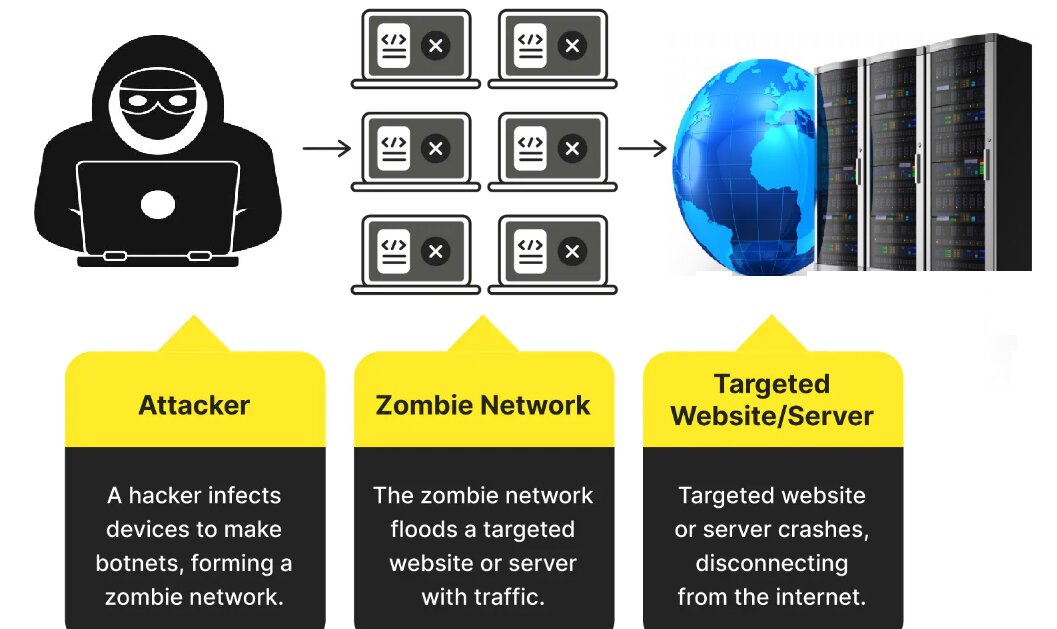
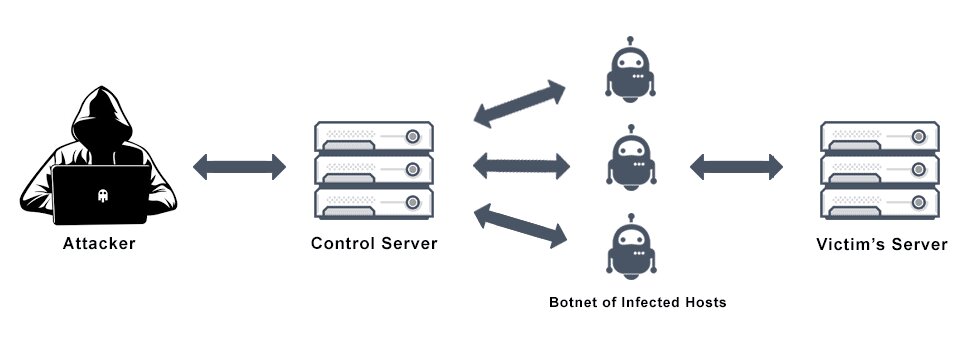
What is a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack?
DDoS attacks were once thought to be minor annoyances carried out by inexperienced attackers for amusement, and they were relatively simple to mitigate. Unfortunately, that situation no longer exists. DDoS attacks are now a sophisticated activity.
So, what exactly is a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack? In this article, we will cover DDoS attacks in great depth. But, before moving on to that, let’s go through the topics that we will be covering in this blog:
- What is a DDoS attack?
- Types of DDoS attacks
- Real-life examples of a DDoS attack
- How does a DDoS attack work?
- What is the duration of a DDoS attack?
- How to prevent DDoS attacks?
- What is the difference between DoS and DDoS attacks?
- Conclusion
What is a DDoS attack?
A DDoS (Distributed denial-of-service) attack is a malicious attempt at making an online service unreachable to users, typically by temporarily interrupting or suspending the hosting server’s services. They target a wide range of critical assets, from financial institutions to news websites, and pose a significant challenge for individuals to publish and access critical information.
DDoS attacks can be classified based on which layer of the OSI model they target. They are most commonly found in the Network (Layer 3), Transport (Layer 4), Presentation (Layer 6), and Application (Layer 7) Layers.
DDoS attacks pose a threat to businesses of all sizes, from Fortune 500 corporations to small e-commerce sites. DDoS attackers most frequently target:
- Online merchants
- Financial and fintech firms
- Governmental organizations
- Providers of information technology services
- Companies that provide online gaming and gambling
Best-suited Cyber Security courses for you
Learn Cyber Security with these high-rated online courses
Types of DDoS attacks
You can classify DDoS attacks into three types.
Application Layer: This attack’s foundation frequently targets applications such as Web Servers. However, application layer attacks have evolved to target application platforms such as WordPress. Application layer attacks are designed for compromising an application, an online service, or a website. An example is a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) flood attack, which would be the equivalent of repeatedly refreshing many web pages.
Protocol attacks: These are also known as state-exhaustion attacks, disrupting service by consuming too many server resources and network equipment resources such as firewalls and load balancers. Protocol attacks take advantage of flaws in the protocol stack’s layers 3 and 4 to render the target inaccessible. An SYN flood attack is one example of this, in which many “initial connection request” packets are sent to the target IP addresses using spoofed source IP addresses.
Volumetric attacks: These attacks consume accessible bandwidth with packet floods and overload a targeted resource. Massive data are sent to a destination using various methods of creating massive traffic, such as botnet requests. An example of this attack is a domain name system amplification attack that sends requests to a DNS server using the target’s IP address. After that, the server floods the target with responses.
Real-life examples of a DDoS attack
AWS attack: In February 2020, AWS reported mitigating a massive DDoS attack. This attack was seeing incoming traffic at a rate of 2.3 Tbps at its peak. AWS did not specify which customer was the target of the attack.
Dyn attack: In October 2016, attackers launched a massive DDoS attack against Dyn. This attack wreaked havoc on many major websites, including Netflix, Visa, Amazon, Reddit, GitHub, and many more.
You can also explore- What is Cyberterrorism? Is it a Real Threat to Security?
How does a DDoS attack work?
DDoS attacks are carried out by cybercriminals gaining unauthorized control of a computer network. Cybercriminals use specially designed malware to turn computers and other systems (such as IoT devices) into bots (or zombies). A botnet is a collection of such bot systems. Cybercriminals will use the remote control of the botnet to launch DDoS attacks.
What is the duration of a DDoS attack?
A DDoS attack’s duration varies. Attacks such as the Ping of Death can be brief. Slowloris attacks take more time to develop. According to one report, 33% of DDoS attacks last an hour, 60% last just under a full day, and 15% last weeks or months.
How to prevent DDoS attacks?
Some of the popular ways to prevent DDoS attacks are:
Utilizing cloud-based protection: Cloud-based protection can quickly scale and handle large volumetric DDoS attacks.
DDoS response plan: Your security team should create an incident response plan to ensure that employees respond quickly and effectively in the event of a DDoS. This plan should include instructions on responding to a DDoS attack, retaining the company’s operations, escalation protocols, and so on.
Elevated levels of network security: Network security is critical for preventing DDoS attacks. Because an attack only impacts if the hacker has enough time to accumulate requests, detecting a DDoS early on is critical to controlling the blast radius.
Continuous network traffic monitoring: Using continuous network traffic monitoring to analyze traffic is a perfect way of detecting DDoS activity traces because it provides real-time monitoring to identify a DDoS attempt before the attack begins.
Limit network broadcasting: To increase the impact of a DDoS attack, a hacker will probably send requests to every device on your network. This tactic can be countered by restricting network broadcasting among devices.
Keep an eye out for warning signs: Only when your data protection team can quickly identify the characteristics of a DDoS attack so that you can take appropriate actions and minimize the effects.
You can also explore – What is safe browsing & how to turn it on?
What is the difference between DoS and DDoS attacks?
Let us try to understand the distinction between these two types of attacks using a table:
| Benchmark | DoS attack | DDoS attack |
| Full form | Denial-of-service | Distributed Denial-of-service |
| No. of computers targeting the victim’s system | The single system targets the victim’s system | Multiple systems attack the victim’s system |
| Speed | Slower in comparison to a DDoS attack | DDoS attacks are more rapid than Dos attacks |
| Blocking | Easy to block as only a single system is used to target the victim’s system | Difficult to block as multiple systems are used to target the victim’s system |
| Tracing | Easy to trace | Difficult to trace |
You can also read – What is a Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack?
Conclusion
DDoS attacks are cheap and simple to launch, but their complexity varies greatly and can significantly impact the businesses targeted. During an attack, no employees can access network resources, so in the case of Web servers hosting eCommerce sites, no customers can buy products or get help. So, it is preferable to use the prevention techniques mentioned above rather than being sorry!
FAQs
What are the three kinds of DDoS attacks?
There are three types of DDoS attacks: Volume based attacks Protocol attacks Application layer attacks
What consequences can a DDoS attack have?
A DDoS attack may make your site more vulnerable to hacking because all of your systems will focus on getting the site back online, and security systems may have been rendered inoperable due to the attack.
What is the most common target of a DDoS attack?
DDoS attacks commonly target the network (layer 3), transport (layer 4), presentation (layer 6), and application (layer 7) layers.
Can a firewall protect against DDoS?
Firewalls cannot prevent DDoS attacks.
How long can a typical DDoS attack last?
A typical DDoS attack lasts less than four hours.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio