview, here is a carefully curated list of CCNA interview questions and answers that will come in handy in your preparation. In this blog, we have listed the 45 most frequently asked CCNA interview questions that will help both the freshers and experienced candidates boost their interview preparation.
Top CCNA Interview Questions and Answers
The list of commonly asked interview-related CCNA questions and answers is given below:
Best-suited Cyber Security courses for you
Learn Cyber Security with these high-rated online courses
Q1. What is a ‘router’?
Ans. A router is a device that forwards data packets along with a network.
Q2. What is a ‘protocol’ in networking?
Ans. A protocol in networking is a set of invisible computer rules that enable two devices to connect and transmit data to one another.
Q3. Differentiate between a switch and a hub.
Ans. Switches are used at the data link layer, while hubs are used at the physical layer.
Explore courses related to CCNA:
| Popular Networking and Hardware Courses | Top Cybersecurity Courses |
| Top Cisco Certifications Courses | Popular Big Data Courses |
Q4. How many layers are there in an OSI reference model? Name them.
Ans. There are 7 layers in an OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) reference model. They are:
- Physical layer
- Data link layer
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Session layer
- Presentation layer
- Application layer
Q5. Explain the difference between a ‘broadcast domain’ and a ‘collision domain’.
Ans. A broadcast domain is a logical division of a computer network in which all nodes can reach others by broadcast at the data link layer.
A collision domain is a network section where data packets can collide with one another when sent on a shared medium or through repeaters.
Q6. What is the size of an IP address?
Ans. 32 it for IPv4 and 128 bit for IPv6.
Gearing up for a Cisco interview? Check out the frequently asked Cisco Interview Questions and Answers
Q7. What is a DLCI?
Ans. DLCI (Data Link Connection Identifiers) uniquely identifies each virtual circuit on the network.
Q8. Name different types of networks.
Ans. There are two types of networks – 1) peer-to-peer and 2) server-based.
Learn about different levels, scope, and career benefits of Cisco Certifications, read our blog – what is cisco certification?
Q9. What is the difference between a ‘half-duplex’ and a ‘full-duplex’ system?
Ans. In a half-duplex system, communication occurs in only one direction, while in a full-duplex system, communication occurs in both directions.
Q10. What is PoE (Power over Ethernet)?
Ans. Power over Ethernet (PoE) refers to the technology allowing electric power and data on Ethernet cabling.
Q11. Explain the use of ‘ping’ command.
Ans. Ping (Packet Internet Groper) is a computer network tool that tests whether a particular host is reachable across an IP network.
Q12. Explain ‘round-trip time’.
Ans. Round-trip time, or round-trip delay, is the time required for a packet to travel from a specific source to a specific destination and back again.
Explore the best Networking Courses
Q13. What is the difference between public and private IP?
Ans. Public IP is used across the internet, while private IP is used within the local LAN.
Q14. What is the difference between ‘cross cable’ and ‘straight cable’?
Ans. Cross cables connect the same group of devices, while straight cables connect different devices.
Q15. At which layer of OSI does frame relay technology work?
Ans. At the data link layer.
Also, explore:
- Paid and free online courses by Coursera
- Popular online Udemy courses
- Top online edX courses
Q16. What is the size of a Cisco ping packet?
Ans. The size of a Ping packet in Cisco by default is 100 bytes.
Q17. How many VTP modes are in a switch? Name them.
Ans. There are three types of VTP modes. They are – server, client, and transparent.
Q18. Explain the difference between static and dynamic IP addressing.
Ans. Dynamic IP addresses can change every time a device connects to the internet. Static IP addresses are reserved. They do not change with time.
Q19. What is a ‘subnet’?
Ans. Subnets are used in IP networks to optimize the performance of a network because it reduces traffic by breaking a large network into smaller networks.
To learn about Networking Courses, Skills and Careers, read our blog – what is Networking?
Q20. What does MTU stand for? What is the default size?
Ans. MTU stands for the maximum transmission unit. The default MTU size is 1500 bytes.
Q21. When does network congestion occur?
Ans. Network congestion happens when applications send more data than the network devices like routers and switches can accommodate. This is a common occurrence when many users try using the same bandwidth.
Q22. What is the LLC sublayer, and what is its function?
Ans. LLC is an abbreviation for Logical Link Control and offers application developers optional services. These options include providing flow control to the network layer using stop/start codes. It also corrects an error in the network.
Q23. What is BootP?
Ans. BootP or Boot Program is a protocol for booting diskless workstations in a network. These diskless workstations use BootP to determine their and a server’s IP addresses.
Q24. What is 100BaseFX?
Ans. 100BaseFX is a version of Fast Ethernet that uses fibre optic cable as the main transmission medium for wiring campus backbones. 100 stands for data speed in Mbps.
Do CCNA certifications guarantee a good career? Find out in our blog – Is CCNA Training the Right Choice for Networking Professionals?
Q25. What is HDLC?
Ans. HDLC stands for High-Level Data-Link Control protocol. It is a popular ISO-standard, bit-oriented Data Link layer protocol for transmitting data. It is applicable for both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communications.
HDLC organizes data into frames that allow the devices to control the data flow. The frame is transmitted via the network to the destination that verifies its successful arrival.
Some of the benefits of HDLC are:
- Supports both half and full-duplex communication.
- Offers full data transparency.
- Offers flexibility, reliability, and efficiency of operation for synchronous data communication.
- Supports both synchronous and asynchronous communication.
Q26. Explain VLAN.
Ans. It is the abbreviation for Virtual Local Area Network. It provides data link connectivity for a subnet.
Check out the list of Top Online IT Courses
Q27. What are the benefits of using VLANs?
Ans. There are three primary benefits of using VLANs, which include –
- Security, reduced number of trunk links
- Reduced costs
- Allows creating collision domains other than physical locations
Q28. What is latency?
Ans. It is the time a data packet takes to move from one designated point to another.
Also Read: Most In-Demand Tech Skills to Master
Q29. Can you tell me which is the second layer of an OSI layer model?
Ans. The data link layer is the second layer of an OSI model.
Q30. What is BOOTP?
Ans. It is the short form of Bootstrap Protocol. BOOTP is a computer networking protocol used in IP networks for automatically assigning an IP address to network devices from a configuration server.
Q31. Tell me the easiest way to configure a router remotely.
Ans. The most popular and easy way to configure a router remotely is using Cisco AutoInstall Procedure. However, it should ensure the router is connected to the WAN or LAN.
Explore Free Online Courses with Certificates
Q32. What is Route Poisoning?
Ans. Route Poisoning is making a route unreachable by inserting a table entry of 16 into it. This is done to prevent the problems of inconsistent updates on a route.
Q33. Name different types of passwords that can be used to secure a CISCO router.
Ans. 5 types of passwords can be used to secure a CISCO router, and these are –
- Console
- Aux
- VTY
- Enable password
- Enable secret
Q34. Why should we use network segmentation to manage a large network?
Ans. Segmenting a network helps to ease network traffic and ensures that users receive high bandwidth at all times. This translates to better performance, especially for a growing network.
Boost your networking interview preparation. Read our detailed networking interview questions and answers blog.
Q35. Which IP address is used for the loopback address and why?
Ans. 127.0.0.1 is used for the loopback address. A loopback address is a special IP address that a network administrator uses to treat the local machine as a remote machine. It is also used for local testing. Any traffic sent by a computer program on the loopback network is addressed to the same computer.
Q36. In the case of RIP, what route entry will be assigned to a dead or invalid route?
Ans. 16 hops will be assigned to a dead or invalid route in case of RIP.
Q37. Explain the different memories used in a CISCO router.
Ans. The following are the different memories used in a CISCO router:
- NVRAM (Non-Volatile Random Access Memory) – It stores the startup configuration file.
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) – It stores the configuration file being executed.
- ROM (Read Only Memory) – The bootstrap software runs and maintains instructions for POST diagnostics.
- Flash Memory – It stores the Cisco IOS.
Check out the popular Cisco Certifications Courses
Q38. What is the difference between User Mode from Privileged Mode?
Ans. The differences between User Mode from Privileged Mode are:
| User Mode | Privileged Mode |
| It is used for the regular task while using a Cisco router. | Offers a lot of options, including those available in User mode. |
| It lets you view system information, connect to remote devices, check the router’s status, and more. | It allows users to make router configurations, such as tests and debugging. |
Q39. What is CDP? Explains its functions.
Ans. CDP stands for Cisco Discovery Protocol. It is a Layer 2 proprietary protocol that runs on Cisco devices, including routers and switches. This protocol collects information about directly connected neighbouring devices.
It discovers the nearby devices, identifies how they are configured, and enables the systems to learn about each other by using different network-layer protocols. CDP simplifies the process of keeping an up-to-date inventory of Cisco network devices.
The CDP finds out the following information:
- iOS version running on Cisco devices
- IP addresses
- The hardware platform of devices
- Interface details
- Hostname
- VTP domain
- Duplex setting
- Native VLAN
Q40. How does TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) differ from UDP (User Datagram Protocol)?
Ans. The difference between TCP and UDP are:
| TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
| It is a connection-oriented protocol. | It is a connectionless protocol. |
| The connection should be established before the data is transmitted over the network. | It sends the data without checking whether the system is ready to receive it. |
| Delivery of data to the destination router is guaranteed. The server will request the lost part if the connection is lost during transferring files. | It doesn’t guarantee the delivery of data to the destination. |
| The message will be delivered in the order it is sent. | The message may not be delivered in the same order. |
| It doesn’t support broadcasting. | It supports broadcasting. |
| Data is read as a stream. When one packet ends, another begins. | Data Packets are transmitted individually. |
| The header size is 20 bytes. | The header size is 8 bytes. |
| It is slower than UDP | UDP is faster and more efficient than TCP |
| This protocol is mainly used where a secure communication process is required. Example: web browsing and e-mail. | This protocol is used when fast communication is required. Example: VoIP, video, and music streaming. |
Q41. What are the different classes of IP addresses? Mention their ranges.
Ans. There are five classes of IP address:
| Class | Range |
| A | 1-126 |
| B | 127-191 |
| C | 192-223 |
| D | 224-239 |
| E | 240-254 |
Q42. How to choose DR in OSPF?
Ans. Below are the different ways to choose DR in OSPF:
- Highest priority
- Highest router ID
- Highest IP address
Q43. Which command is used if router IOS is stuck?
Ans. If router IOS is stuck, we use the Ctrl+Shift+F6 and X commands.
Q44. Explain the types of routes available in routers.
Ans. There are three types of routing including dynamic routing, default routing and static routing. These are as follows:
- Static route is also known as non-adaptive route. It is either directly configured on active interface of router or it is added to routing table by administrator.
- Default route is configured to send all packets towards single router. It does not matter if it belongs to a specific network. Such nodes are used when the network deals with single exit point.
- Dynamic route is also known as adaptive route, it makes automatic adjustments of routes as per current state of route on routing table. It uses routing protocols for finding network destinations.
Q45. What is LAN switching? What are its benefits?
Ans. LAN Switching is a form of packet switching used in Local Area Networks. It is a vital component of most networks and helps improve LAN’s overall efficiency and address the existing bandwidth issues. It enables multiple users to communicate directly with each other. LAN switching creates a system of simultaneous, point-to-point connections between pairs of devices. It provides a collision-free network and high-speed networking.
The following are the benefits of LAN Switching:
- Increased network scalability
- Improved bandwidth performance
- Multiple simultaneous connections
- Reduced congestion and transmission delay
- No single point of failure
- Full-duplex data transmission
- Improved manageability and security
Check Out the Best Online Courses
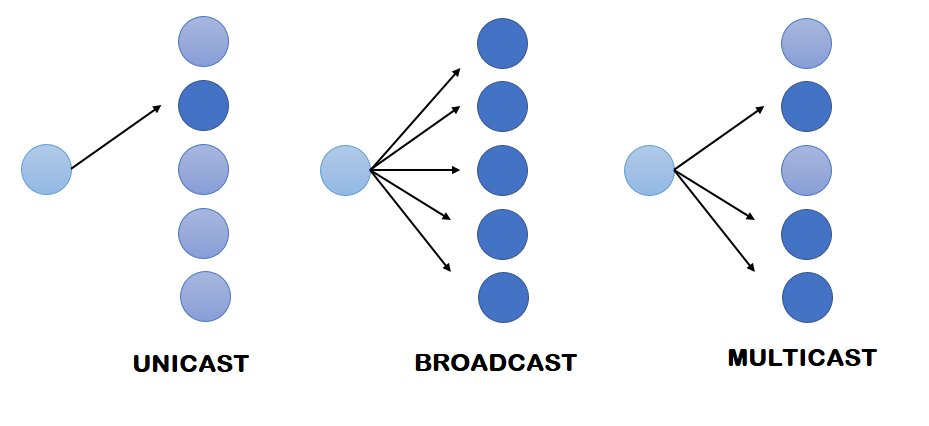
Q46. Explain the terms Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast
Ans. In all these three terms, ‘cast’ refers to transmitting data packets from the client to the recipient over the communication channel.
1. Unicast (One-to-One):
It is a one-to-one communication technique in which data communication occurs between a single sender and a single recipient in the network.
Examples of Unicast are:
- Browsing a website. The web server is the sender, and your computer is the receiver.
- Downloading a file from an FTP Server. FTP Server is the sender, and your computer is the receiver.
2. Broadcast (One-to-All):
It specifies one to all communication. Data communication takes place among all the devices available in the network. The data is sent from one computer once and a copy of that data will be forwarded to all the connected devices. Two types of Broadcast are Limited Broadcasting and Direct Broadcasting.
Example of Broadcast:
- Television networks for video and audio distribution.
3. Multicast (One-to-Many):
Multicast specifies one to group or one to many communication. In Multicast, one or more senders and one or more recipients participate in data transfer. IP multicast traffic is sent to a group and only members of that group receive the Multicast traffic. It uses IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) protocol to identify the group.
Examples of Multicast:
- Sending an e-mail to a particular mailing group.
So, these are some of the most important CCNA interview questions. We hope this blog will help you ace your next CCNA interview.
FAQs
Is CCNA a good career?
CCNA experts are in high demand. They are required by almost every organization to look after their networking infrastructure and for the optimal utilization of the various technological solutions that it constantly improvises or introduces. CCNA is a great career that opens doors to a world full of job opportunities in the field of data networking and also offers a good salary range.
Why should I pursue CCNA certification?
The CCNA certification will help you gain a good understanding of data networking and prepare you for a long-term career. Besides building or enhancing your knowledge, a CCNA certification will help you land a networking job or even switch from your existing job to a better paying and more challenging job.
What are the job roles available after completing CCNA certification?
After completing the CCNA certification, you will be eligible for a variety of job roles like Network Support Engineer, Network Technician, System Engineer, System Administrator, Network Associate, Service Desk Engineer, and Service Desk Technician.
Can I get a job with just a CCNA?
A CCNA certification can help you land an entry-level IT or cybersecurity job. However, your chances of landing a higher-level job will increase if you can combine your CCNA with experience in the IT field another relevant skill certification. Willingness to improve, determination, and soft skills will also help you to a great extent.
Which CCNA certification course should I choose to get into this field?
Many institutes offer online and offline CCNA courses. You should check the ones offering you an in-depth knowledge of the required field. Also, opt for the course that provides practical training along with theoretical knowledge.
What is the salary of a CCNA certified professional in India?
The average salary of a CCNA certified professional depends on the role. The average salary of a Network Support Engineer is Rs. 5,00,000 (approx.) while the average salary of a Network Engineer is Rs.4,85,000 (approx.).
What are the top companies hiring CCNA certified professionals?
The top companies hiring CCNA certified professionals are TCS, AT&T Communications, HCL, Cisco Systems, Reliance Communications, Tech Mahindra, Accenture, Erricson, and Wipro.
What are the roles and responsibilities of a CCNA certified professional?
Cisco certified professionals are primarily responsible for maintaining the networking infrastructure and equipment such as routers and switches. They troubleshoot issues, ensure network security, create and configure networks, and provide technical support.
What is the scope of CCNA in India?
CCNA has immense scope in India as almost every organization is on the lookout for certified professionals who can look after their networking infrastructure and help them grow.
What are the top industries hiring CCNA certified professionals?
The top industries hiring CCNA certified professionals are those that have sophisticated IT systems and typically include schools and hospitals, banks, retailers, and large government departments.
What are the prerequisites for a CCNA certification?
There are no prerequisites for the CCNA certification. However, CCNA candidates usually have one or more years of experience implementing and administering Cisco solutions, knowledge of basic IP addressing, and an understanding of network fundamentals.
Comments
(1)