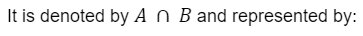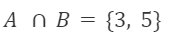Conditional Probability
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss one of the important concepts of statistics, Conditional Probability which is used in one of the machine learning algorithms known as the Naive Bayes Classifier.
As the name suggests Conditional Probability, is the probability of an event under some given condition.
Confused! Don’t worry, we will discuss it briefly with some examples.
Best-suited Statistics for Data Science courses for you
Learn Statistics for Data Science with these high-rated online courses
Table of Content:
Events
Any particular performance of a random experiment is called a trial and the combination of outcomes of these trials is termed as an event.
Example:
- Rolling dice is a trial
- Possible outcome {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
- Possible events corresponding to rolling dice
- Odd number of points: {1, 3, 5}
- Even number of points: {2, 4, 6}
- Points between 2 and 6: {3, 4, 5}
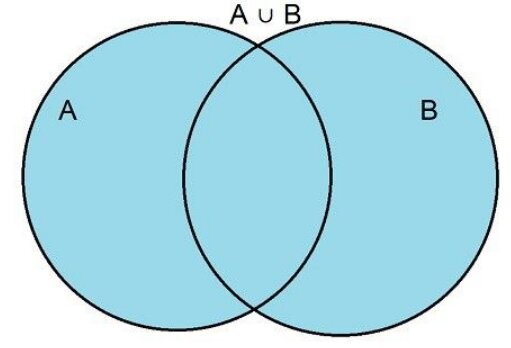
Union of Events:
If we have two events A and B, then Union of Events is defined as
Collection of all the outcome that are elements of either the set A or Set B or both of them.
It is denoted by A U B and represented by:
Example:
From the above example of dice:
- A- Odd number of points
- {1, 3, 5}
- B- Points between 2 and 6
- {3, 4, 5}
Then, A U B = {1, 3, 4, 5}
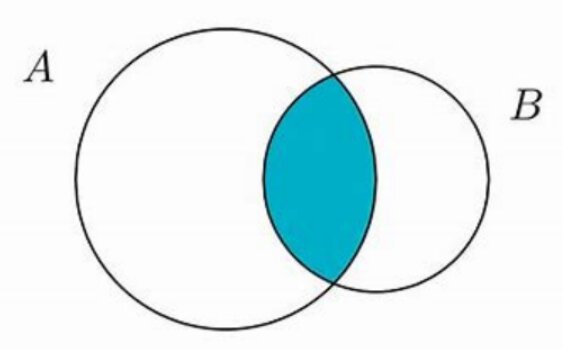
Intersection of Events:
If we have two events A and B, then Intersection of Events is defined as:
Collection of all the outcome that are common in both the sets A and B.
Example:
From the above example of dice:
- A- Odd number of points
- {1, 3, 5}
- B- Points between 2 and 6
- {3, 4, 5}
Then,
Disjoint Events:
Events that don’t occur at the same time are known as disjoint events.
Or
If we have two events A and B and they have no common element then both the events are termed as Disjoint events.
Example:
From the above example of dice:
- A- Odd number of points
- {1, 3, 5}
- B- Even number of points
- {2, 4, 6}
Event A and B both have no common points, so A and B are disjoint.
Independent Events:
Two events A and B are said to be independent if the outcome of event A doesn’t depend on event B and vice versa.
Example: In throwing a coin, getting Head and Tails both of these events are independent.
Mutually Exclusive Events:
Two events A and B are said to be mutually exclusive or disjoint if both of them can’t occur at the same time.
Example: Tossing a coin, the event Head and Tail are mutually exclusive events.
Probability of Mutually exclusive events: P (A U B) = P (A) + P (B)
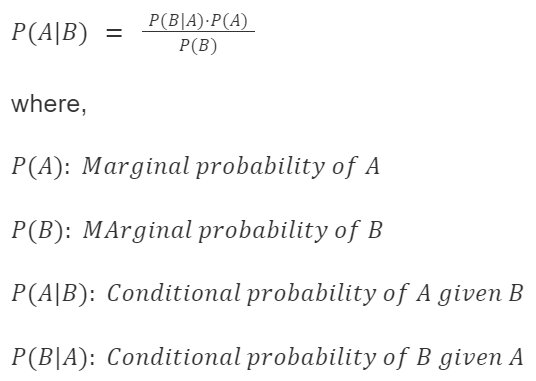
Conditional Probability:
Condition Probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
i.e. we try to calculate the probability of the second event given that the first event has already occurred.
Example:
It will be raining at the end of the hottest day.
Here the probability of occurrence of rainfall depends on the temperature throughout the day.
Mathematical Formula:
Let’s understand the conditional probability with an example
Example:
Let there are 100 (47 boys, 53 girls) students in a classroom, the given table describes the number of students (boys and girls) who pass or fail in the exam.
| Pass | Fail | Total | |
| Boys | 15 | 32 | 47 |
| Girls | 29 | 24 | 53 |
| Total | 44 | 56 | 100 |
Let A: represent passed in the exam
And B: represent student is a Boy
Bayes’ Theorem:
Bayes’ theorem is an extension of Conditional Probability.
It includes two conditional probabilities.
It gives the relation between conditional probability and its reverse form.
Conclusion
In this article, we have briefly explained one of the important concepts of probability Conditional Probability which is widely used in machine learning algorithms.
Hope this article will help you in your data science and machine learning journey.
Top Trending Articles:Data Analyst Interview Questions Data Science Interview Questions Machine Learning Applications Big Data vs Machine Learning Data Scientist vs Data Analyst How to Become a Data Analyst Data Science vs. Big Data vs. Data Analytics What is Data Science What is a Data Scientist What is Data Analyst