Difference Between Collection and Collections
Collection and Collections in Java are integral parts of Java Collection Framework. Both the terms looks similar but have different applications and can’t be used interchangeably. In this article, we will learn the difference between collection and collections in Java with the help of example.
Collection and Collections in Java are integral parts of Java Collection Framework. Both the terms looks similar but have different applications and can’t be used interchangeably.
Collection in JAVA refers to the root interface in the Java Collections framework. It represents a group of objects known as its elements. Whereas Collections is a utility class in Java that provides static methods to perform operations like sorting, reversing, and searching.
In this article, we will learn how collection and collections are different from each other.
Table of Content
Best-suited Java courses for you
Learn Java with these high-rated online courses
Difference Between Collection and Collections: Collection vs Collections
| Collection | Collections | |
| Definition | It is an interface that forms the root of the Java Collections Framework. | This utility class provides static methods to perform operations on collections. |
| Usage | Act as an interface for other interfaces like List, Set, and Queue. Some of the common methods include add(), remove(), and size(). | This class offers utility functions that operate on or return collections. For example, the Collections.sort() method sorts elements in a list. |
| Implementation | It doesn’t have any direct implementation as it is an interface. But you can implement the collection interface by using various Java classes, like ArrayList, HashSet, and PriorityQueue. | As it is a final class, meaning it can not be subclassed. It doesn’t have any public constructors, so its methods are accessed statically. |
| Flexibility | Since it’s an interface, developers can create custom implementations if required. | As a utility class, it provides ready-to-use methods that help the developer to save time while performing common operations on collections. |
| Purpose | The purpose is to provide a standard way to handle and manage a group of objects. | It offers a utility function that simplifies common tasks associated with collections. |
What is Collection in JAVA?
It is an interface which is a member of the collection framework. It provides the foundation for the data structure representation in Java, representing a group of objects.
The collection is the root from which other collection interfaces, such as ‘List’, ‘Set’ and ‘Queue’ are derived. It also provides basic methods like ‘add()’, ‘remove()’, ‘size()’, and ‘iterator()’.
Related Reads: Features of JAVA
Need of Collection
- It provides a unified way to represent and manipulate groups of objects, ensuring a consistent approach across different types of collections.
- It gives the foundation for other collection frameworks like set, List, and Queue, so all collection types have a standard set of basic operations.
- Allows developers to create custom data structures by implementing its methods.
- It provides methods to control access to the elements, such as adding, removing, or checking the size that help developers to manipulate the data.
What is Collections in JAVA?
It is a utility class in Java that provides a set of static methods to perform operations on collections.
These methods include algorithms for sorting, reversing, shuffling, and searching. It also provides methods to return synchronized and unmodified versions of collections.
Need of Collections
- It offers static utility methods that simplify common tasks like sorting, reversing, and searching in collections.
- Instead of writing the codes from scratch, the developers can use collections class to perform operations, which helps them to save time and increase efficiency.
- Methods like unmodifiableList() or unmodifiableSet() in Collections provide developers to create an immutable view of collections that helps to enhance security.
- It provides methods like synchronizedList() or synchronizedSet to return a thread-safe version of the collection, ensuring concurrent access.
Let’s take an example to get a better understanding of how to implement collection and collections in JAVA.
How to Implement Collection and Collections in JAVA
Problem Statement: Suppose you have a list of student names and want to:
- Add names to the list.
- Sort the names in alphabetical order.
- Search for a specific student’s name in the list.
Solution:
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;
public class StudentList {
public static void main(String[] args) { // Step 1: Create a list of student names using the Collection interface List<String> students = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding names to the list students.add("Digvijay"); students.add("Chiranjivi"); students.add("Barbie"); students.add("Aryan");
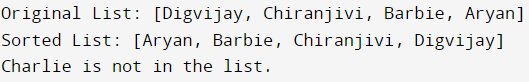
System.out.println("Original List: " + students);
// Step 2: Sort the names using the Collections utility class Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println("Sorted List: " + students);
// Step 3: Search for a specific student's name int index = Collections.binarySearch(students, "Charlie"); if (index >= 0) { System.out.println("Charlie is found at index: " + index); } else { System.out.println("Charlie is not in the list."); } }}
Output
Explanation
- Import the required classes.
- Create a list of student names using the ArrayList class, which implements the Collection interface.
- Use add method to add names to the list.
- Use the sort method from the Collection utility class to sort the list alphabetically.
- Finally, search a specific student’s name using the binarySearch method from the Collection class.
Key Differences and Similarities Between Collection and Collections in JAVA
- Both Collection and Collections are integral parts of the Java Collections Framework.
- Both are centred around the concept of data manipulation.
- Collection and Collection supports Java Generic, allowing type-safe operations and enhancing data handling capabilities.
- Collection is an interface that forms the root of the Java collections Framework. At the same time, Collections is a utility class that provides static methods to perform operations on collections, such as sorting, searching, and reversing.
- The Collection interface defines the standard operation for data structure, whereas the Collections class provides utility methods to perform common operations on these structures.
- Since the collection is an interface, the developer can create custom implementations if required. But Collections is a utility class, it provides ready-to-use methods to save time while performing common operations on a collections.
Conclusion
Collection and Collections in Java are integral parts of Java Collection Framework. Both the terms looks similar but have different applications and can’t be used interchangeably. Where Collection is an interface, collection is an utility class.
In this article, we have discussed the difference between collection and collections in Java with the help of example.
Hope you will like the article.
Keep Learning!!
Keep Sharing!!


















FAQs
What is Collection in JAVA?
It is an interface which is a member of the collection framework. It provides the foundation for the data structure representation in Java, representing a group of objects. The collection is the root from which other collection interfaces, such as List, Set and Queue are derived. It also provides basic methods like add, remove, size, and iterator.
What is the need of Collection in JAVA?
It provides a unified way to represent and manipulate groups of objects, ensuring a consistent approach across different types of collections. It gives the foundation for other collection frameworks like set, List, and Queue, so all collection types have a standard set of basic operations. Allows developers to create custom data structures by implementing its methods. It provides methods to control access to the elements, such as adding, removing, or checking the size that help developers to manipulate the data.
What is Collections in JAVA?
It is a utility class in Java that provides a set of static methods to perform operations on collections. The collection is the root from which other collection interfaces, such as List, Set and Queue are derived. It also provides basic methods like add, remove, size, and iterator.
What is the need of Collections in JAVA?
It offers static utility methods that simplify common tasks like sorting, reversing, and searching in collections. Instead of writing the codes from scratch, the developers can use collections class to perform operations, which helps them to save time and increase efficiency. Methods like unmodifiableList or unmodifiableSet in Collections provide developers to create an immutable view of collections that helps to enhance security. It provides methods like synchronizedList or synchronizedSet to return a thread-safe version of the collection, ensuring concurrent access.

Vikram has a Postgraduate degree in Applied Mathematics, with a keen interest in Data Science and Machine Learning. He has experience of 2+ years in content creation in Mathematics, Statistics, Data Science, and Mac... Read Full Bio