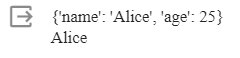Difference Between Set and Dictionary in Python
Sets vs. Dictionaries in Python: Unravel the nuances of these two dynamic data structures, from uniqueness to data storage, and optimize your Python programming.
Python offers several built-in data structures like tuples, sets, and dictionaries. These data structures help to store and organize data efficiently. This article will briefly discuss the difference between two such data structures, a set and a dictionary.
So, without further delay, let’s start the article.
Must Check: Top Python Online Courses and Certifications
Table of Contents
- Difference Between Set and Dictionary in Python
- What is Set in Python?
- What is Dictionary in Python
- Key Difference Between Set and Dictionary in Python
Difference Between Set and Dictionary in Python: Set vs Dictionary
| Parameter | Set | Dictionary |
| Definition | An unordered collection of unique elements. | An ordered collection of key-value pairs. |
| Representation | Curly braces {}. | Curly braces {}, but with key-value pairs. |
| Order | Unordered. | Ordered (from Python 3.7 onwards). |
| Duplicates | Does not allow duplicate elements. | Does not allow duplicate keys. |
| Mutability | Mutable (can add or remove elements). | Mutable (can add, modify, or remove key-value pairs). |
| Access Method | Elements are accessed directly. | Values are accessed using keys. |
| Use Case | To store unique elements. | To store related pieces of information. |
| Example | my_set = {1, 2, 3} | my_dict = {“name”: “Alice”, “age”: 30} |
Best-suited Python courses for you
Learn Python with these high-rated online courses
What is Set in Python?
A set in Python is an unordered collection of unique elements. Think of it as a bag where you can throw in items, but each item can exist only once. But if you try to add a duplicate, python will simply ignore it. This characteristic of the set makes it extremely useful for tasks like eliminating duplicate entries from a list or checking the membership of an element in a collection.
Now, let’s have an example of sets in Python.
#create a setmy_set = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])print(my_set)
#create a set with the string
my_set_1 = set("hello world")print(my_set_1)
# Perform set operations.
my_set2 = {1, 2, 3, 4}my_set3 = {4, 5, 6, 7}print(my_set2.union(my_set3)) # unionprint(my_set2.intersection(my_set3)) #intersectionprint(my_set2.difference(my_set3)) #difference
Output
Must Read: Python Practice Set for Beginners
Find out about top job-oriented courses available after 12th. Also, explore specialized online degree programs for a amazing career path.
Operation Performed on Sets
- add(): Add an element to the set.
- remove(): Remove an element from the set.
- discard(): Remove an element from the set, but only if it is present.
- clear(): Remove all elements from the set.
- union(): Return a new set containing the union of two sets’ elements.
- intersection(): Return a new set containing the intersection of two sets’ elements.
- difference(): Return a new set that contains the difference of the elements of two sets.
- issubset(): Return True if the first set is a subset of the second set; otherwise, return False.
- issuperset(): Return True if the first set is a superset of the second set; otherwise, return False.
Key Features of Set in Python
- Unordered: The elements in the set are unordered, i.e., elements are not in a specific order.
- Mutable: You can add or delete elements from a set.
- No Duplicate: Sets automatically remove duplicate elements.
- Representation: Represented by curly ({}) braces.
Application of Sets in Python
- Web scraping: Sets can be used to remove duplicate elements from a list of URLs to scrape or to find the unique elements in a list of scraped data.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Sets can be used to remove stop words from a text corpus or to find the unique words in a text document.
- Machine learning: Sets can be used to represent features in a machine learning dataset or to find the unique values of a target variable.
- Data analysis: Sets can group data into categories or find a variable’s unique values.
What is a Dictionary in Python?
A dictionary in Python is an ordered collection of key-value pairs. Imagine a real-life dictionary where you look up a word (the key) to find its definition (the value). Similarly, you use a key in a Python dictionary to retrieve its corresponding value.
Similar to sets in Python, dictionaries are also mutable, meaning that you can add, remove, or change their key-value pairs. In Python, dictionaries are created using the dict() function.
Now, let’s have a simple example:
#create a dictionary
my_dict = dict([('name', 'Alice'), ('age', 25)])print(my_dict)
# Store data in a structured way.my_dict1 = { 'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25, 'occupation': 'Software Engineer'}print(my_dict1['name'])
Output
Must Read: Python Dictionary Practice Program for Beginners
Operations Performed on Dictionaries
- get(): Get the value associated with a key. The default value is returned if the key is not present in the dictionary.
- items(): Return a list of key-value pairs in the dictionary.
- keys(): Return a list of keys in the dictionary.
- values(): Return a list of values in the dictionary.
- update(): Update the dictionary with a new set of key-value pairs.
- clear(): Remove all key-value pairs from the dictionary.
Key Features of Dictionaries
- Key-Value Pairs: Each entry in a dictionary consists of a key and its associated value.
- Ordered: Since Python 3.7, dictionaries maintain the order of insertion.
- Mutable: You can modify a dictionary by adding or removing key-value pairs after its creation.
- Unique Keys: While values can be duplicated, each key in a dictionary must be unique.
- Representation: Dictionaries also use curly braces {} but with key-value pairs.
Application of Dictionary
- Data storage: Dictionaries can store data in a structured way, making it easy to access and manage. For example, you could use a dictionary to store the contact information for your customers or employees.
- Configuration files: Dictionaries can be used to create configuration files that store settings for your application. This can be useful for storing database connection settings, API keys, or user preferences.
- Caching: Dictionaries can be used to implement caching, which can improve the performance of your application by storing frequently accessed data in memory.
- Data Analysis: Dictionaries can analyze data by grouping it into categories or counting the occurrences of different values. For example, you could use a dictionary to count the number of times each word appears in a text document.
- Web Development: Dictionaries are commonly used to store data about users, sessions, and other aspects of the web application.
Key Differences and Similarities Between Set and Dictionary in Python
- Sets are an unordered collection of unique elements, whereas a dictionary is an ordered collection of key-value pairs.
- Sets store unique elements, while dictionaries store related pieces of information.
- Elements of both sets and dictionaries are mutable.
- Both sets and dictionaries do not allow duplicate entries.