Difference Between Primary Memory and Secondary Memory
Computer memory is simply the computer’s brain where data and information are stored for easy retrieval. Memory is the computer’s storage space that temporarily or permanently stores data or programs. Learn what primary and secondary memory is, what their types are, and the difference between primary and secondary memory. The article covers the concepts of primary memory and secondary memory, along with the difference between both.
Content
- Difference between Primary and Secondary Storage
- What is Primary Memory?
- What Is Secondary Memory?
- Comparison Between Primary and Secondary Memories
Courses ALERT: Explore FREE Online Courses by top online course providers like Coursera, edX, Udemy, NPTEL, etc., across various domains, like Technology, Data Science, Management, Finance, etc., and improve your hiring chances.
Difference between Primary and Secondary Memory – Comparison Table
Primary memory is used for temporarily storing data that is actively being used by the computer's CPU, while secondary memory (storage) is used for long-term data storage, such as files and programs that are not currently in use. Listed below are some other primary and secondary memory differences.
Comparison Parameters |
Primary Memory |
Secondary Memory |
| Storage Validity |
Primary memory is the main memory and stores data temporarily. |
Secondary memory is the external memory and stores data permanently. |
| Access |
The CPU can directly access the data from the Primary Memory |
The CPU cannot directly access the data from Secondary Memory. |
| Volatility |
Primary memory is volatile. It loses data in case of a power outage. |
Secondary memory is non-volatile; data is stored even during a power failure. |
| Storage |
Data is stored inside costly semiconductor chips. |
Data is stored on external hardware devices like hard drives, floppy disks, etc. |
| Division |
Primary memory can be divided into RAM and ROM. |
Secondary memory does not have such classification. Secondary memories are permanent storage devices like CDs, DVDs, etc. |
| Examples |
RAM (Random Access Memory), ROM (Read-Only Memory). |
HDD (Hard Disk Drive), SSD (Solid State Drive), USB drives, CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray, and cloud storage. |
| Speed |
Faster |
Slower |
| Stored data |
Saves the data that the computer is currently using. |
It can save various types of data in various formats and huge sizes. |
| Cost |
More expensive per GB due to high-speed and advanced semiconductor technology. |
More affordable per GB due to the availability of diverse storage technologies like HDDs and SSDs. |
| Power Dependency |
Operates only when the computer is powered on. Data is wiped off in case of power loss. |
Functions independently of power status. Data remains saved in the storage device. |
| Usage |
Essential for the execution of programs and real-time processing by the CPU. |
Primarily used for long-term data storage and archival purposes. |
Now that you know how to differentiate between primary and secondary memory let us understand what primary memory and secondary memory are.
What is Primary Memory?
Best-suited Operating Systems courses for you
Learn Operating Systems with these high-rated online courses
Primary memory is a computer system's internal memory. It stores and retrieves data, instructions, and information. The CPU directly and randomly accesses primary memory, also called Random Access Memory (RAM). Primary memory is volatile and loses data and instructions when the power turns off.
Types of Primary Memory:
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Random Access Memory, or RAM, is usually provided as the computer system’s main memory. It is also regarded as temporary or cache memory constantly being written to and read. Information saved in primary memory will be lost when the computer or laptop's power supply turns off. Simply put, RAM is a primary memory from which you can only read information.
Must Read – What is an Operating System?
ROM (Read-Only Memory)
ROM is a non-volatile memory containing data that we cannot change. In this case, information is not lost when the power supply is turned off. The computer manufacturer determines ROM information. It is permanently stored at the time of manufacture so that the user cannot overwrite it.
Develop a strong foundation in memory management with specialized online operating systems courses. Gain hands-on experience in RAM, ROM, flash memory, and next-gen memory solutions for high-speed computing.
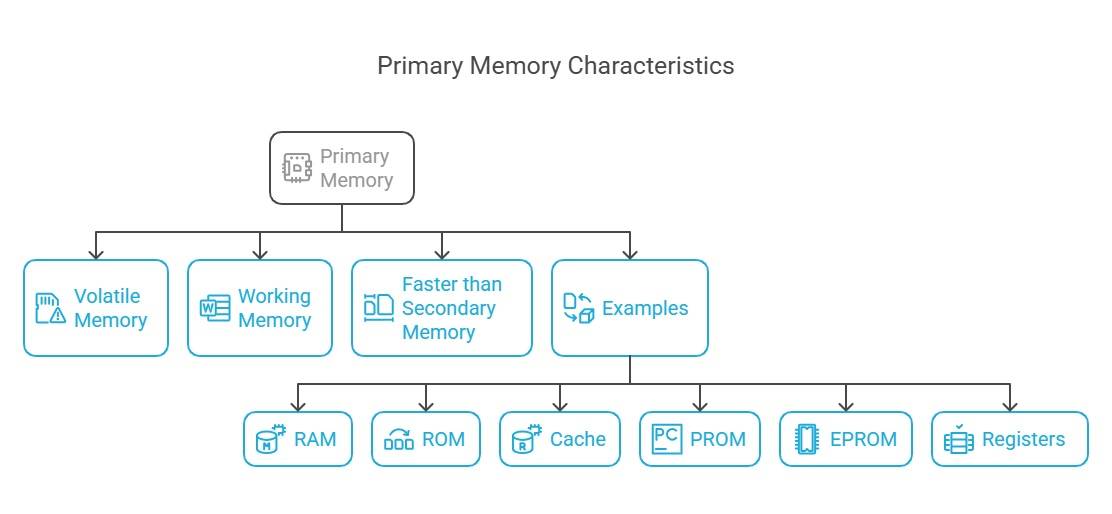
Primary Memory Characteristics
- The computer cannot function without primary memory.
- Primary memory is also known as the main memory.
- You may lose data in case the power is off
- Also known as volatile memory
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- It is faster as compared to secondary memory.
- Examples: RAM, ROM, cache, PROM, EPROM, registers, etc.
Limitations of Primary Memory:
- Size is Limited: Primary memory holds less than the storage size in secondary memory, often just a few GBs.
- Not Volatile: It is lost when the computer is shut off or faces a power failure.
- Costly: Primary memory is expensive and considering its inability to store huge data volume, it can sometimes prove to be impractical.
- Saves Data Temporarily: Data is stored in primary memory only when used. So, one cannot keep any files stored permanently there.
What is Secondary Memory?
Secondary memory is a permanent storage device that the CPU cannot access directly.
The CPU accesses these devices through an input/output channel. Data is first transferred to primary from secondary storage before its assessment. Modern computers often use hard drives and optical storage devices (CDs, DVDs) as secondary storage devices.
A secondary storage device organizes data into files and directories based on a file system. It also allows the user to access or use additional information like access permissions, owner, last access time, etc. Also, secondary memory temporarily keeps less used data when primary memory is full.
Secondary memory devices are less expensive and can store vast amounts of data, audio, video, and multimedia files. Organizations can store the equivalent of a roomful of data on disks that consume dramatically and significantly less physical space.
Types of Secondary Memory
- Solid-state storage devices, such as USB memory sticks.
- Optical storage devices, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.
- Examples: Magnetic storage devices include zip, floppy, and hard disk drives.
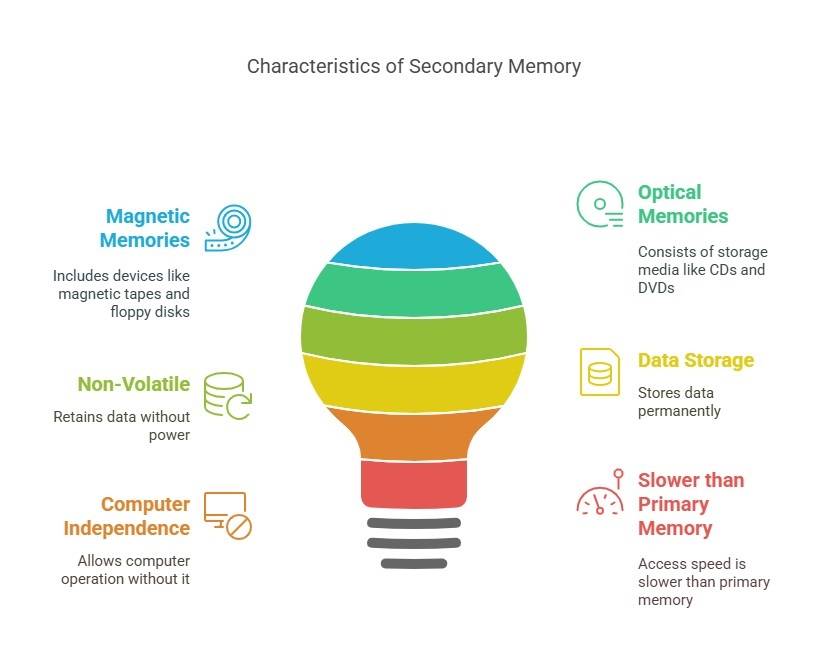
Secondary Memory Characteristics
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is a type of non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even when the computer is turned off
- It helps store data on a computer
- The computer can function without secondary memory
- Slower than primary memory
- Examples: magnetic tapes, optical discs, floppy disks, flash memory [USB drives], paper tape, punched cards, etc.
- Slower Access: Secondary memory is slower than primary memory, which can delay data retrieval.
- Indirect Access: The CPU cannot directly access data from secondary memory; it must first be loaded into primary memory.
- Damage Risk: External devices like hard drives and USBs are susceptible to physical damage, leading to data loss.
- Dependence on Devices: Secondary memory depends on additional hardware, which might fail or require regular maintenance.
Comparison Between Primary And Secondary Memories
- Primary memory is the computer’s main memory and stores data temporarily.
- Secondary memory is external memory and saves data permanently.
- Data stored in primary memory can be directly accessed by the CPU, which cannot be accessed in secondary memory.
- Primary memory is lost during a power outage, while secondary memory saves the data.
- Secondary memory is non-volatile, while primary memory is volatile.
- Primary memory is stored on semiconductor chips, while secondary memory is stored on external devices.
- Primary memory is classified into cache and random access memory, while secondary memory has no such categories.
- Secondary memory can save data in various formats that can be accessed anytime, while primary memory uses the computer’s current data.
- Primary memory is faster.
Conclusion
Both types of memory have several differences. Although different, they work together to allow the computer to run smoothly. Primary memory itself can’t save more than a few gigabytes of data, but secondary memory fills that gap by providing up to a terabyte of space. While the latter lags in processing data, primary memory is faster and easily accessible.
Both primary and secondary memories are crucial for a computer’s effortless and efficient functioning, and they complement each other. I hope this article helped you to differentiate between primary and secondary memory, or understand the difference between primary and secondary storage.
Recommended Reads
FAQs
How is primary memory different from secondary memory in terms of speed?
Primary memory is much faster than secondary memory. It provides quick access to data and instructions, enabling the CPU to read and write data at high speeds. In contrast, secondary memory devices have relatively slower access times and transfer rates than primary memory.
Can programs be directly executed from secondary memory?
No, programs cannot be directly executed from secondary memory. They must be loaded into primary memory before the CPU executes them. The operating system retrieves the required programs and data from secondary memory and copies them into primary memory for execution.
What is the capacity difference between primary memory and secondary memory?
Primary memory typically has a smaller capacity compared to secondary memory. While primary memory capacity is usually measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB), secondary memory devices like hard drives or SSDs can have capacities ranging from several gigabytes to multiple terabytes or more.
Can primary memory be upgraded or expanded?
Primary memory can be upgraded or expanded by adding more RAM modules to the computer's motherboard. This increases the amount of data and programs that can be stored and processed simultaneously, improving system performance.
Which memory type is more expensive: primary or secondary?
Primary memory is generally more expensive than secondary memory on a cost-per-byte basis. This is because primary memory technologies, such as DDR4 RAM, are faster and provide the real-time processing capabilities required by the CPU. Secondary memory devices, like hard drives or SSDs, offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost.

Comments
(3)