5 V’s of Big Data Demystified
Here is all you should know about the 5V’s of big data. Learn how they are important today.
In today’s digital age, we generate an enormous amount of data daily. With the proliferation of the internet, social media, smartphones, and other digital devices, the volume of data is increasing at an unprecedented rate. To make sense of this data, we need to use specialized tools and techniques that can help us extract valuable insights and knowledge. This is where big data comes into play.
Big data refers to the massive volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that are generating every day. However, big data is more than just the volume of data. Five important characteristics or dimensions define big data, known as the 5 V’s of big data – Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value. In this article, we will explore these dimensions in detail and understand why they are critical for making sense of big data.
First V: Volume
When we talk about Volume in the context of Big Data, we’re referring to the sheer amount of data generated and collected. This can include anything from structured data (like numbers and dates) to unstructured data (like text, images, and videos).
The amount of data every day is truly staggering. For example, according to IBM, we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day. To give you a sense of what that means, one quintillion is a 1 followed by 18 zeros! And that amount of data is only going to keep growing as more and more devices become connected to the internet.
All this data presents a major challenge for organizations. How do we store it all? How do we process it? How do we make sense of it? These are just a few of the questions that arise when we start talking about Big Data.
So, to address these challenges, we need specialized tools and technologies that are capable of handling massive amounts of data. That’s where technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases come in. These tools are scalable, fault-tolerant, and capable of processing data in parallel across multiple nodes.


Best-suited Data Science courses for you
Learn Data Science with these high-rated online courses
Second V: Velocity
Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated, processed, and analyzed. And, in the modern world, data is generated at an unprecedented pace, and organizations need to be able to process and analyze it in near-real-time to stay competitive.
Many sources of data generate at a high velocity, such as social media, internet-connected devices, and sensors. For example, look at the following image to consider the sheer volume of data generated on the internet EVERY MINUTE! Do you see how far we have come in ten years?
Processing this data in real time is crucial for businesses that must make quick decisions. For example, financial institutions need to analyze large volumes of financial transactions in real-time to detect fraudulent activities. And e-commerce companies need to process customer behavior data in real-time to personalize product recommendations.
Velocity is an important aspect of Big Data because it allows businesses to gain insights quickly, respond to changes in the market, and make informed decisions. To handle high-velocity data, businesses need to invest in technologies that can process and analyze data quickly. This is real-time data streaming, complex event processing, and in-memory computing.
Third V: Variety
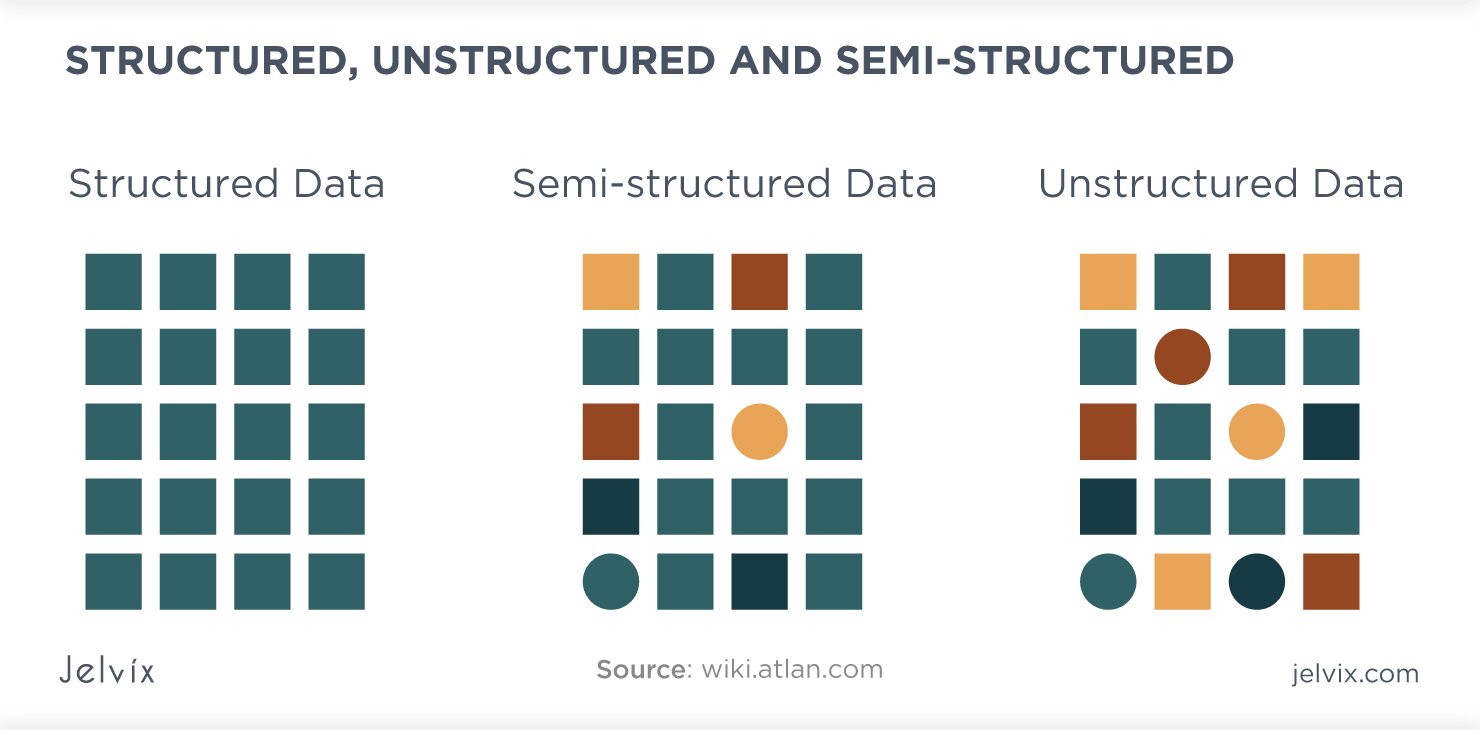
Variety refers to the diverse types and data sources generated and collected in today’s digital world. It’s not just limited to structured data like that of traditional databases. With the proliferation of social media, the internet of things, and other technologies, data is now available in various forms, such as text, images, audio, video, and even sensor data. This data is of three types: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured.
Structured Data is the traditional form of data that follows a formal structure. It can be easily organized in a relational database. A good example of structured data is a bank statement that contains specific fields like date, time, and amount.
Semi-structured Data is partially organized data that does not conform to the formal structure of data. Examples of semi-structured data include log files, JSON files, sensor data, and CSV files.
Unstructured Data is data that does not have a defined structure. You cannot categorize it into rows and columns like in a relational database. Examples of unstructured data include text files, emails, images, videos, voicemails, and audio files.
Traditional data management tools and techniques may not be enough to handle the huge volumes and variety of big data. It requires a flexible and scalable approach to data storage, processing, and analysis. It also requires the ability to handle and integrate various data types from different sources.
This is where Big Data technologies like Hadoop and Spark come into play. They specifically handle a wide range of data types.
Fourth V: Veracity
The fourth V of Big Data is Veracity, which refers to the accuracy and trustworthiness of the data. With the increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data, it becomes important to ensure that the data we are using is reliable and truthful.
Data can often be incomplete, inconsistent, or even intentionally misleading. This can happen due to various reasons, such as human error, data entry mistakes, data tampering, or biases. Therefore, it is essential to verify the data sources, validate the data quality, and ensure the authenticity of the data.
Veracity also includes the concept of data governance, which refers to the policies, procedures, and controls organizations use to manage their data assets. And, so, it is important to have proper data governance practices in place to maintain the accuracy and reliability of the data.
To ensure the veracity of the data, organizations use various tools and techniques such as data profiling, data cleansing, data validation, and data auditing. These techniques help identify and correct data errors, remove duplicates, and ensure consistency across different data sources.
Fifth V: Value
One of the most important 5 V’s of Big Data is Value. It refers to the ability of Big Data to provide valuable insights and create value for businesses and organizations. In other words, it’s the usefulness of the data to achieve a specific goal or objective.
The value of Big Data appears in various ways, such as improving decision-making processes, creating new revenue streams, reducing costs, increasing operational efficiency, and enhancing customer experiences. For instance, by analyzing customer data, businesses can better understand their customers’ preferences and behavior, which can help them tailor their products and services to meet customer needs and ultimately increase sales.
The value of Big Data also depends on the quality of the data and the insights derived from it. Therefore, it’s important to have reliable data sources, effective data management processes, and skilled data professionals to ensure the accuracy and relevancy of the data.
Endnotes
In conclusion, the 5 V’s of Big Data – Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value – provide a framework for understanding the challenges and opportunities of the vast amounts of data in today’s digital world. Understanding and effectively leveraging the 5 V’s of Big Data can be a key driver of innovation, growth, and success in today’s data-driven economy.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio