Improving ML Model Performance Using AdaBoost
In this article, we will discuss how to improve machine learning model using AdaBoost which is most commonly used meta-algorithms in boosting
Introduction
As a machine learning practitioner, your ultimate goal is to obtain an ML model with the best possible predictive accuracy. So, rather than relying on the results of one specific model, it makes more sense to involve different models and aggregate their outcomes to obtain the best-fitted model for your ML problem. This is done through ensemble learning methods.
Boosting is an ensemble method that involves combining ML models in an adaptive manner to obtain an ensemble model. This ensemble model is nothing but a final powerful ML model that is capable of making more accurate predictions than any single one of them would alone.
AdaBoost is one of the most commonly used meta-algorithms in boosting. In this article, we will implement AdaBoost using Python to improve our model performance.
Best-suited Data Science courses for you
Learn Data Science with these high-rated online courses
Table of Content
- Why Boosting?
- How Boosting Works?
- Understanding AdaBoost
- How AdaBoost Works?
- Building an AdaBoost Model in Python
Why Boosting?
As discussed above, the different ML models being combined are referred to as base models aka weak learners which are aggregated to produce an ensemble model aka a strong learner.
Now that we have got the basic jargon out of our way, let’s talk about why boosting is even required.
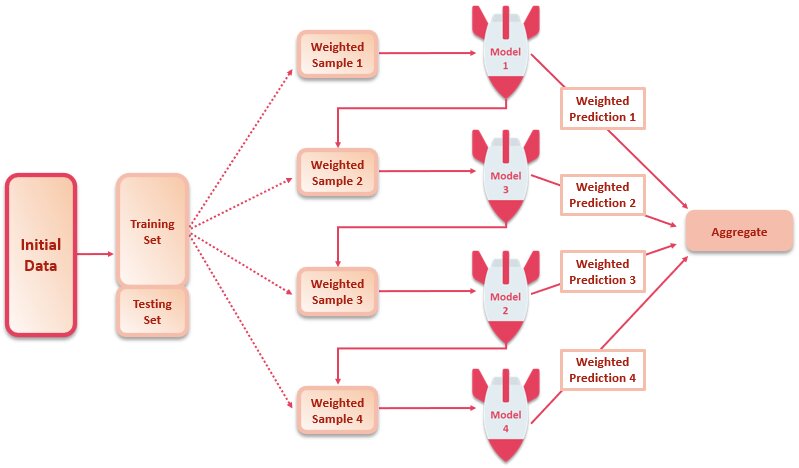
Through boosting methods, you can improve your model performance by training homogenous weak learners in an iterative manner such that each weak learner depends on the outcome of the previously fitted weak learner. So, the eventually obtained model is actually the weighted sum of all constituent base learners.
Must Check: What is Machine Learning?
Must Check: Machine Learning Online Courses & Certifications

How Boosting works?
In boosting, the base models are trained sequentially in a way that each base model gives more weight to the observations that have been poorly classified by the predecessor base models.
The intuition here is that individual ML models may not work efficiently on the entirety of a given dataset, but they might perform well on parts of the data. The ensemble method attempts to correct misclassifications in the training data. Hence, each base model in the ensemble actually boosts the overall performance when combined iteratively.
By the end of it, you will obtain an ensemble model with lesser bias than its constituent individual base models. Lowering the bias would help avoid underfitting of the model, hence improving its performance.
Understanding AdaBoost
AdaBoost or Adaptive Boosting is an instance-based supervised learning technique, which means that instead of creating a separate ML model for each new observation, AdaBoost creates multiple base models during training and uses them to make predictions about new observations.
This algorithm was designed for classification problems but has been extended to regression problems as well. Here, we are going to focus on the classification side of the technique.
AdaBoost improves the generalization capabilities of the multiple models it combines and simplifies their maintenance.
Let’s look at how it works:
How AdaBoost Works?
AdaBoost makes predictions by calculating the weighted average of weak classifiers, where the weights are based on their performance and updated using a learning rate.
- The weak models are trained sequentially using weighted data samples that have been classified incorrectly.
- Once an individual weak classifier is trained, the weight of the sample next in the sequence gets updated.
- The weighted sample is then used to train the next weak classifiers which intuitively focuses on the samples having greater weight assigned to them to make better predictions.
- The process continues until either of the two conditions are met:
- A pre-decided number of weak classifiers have been aggregated
- No further improvement can be made to the training dataset
- Once the process is completed, you have a pool of weak classifiers each with a score.
- You then update the weights based on how poorly each weak classifier performed on the test data, using some function that includes a learning rate.
- The weights are then fed back into your strong classifier (ensemble model) via a weighted average of sorts.
Building an AdaBoost Model in Python
Problem Statement:
Let’s build our first AdaBoost classifier. For this, we will implement a Decision Tree as the base learner using the scikit-learn library in Python.
Dataset Description:
We will be making use of the wine dataset already present in the scikit-learn library.
The dataset features are given below:
- alcohol – Alcohol percentage in that particular type of wine
- malic_acid – Malic acid percentage in that particular type of wine
- ash – Amount of ash in that particular type of wine
- alcalinity_of_ash – Amount of alkalinity of ash in that particular type of wine
- magnesium – Amount of magnesium in that particular type of wine
- total_phenols – Amount of phenols in that particular type of wine
- flavanoids – Amount of flavonoids in that particular type of wine
- nonflavanoid_phenols – Amount of non flavonoid phenols in that particular type of wine
- proanthocyanins – Amount of proanthocyanins in that particular type of wine
- color_intensity – The color intensity of that particular type of wine
- hue – The hue of that particular type of wine
- od280/od315_of_diluted_wines – Amount of dilution of that particular type of wine
- proline – Amount of proline in that particular type of wine
- target – Class label of the wine (1,2, or 3)
The ‘target’ column is used to predict the class of wine.
Tasks to be performed:
- Import the required libraries
- Load the dataset
- Split the data into training and testing sets
- Build a Decision Tree Stump Model and get its Accuracy Score
- Build an AdaBoost Classifier and get its Accuracy Score
Step 1 – Import the required libraries
The Python implementation of the AdaBoost classifier is fulfilled by the Scikit-learn class: AdaBoostClassifier(), as shown below:
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier #Importing the rest of the libraries from sklearn.datasets import load_wine from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
Step 2 – Load the dataset
#Load the wine dataset wine = load_wine() X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names) y = pd.Series(wine.target)
Step 3 – Split the data into training and testing sets
#Split the dataset into 70% training set and 30% testing set X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=23)
Step 4 – Build a Decision Tree Stump Model and get its Accuracy Score
We are going to create a decision stump on the wine data by stopping the tree growth at max_depth=1. This stump model will be used as the weak learner in our AdaBoost classifier.
#Train a Decision Tree Classifier dtclf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, criterion='gini', random_state=23) dtclf.fit(X_train,y_train) dtclf_pred = dtclf.predict(X_test) dtclf_acc = round(accuracy_score(y_test,dtclf_pred),3) print(f"Decision Tree Classifier Test Accuracy Score: ", dtclf_acc)
Given the value we chose for our tree growth, the model’s performance is quite poor, as expected.
Step 5 – Build an AdaBoost Classifier and get its Accuracy Score
Let’s initialize our AdaBoost classifier model with the following hyperparameters:
- base_estimator = Decision Tree (default)
- n_estimators = 50 – Create 50 samples to train 50 decision tree base learners
- learning_rate = 0.5 – Shrinks the contribution of each base learner by the given value
#AdaBoost Classifier using Decision Tree as base learner adaclf = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=dtclf, n_estimators=50, learning_rate=0.5, random_state=23) adaclf.fit(X_train,y_train) adaclf_pred = adaclf.predict(X_test) adaclf_acc = round(accuracy_score(y_test,adaclf_pred),3) print(f"Decision Tree AdaBoost Model Test Accuracy Score: ", adaclf_acc)
See that score! Our AdaBoost classifier is performing really well as compared to the base Decision Tree model.



Conclusion
AdaBoost is often used to work with high-dimensional datasets. The reason this boosting technique works so well is because it considers the concept of information gain and hence, improves its predictions based on the data it is fed. I hope this article helped get you started with implementing AdaBoost in Python.
Top Trending Articles:
Data Analyst Interview Questions | Data Science Interview Questions | Machine Learning Applications | Big Data vs Machine Learning | Data Scientist vs Data Analyst | How to Become a Data Analyst | Data Science vs. Big Data vs. Data Analytics | What is Data Science | What is a Data Scientist | What is Data Analyst
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio