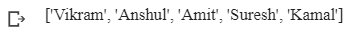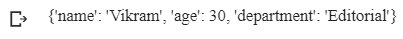Difference Between Mutable and Immutable in Python
Data types in Python are categorized into mutable and immutable data types. Mutable data types are those whose values can be changed, whereas immutable data types are ones in which the values can’t be changed. In this article, we will discuss the difference between mutable and immutable in Python.
Python is one of the most popular programming languages that offers a rich set of data types. A Python data type defines the type of data stored in a variable. Unlike Java, C, and C++ in Python, we do not specify the variable’s data type explicitly. The data type in Python is automatically detected when the value is stored in the variable.
Python data type is categorized into two types:
- Mutable Data Type – A mutable data type is one whose values can be changed.
- Example: List, Dictionaries, and Set
- Immutable Data Type – An immutable data type is one in which the values can’t be changed or altered.
- Example: String and Tuples
In this article, we will discuss Mutable and Immutable data types and the Difference Between them in Python based on different parameters.
So, let’s start the article.
Table of Content
- Difference Between Mutable and Immutable Data Types in Python: Mutable vs Immutable
- Mutable Data Type in Python
- Immutable Data Type in Python
- Key Difference Between Mutable and Immutable Data Type
Difference Between Mutable and Immutable Data Type: Mutable vs Immutable
| Mutable | Immutable | |
| Definition | Data type whose values can be changed after creation. | Data types whose values can’t be changed or altered. |
| Memory Location | Retains the same memory location even after the content is modified. | Any modification results in a new object and new memory location |
| Example | List, Dictionaries, Set | Strings, Types, Integer |
| Performance | It is memory-efficient, as no new objects are created for frequent changes. | It might be faster in some scenarios as there’s no need to track changes. |
| Thread-Safety | Not inherently thread-safe. Concurrent modification can lead to unpredictable results. | They are inherently thread-safe due to their unchangeable nature. |
| Use-cases | When you need to modify, add, or remove existing data frequently. | When you want to ensure data remains consistent and unaltered. |
Best-suited Python courses for you
Learn Python with these high-rated online courses
Mutable Data Type in Python
In Python, a data type is mutable if its values can be changed, updated, or modified after the data type has been created. In other words, once an object of the mutable data type is initialized, you can update its content without creating a new object.
Examples of Mutable Data Type:
Python Lists
Python lists methods are mutable; the list’s contents are modified in place. You can change a list in place, add new elements, overwrite existing elements, or delete them. Also, note that the same value can occur in a list more than once.
Example: List1 = [‘Python’, 3.0, ‘Shiksha Online’, ‘Python Courses’]
Now, let’s take an example to check whether lists are mutable or not.
#create a list of student
name = ['Vikram', 'Anshul', 'Amit', 'Suresh']
#add element in the existing listname.append('Kamal')
#print the resultprint(name)
Output
Must Read: List in Python
Must Read: Python List Program for Beginners
Check out the best-rated job-centric courses after the 12th. Explore how online degree programs can prepare you for the job market.
Python Dictionary
Dictionaries are likely Python's most important and flexible mutable built-in data types. In simple terms, a Python dictionary is a flexible-sized arbitrary collection of key-value pairs, where key and value are both Python objects.
Example: Dict_1 = {‘first_name’: ‘Amit’, ‘age’: 44, ‘job’:’Professor’}
Now, let’s take an example to check whether Python dictionaries are mutable.
# create a dictionary: Employee
employee = {'name' : 'Vikram', 'age' : 30, 'department' : 'Content Management'}
# change the department name from Content Management to Editorial
employee['department'] = 'Editorial'
#print the dictionary
print(employee)
Output
Must Read: Python Dictionary
Must Read: Python Dictionary Practice Program for Beginners
Python Sets
Sets are unordered collections of unique elements and immutable objects. You can think of them as a dictionary with just the keys and their values thrown away. Each item of a set should be unique. While sets themselves can be mutable, that is you can add or remove items, however, the items of a Python set must be of an immutable type.
Example: set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Now, let’s take an example to check whether sets in Python are mutable or not.
# Creating a setname = {'Vikram', 'Anshul', 'Amit', 'Suresh'}
# Displaying the original setprint("Original set:", name)
# Adding an element to the setname.add("Kunal")print("After adding 'Kunal':", name)
# Removing an element from the setname.remove("Amit")print("After removing 'Amit':", name)
# Adding multiple elements using the update methodname.update(["Ankit", "Harsh"])print("After adding 'Ankit' and 'Harsh':", name)
Output
Must Read: Python Sets
Must Read: Python Set Practice Problem for Beginners
Immutable Data Type in Python
Data types in Python whose values can’t be changed or modified are known as Immutable Data Types. Once the value or the object of the immutable data type is initialized, its value remains constant throughout its lifetime.
But, if you want to change the original object, a new object will be created with the modified values.
Common Immutable Data Types in Python are:
Integers (int)
- It represents whole numbers, both positive and negative.
- Once an integer object is created, its value remains fixed. You cannot change the value of an existing integer object.
Floating Points (float)
- It represents real numbers with decimal points.
- Like integers, once a floating-point number is initialized, its value remains constant and cannot be altered.
Strings (str)
- Strings are ordered sequences of characters used to represent text.
- Once a string is initialized, its content is fixed. You cannot modify individual characters within the string.
Tuples (tuple)
- They are ordered collections of elements, similar to lists.
- The main distinction between tuples and lists is that tuples are immutable.
- This means that once a tuple is created, its content cannot be changed.
Booleans (bool)
- Booleans represent truth values and can only take True or False values.
- These values are constants in Python and cannot be changed.
Frozensets (frozenset)
- They are like sets, but they are immutable.
- This means you can’t add or remove elements from a frozen set after it’s been created. They are useful when you need a set-like structure that shouldn’t be modified.
Now, let’s take an example of string and tuples to check whether they are immutable or not?
"""This program shows how strings and tuples are immutable in Python."""
my_string = "Hello, world!"
try: """ This code tries to change the first character of the string to "H". However, the code will throw a TypeError because strings are immutable. """ my_string[0] = "H"except TypeError: print("Strings are immutable and cannot be changed.")
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
try: """ This code tries to change the first element of the tuple to 4. However, the code will throw a TypeError because tuples are immutable. """ my_tuple[0] = 4except TypeError: print("Tuples are immutable and cannot be changed.")
print("The value of the string is:", my_string)
print("The value of the tuple is:", my_tuple)
Output
Key Similarities and Difference Between Mutable and Immutable Data Types in Python
- Both Mutable and Immutable data types can be used to store data and can be accessed using the same syntax.
- Mutable data types can be changed after creation, whereas immutable data types can’t be changed after creation.
- i.e., you can add, remove, or modify the contents of a mutable data type but can’t do the same with an immutable data type.
- Mutable data types are more memory-intensive than immutable data types, as mutable data types store a copy of their content whenever they are changed.
- Immutable data types are less prone to errors than mutable data types.
Conclusion
Data types in Python are categorized into mutable and immutable. Mutable data types have values that can be changed, whereas immutable data types have values that can’t be changed.
In this article, we discuss the difference between mutable and immutable in Python.
Hope you will like the article.
Keep Learning!!
Keep Sharing!!









FAQs
What is an example of mutable and immutable data type in Python?
List, Dictionary, and Sets are examples of mutable data type where sets and tuples are immutable data types in Python.
What is an example of mutable data type in Python?
List, Dictionary, and Sets are examples of mutable data type in Python.
What is an example of immutable data type in Python?
Sets and tuples are immutable data types in Python.
Are dictionaries mutable in Python?
Yes dictionaries are mutable in Python, i.e., you can edit or modify the existing dictionary.
Dictionary is mutable or immutable in Python?
Dictionaries are mutable data types in Python, i.e., you can edit or modify the existing dictionary.
List is mutable or immutable in Python?
List mutable data types in Python, i.e., you can edit or modify the existing list.
Is tuple mutable in Python?
No tuples are not mutable in Python, i.e., you can not edit or modify the existing tuple.
Tuples are mutable or immutable in Python?
Tuples are immutable data types in Python, i.e., you can not edit or modify the existing tuple.

Vikram has a Postgraduate degree in Applied Mathematics, with a keen interest in Data Science and Machine Learning. He has experience of 2+ years in content creation in Mathematics, Statistics, Data Science, and Mac... Read Full Bio