Difference Between Distance and Displacement
Confused with the difference between distance and displacement. Don’t worry; this article will briefly define distance, displacement, and the difference between them.
Distance and Displacement are two important concepts in Physics as well as Mathematics. Distance is the total length of an object’s path; it is a scalar quantity. In contrast, Displacement is the change in the position of an object; it is a vector quantity. Displacement is also referred to as the distance with direction.
This article will discuss distance and Displacement and their differences and properties.
Table of Content
- Difference Between Distance and Displacement
- What is Distance?
- What is Displacement?
- Key Differences and Similarities Between Distance and Displacement
What is the difference between Distance and Displacement?
| Parameter | Distance | Displacement |
| Definition | Total length covered by an object. | Total change in the position of an object. |
| Quantity | Scalar | Vector |
| Unit | Meter, kilometer | Meter, kilometer |
| Formula | Distance = speed x time | Displacement = Final Position – Initial Position |
| Magnitude | Non-negative | Positive or Negative, depends on the change in direction |
| Path Dependent | Depend on the actual path taken by an object | Independent of the path taken |
| Net Effect | Distance can be greater than or equal to displacement | Displacement is always less than or equal to zero. |
Best-suited Maths for Data Science courses for you
Learn Maths for Data Science with these high-rated online courses
What is Distance?
Distance is the measure of space between two points. It quantifies the extent to how far apart they are from each other. It considers every possible route taken by an object.
Now, let’s take an example to understand distance better. If you are travelling along any triangular road (ABC)
Length of road AB = 3 km
Length of road BC = 5 km
Length of road CA = 4 km
Hence, the total distance covered by you = (3 + 4 + 5) km = 12 km
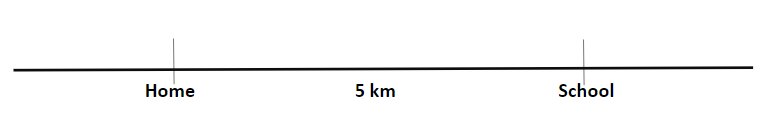
Let’s take another example: The distance between your schools and yours is 5 km. Then the total distance you cover while going to your school and returning home will be 10 km.
Distance = Length between Home and School + Length between School and Home = 5 km + 5 km



Properties of Distance
- Scalar Quantity: Distance is a scalar quantity, i.e., it has a magnitude but not direction. It is represented by a single value, such as a meter (m) or kilometre (km).
- Non-negative: Distance is always non-negative. It is a measure of the magnitude or length of the path travelled.
- Path Dependency: It is path dependent, i.e., it considers the entire path taken by an object.
- Additivity: Distance can be added, i.e., if an object cover multiple sub-paths, the total distance is obtained by adding the distance of each sub-path.
What is Displacement?
Displacement refers to the change in the position of an object or point relative to its starting point. In simple terms, displacement measures the distance and direction from the initial to the object’s final position.
Now, let’s take the above example to understand displacement better.
If you move from home to school, the displacement will be 5 km. Let you travel from your home to your school.
Here, the displacement is positive since you are moving forward in the same direction from your starting point.
But, if you return from school to home, the displacement would be – 5km.
Here, the negative difference represents the opposite direction relative to your starting point.
Hence, the total displacement = 0 (= displacement from home to school + displacement from school to home)



Properties of Displacement
- Magnitude: It represents the distance between the initial and final position. It is a scalar quantity, and it is either positive or zero.
- Direction: Direction can be expressed using a direction compass (e.g., north, south, east, west) or angles concerning a reference direction.
- Vector Quantity: Displacement has both directions as well as distance. It follows the rule of vector addition, including vector addition and subtraction.
- Path Independent: It is independent of the path taken. It only depends on the initial and final position.
Key Differences and Similarities Between Distance and Displacement
- Both are used to measure the change in the position of an object or particle.
- Both can be expressed in length units, such as meters or kilometres.
- Distance is a scalar quantity, whereas Displacement is a vector quantity, i.e., distance refers to the total length covered along a path, regardless of the direction. In contrast, Displacement represents the change in position from the initial to the final position.
- Distance depends on the actual path taken by an object, considering all twists and turns. In contrast, Displacement is path independent and only considers the change in position from the initial and final points.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed what distance and displacement are, difference between them, and some of their properties.
Hope you will like the article.
Keep Learning!!









FAQs
What is Distance?
Distance is the measure of space between two points. It quantifies the extent to how far apart they are from each other. It considers every possible route taken by an object.
What is Displacement?
Displacement refers to the change in the position of an object or point relative to its starting point. In simple terms, displacement measures the distance and direction from the initial to the object's final position.
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
Distance is a scalar quantity that measures the total length covered by an object. In contrast, displacement is a vector quantity that measures the total change in the position.





Comments
(1)
B
2 months ago
Report
Reply to B B PRASAD