HTML Tags: Essential and Basic Tags for Creating an HTML Document
HTML, or HyperText Markup Language, is the foundational language used to create and structure content on the web. Tags form the heart of HTML, essential building blocks that define how elements on a webpage are displayed and interacted with. This blog will discuss some essential and basic HTML tags with examples.
Table of Contents
Best-suited HTML & CSS courses for you
Learn HTML & CSS with these high-rated online courses
What are HTML tags?
HTML tags are special keywords that specify how a web browser must format and display the content. Tags are wrapped in brackets < and >. They start with an open angle bracket (<) and close with a closed angle bracket (>). The ending tag has a forward slash before the name of the element. They can nest (be placed) inside one another.
HTML Tag Syntax:
<example>The first tag is the opening tag that indicates the start, while the second tag is the closing tag that depicts the end </example>.
For Example –
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
In the above example, the opening <p> tag indicates the start of a new paragraph. The </p> is the closing tag that ends it.
Why do we need to open and close HTML tags?
Opening and closing HTML tags are crucial because they outline the structure and content of a webpage, allowing the browser to know how to render the information. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Purpose of Opening and Closing Tags:
- Opening Tag: Marks the beginning of an element. For instance, <p> indicates the start of a paragraph.
- Closing Tag: Marks the end of that element. For example, </p> tells the browser the paragraph ends.
Together, these tags help encapsulate content, ensuring that the webpage layout and styling remain organized and predictable.
Importance in Browser Interpretation:
The browser reads in HTML code sequentially. One missing closing tag can make it puzzling for the browser, so it will render an unexpected overlap or misplaced element. For example, a browser might try to consider all the following elements as part of that <div>, which will cause positioning issues.
Error Prevention and Debugging:
When debugging HTML, developers often look for missing closing tags. The browser developer console or validation services usually point to such errors.
Self-Closing Tags:
Not all tags require a closing counterpart. Self-closing tags represent elements that don't contain any content. Examples include:
- <img> for embedding images
- <br> for line breaks
- <hr> for horizontal rules

Essential HTML Tags
Every HTML document must have some essential tags so that a web browser can understand and display it correctly. These tags help web browsers distinguish between simple text and HTML text. Let’s understand how many HTML tags are there.
Four essential HTML tags form the basic structure for every HTML file:
- <html></html>
- <head></head>
- <title></title>
- <body></body>
Before discussing the essential tags, let’s learn about the HTML document declaration, i.e. <!DOCTYPE>.
<!DOCTYPE>
<!DOCTYPE> is not a tag but a declaration that tells the browser about the document type. It specifies the version of HTML that the document is using so that browsers can display web pages correctly. All HTML documents must start with this declaration. It is not case-sensitive.
Syntax in HTML5:
<!DOCTYPE html>
Or
<!doctype html>
Now, let us understand the essential tags in detail.
1. <html></html>
The <html> tag defines the document as a web page. It also specifies the beginning and end of the HTML document.
It contains all HTML elements except the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration. All other tags are nested between the <html> and </html> tags.
Syntax:
<html>Content</html>
2. <head></head>
The <head> tag represents the head section of the HTML document. It gives information about the webpage, which is not displayed on the browser window. It contains the information related to the webpage and contains tags such as <title>, <meta>, <link>, etc. The <head> tag is located between the <html> tag and the <body> tag.
Syntax:
head><title>Webpage Title</title></head>
3. <title></title>
As the name suggests, the <title> tag specifies the web page's title. This tag is described in the head tag. The content in between the <title>…</title> tag appears on the tab or title bar in the browser window.
Syntax:
<title>Webpage Title</title>
4. <body></body>
This tag contains all the information and other visible content that we want to display on the web page. All the images, links, plain text, videos, etc. go between the <body> and </body> tags.
The body tag contains other tags such as the <p> tag for paragraph, <strong> tag for bold text, <a> tag for images, <ol> tag for ordered list, etc.
Syntax:
<body> Content </body>



Basic HTML Tags
Apart from essential tags, an HTML document can have as many tags as you want to display your content properly. Using the basic tags, you can format content, add headings, align content, add sections, and do a lot more on a website. Here is a list of some of the commonly used basic HTML tags.
1. <h1></h1>
This tag defines the HTML headings. The heading tag makes the text bigger and bolder than plain text. HTML has six heading tags: h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6. The <h1> tag represents the most important heading while <h6> is for the least important ones.
Syntax:
<h1>Heading 1</h1><h2>Heading 2</h2><h3>Heading 3</h3><h4>Heading 4</h4><h5>Heading 5</h5><h6>Heading 6</h6>
2. <p></p>
This tag defines a paragraph. When we use the <p> tag, the web browser automatically inserts a single blank line before and after each <p> element to make the text more readable.
Example:
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
3. <img>
The image tag allows us to insert images into a web page. It has no closing tag. The attributes of the image tag include:
- src: the source file (src)
- alt: alternative text
- width
- height
Example:
<img src="naukrilearning.jpg" alt="naukri learning" width="100" height="100">
4. <a></a>
The <a> tag or the anchor tag allows us to link one web page to another page or a section of the same page. The <a> tag has an href attribute that holds the destination URL. Using the anchor tag, we can create a hyperlink to web pages, files, email addresses, segments on the same page, etc.
Example:
<a href="https://www.shiksha.com/online-courses/">This is a link</a>
5. <!– Comment –>
The comment tag helps programmers to understand the HTML source code. The comments are not visible on the web page in a browser.
Syntax:
<a href="https://www.shiksha.com/online-courses/">This is a link</a>
To get started with your first HTML document:
- Copy the code given below
- Paste it into your editor (for example – Notepad in Windows)
- Save the file with .htm or .html extension (example – mypage.html)
- Open the HTML page in your web browser
Here is the code to create an HTML document with all the essential and basic tags of HTML as discussed above.
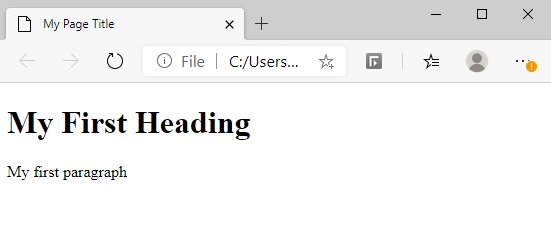
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <title>My Page Title</title></head> <body> <h1>My First Heading</h1> <p>My first paragraph</p></body> </html>
It will display as below on your web browser:

Conclusion
This article discussed the essential HTML tags for creating an HTML document or web page. You should understand that they work at a basic level to form an HTML document. In our upcoming articles, we will dive deep into some of the topics introduced in this blog and present other important HTML concepts.
FAQs
Do all HTML tags need to have closing tags?
No, not all HTML tags have closing tags. In HTML, singleton tags or self-closing tags, or void tags do not require a closing tag to be valid. For example, the tag to break the line does not require a closing tag.
What is a list tag in HTML5?
The list tag or tag allows us to add the contents in an HTML document in listed order. There are two types of HTML lists: Ordered list (by default, list items will be marked with numbers) and Unordered list (list items will be marked with bullets).
How many HTML tags are there?
Mozilla Developer Network mentions that there are 142 HTML tags.
Why do we use HTML tags?
HTML tags are essential for structuring content on the web. They allow browsers to interpret and display text, images, links, and other elements correctly. Tags help organize content into headings, paragraphs, lists, and more, making it easier for users to read and navigate.
What is the difference between block-level and inline HTML tags?
Block-level tags create a new block of content and typically start on a new line (e.g., <div>, <p>, <h1>). Inline tags do not start on a new line; they only occupy as much width as necessary (e.g., <span>, <a>, <img>). This distinction affects how elements are displayed on the page.

Rashmi is a postgraduate in Biotechnology with a flair for research-oriented work and has an experience of over 13 years in content creation and social media handling. She has a diversified writing portfolio and aim... Read Full Bio



Comments
(1)
R
3 weeks ago
Report
Reply to Rajesh Sisodiya