Data Types in Java – Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types Explained
In Java, data types play a crucial role in defining the kind of information that can be stored and manipulated. Primitive data types, such as integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and booleans, provide the foundation for representing simple values. On the other hand, non-primitive data types, like arrays, classes, and interfaces, enable the creation of more complex structures and allow for the organization and manipulation of larger sets of data. Understanding and effectively utilizing these data types is essential for developing robust and efficient Java programs. Let’s understand!!
A data type is a classification of data. It tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer aims to use the variables or method. Data types are a crucial factor in all computer programming languages. The task of a programmer is to develop a workable program by assigning the right types of data to the right variables. Data types represent the type, nature, and set of operations for the value which they store. There are two data types of categories in Java: Primitive and Non-Primitive.
Explore Online Java Courses
What are Data Types in Java?
Data types in Java specify how memory stores the values of the variable. Each variable has a data type that decides the value the variable will hold. Moreover, Primitive Data Types are also used with functions to define their return type.
Unlock the secrets of Java with our career prospects and comprehensive guide; discover information on top colleges, specialised programmes and online courses to excel in the world of Java!
Best-suited Java courses for you
Learn Java with these high-rated online courses
Data Types in Java
Data types in Java are divided into 2 categories:
Source: Crunchify
Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types specify the size and type of variable values. They are the building blocks of data manipulation and cannot be further divided into simpler data types.

Source: Crunchify
There are 8 Primitive data types in Java – Boolean, char, byte, int, short, long, float, and double.



For more information, Read Access Modifiers in Java.
Boolean type – Boolean
A boolean data type can store either True or False. They can be used to check whether two values are equal or not (basically in conditional statements to return True or False). Typically, programmers use it as a flag variable to track true or false conditions.
The default boolean value is False. Moreover, the boolean type’s size depends on the Java Virtual Machine. Therefore, it fluctuates on different platforms.
Example-
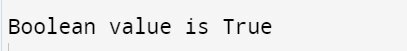
class BooleanDataTypes{ public static void main(String args[]) { boolean var1 = true; if (var1 == true) //checks if the value is true or false { System.out.println("Boolean value is True"); } else { System.out.println("Boolean value is False"); } }}
Output-
Character type – char
The char data type stores a single character. It stores lowercase and uppercase characters, which must be enclosed in single quotes. The char data type in Java supports Unicode characters and provides provision to multiple languages like English, French, German, etc. It takes memory space of 16 bits or 2 bytes. The values stored range between 0 to 65536.
Example:-
class CharDataType { public static void main(String[] args) { char var1 = 'A'; char var2 = 'd'; System.out.println(var1); System.out.println(var2); }}
Output:
Integer type –
An integer type stores an integer number with no fractional or decimal places. Java has four integer types – byte, short, int, and long.
Byte
The byte is the smallest data type among all the integer data types. It is an 8-bit signed two’s complement integer. It stores whole numbers ranging from -128 to 127.
Syntax:
byte byteVariable;
Short
Short is a 16-bit signed two’s complement integer. It stores whole numbers with values ranging from -32768 to 32767. Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
short shortVariable;
Int
Int is a 32-bit signed two’s complement integer that stores integral values ranging from 2147483648 (-2^31) to 2147483647 (2^31 -1). Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
int intVariable;
Long
long is a 64-bit signed two’s complement integer that stores values ranging from -9223372036854775808(-2^63) to 9223372036854775807(2^63 -1). It is used when we need a range of values more than those provided by int. Its default value is 0L. This data type ends with ‘L’ or ‘l’.
Syntax:
long longVariable;
Example:
class IntegerDataTypes{ public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 10; short s = 2; byte b = 6; long l = 125362133223l; System.out.println("The integer variable is " + a + '\n'); System.out.println("The short variable is " + s + '\n'); System.out.println("The byte variable is " + b + '\n'); System.out.println("The long variable is " + l); }}
Output:
Float type –
Floating-point is used for expressions involving fractional precision. It has two types: float and double.
Float
It is a floating-point data type that stores the values, including their decimal precision. It is not used for precise data such as currency or research data.
A Float value:
- is a single-precision 32-bit or 4 bytes IEEE 754 floating-point
- can have a 7-digit decimal precision
- ends with an ‘f’ or ‘F’
- default value = 0.0f
- stores fractional numbers ranging from 3.4e-038 to 3.4e+038
Syntax:
float floatVariable;
Double
The double data type is similar to float. The difference between the two is that is double twice the float in the case of decimal precision. It is used for decimal values just like float and should not be used for precise values.
A double value:
- is a double-precision 64-bit or 8 bytes IEEE 754 floating-point
- can have a 15-digit decimal precision
- default value = 0.0d
- stores fractional numbers ranging from 1.7e-308 to 1.7e+308
Syntax:
double doubleVariable;
Example:
class FloatDataTypes{ public static void main(String args[]) { float f = 65.20298f; double d = 876.765d; System.out.println("The float variable is " + f); System.out.println("The double variable is " + d); }}
Output:
Primitive Data Types Table – Default Value, Size, and Range
| Data Type | Default Value | Default size | Range |
| byte | 0 | 1 byte or 8 bits | -128 to 127 |
| short | 0 | 2 bytes or 16 bits | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | 0 | 4 bytes or 32 bits | 2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| long | 0 | 8 bytes or 64 bits | 9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| float | 0.0f | 4 bytes or 32 bits | 1.4e-045 to 3.4e+038 |
| double | 0.0d | 8 bytes or 64 bits | 4.9e-324 to 1.8e+308 |
| char | ‘\u0000’ | 2 bytes or 16 bits | 0 to 65536 |
| boolean | FALSE | 1 byte or 2 bytes | 0 or 1 |
Non-Primitive Data Types
Non-primitive data types or reference data types refer to instances or objects. They cannot store the value of a variable directly in memory. They store a memory address of the variable. Unlike primitive data types we define by Java, non-primitive data types are user-defined. Programmers create them and can be assigned with null. All non-primitive data types are of equal size.

Source: Crunchify
Array
An array holds elements of the same type. It is an object in Java, and the array name (used for declaration) is a reference value that carries the base address of the continuous location of elements of an array.
Example:
int Array_Name = new int[7];
For more insights about Arrays in Java, Read: Implementing Arrays in Java
String
The String data type stores a sequence or array of characters. A string is a non-primitive data type, but it is predefined in Java. String literals are enclosed in double quotes.
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // create strings String S1 = "Java String Data type"; // print strings System.out.println(S1); }}
Class
A class is a user-defined data type from which objects are created. It describes the set of properties or methods common to all objects of the same type. It contains fields and methods that represent the behaviour of an object. A class gets invoked by the creation of the respective object.
There are two types of classes: a blueprint and a template. For instance, the architectural diagram of a building is a class, and the building itself is an object created using the architectural diagram.
Example:
For more details, read: OOPs Concepts in Java
Interface
An interface is declared like a class. The key difference is that the interface contains abstract methods by default; they have nobody.
Example:
interface printable { void print(); } class A1 implements printable { public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");} public static void main(String args[]) { A1 obj = new A1(); obj.print(); } }
Also Read: Python Vs Java – Which One is Better to Learn?
Enum
An enum, similar to a class, has attributes and methods. However, unlike classes, enum constants are public, static, and final (unchangeable – cannot be overridden). Developers cannot use an enum to create objects, and it cannot extend other classes. But, the enum can implement interfaces.
//declaration of an enum
enum Level {
LOW,
MEDIUM,
HIGH
}
Conclusion
Data types are the basis of programming languages. It is essential to know about Java data types before moving to the advanced concepts of Java. Understanding data types will help you create a simple program or develop any application or software.
Suggested Reads:



FAQs
What is a data type in Java?
A data type in Java represents the size and different values that can be stored in a variable. In other words, a Java data type is a set of values and operations defined on those values.
What is the difference between primitive and non-primitive data types in Java?
Primitive data types in Java are built-in data types that are predefined whereas non-primitive data types are not predefined and are created by the programmer. A primitive data type always has a value while a non-primitive data type can be null.
What are 8 primitive data types in Java?
There are eight built-in primitive data types in Java. They are int, char, byte, short, long, float, double, and boolean.
What are non-primitive data types in Java?
Non-primitive data types in Java are not predefined. They are created by the programmer. Non-primitive data types are also called 'reference variables' or 'object references' as they reference a memory location where data is stored. Some of the examples of non-primitive types include strings, arrays, and classes.
What are the Java Literals?
Java Literal is a source code representation of a fixed value. They are constant values that appear directly in the program. We can assign a literal directly to a variable. There are four types of literals in Java, namelyu00a0Integer Literal, Character Literal, Boolean Literal, and String Literal.
What is the function of Data type?
In Java, data types serve as a way to classify and represent the different types of values that can be stored and manipulated by a program. Data types provide a way for the Java compiler to determine how much memory to allocate for a particular value, as well as how the value can be used in expressions and operations.
What is Variable in Java?
In Java, a variable is a named container with a value of a particular data type. Variables are used to store and manipulate data in a program. They can be assigned a value when declared, which can be changed later in the program as needed.
Is array an data type in Java?
In Java, an array is not a data type in itself, but rather a data structure that holds a fixed number of values of the same data type. Arrays can be declared with any of the primitive data types, such as int, double, boolean, etc., or with reference types, such as String or any other class or interface.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio








Comments
(2)
D
3 months ago
Report Abuse
Reply to Douglas Potter
F
7 months ago
Report Abuse
Reply to Florence Jenny