Inflation: What Is It And How Is It Measured?
Inflation, though not a new term, remains unfamiliar to many, leaving them unsure about its meaning and workings. Understanding inflation is essential because it affects our daily lives and the overall health of the economy. It refers to the gradual increase in the prices of goods and services within an economy. As a result of inflation, the purchasing power of money decreases, meaning that the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services than before. Let’s explore this important concept further.
Did you know that in the 1990s, 10 gm of gold was worth 3,200 rupees? Now, even 1 gm of gold is more costly than Rs. 3200. This rise in the prices of gold is an example of inflation.
By definition:
“Inflation is a progressive increase in the price of goods and services within the economy.”
It means that an increase in inflation lowers your ability to buy more things. You can buy lesser commodities in the same amount over time. The purchasing power of money goes down with time due to inflation. In this article, you will learn about the various aspects of it, such as how it is calculated using different methods and its disadvantages and advantages.
Table of Content
- Why does inflation happen?
- What are the pros and cons of inflation?
- How is it calculated?
- Inflation in India
- Why do you need to learn about inflation?
Must read: Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Why Does Inflation Happen?
The major reason behind inflation may include:
- Excess printing of the currency
- Production cost increases
- Increase in demand for goods and services
- Lack of supply of commodities
- When workers demand an increase in salaries
Suggested read: What is Microeconomics?
What are the Pros and Cons of Inflation?
You might believe that inflation is bad for the economy. However, it is an inevitable part of the economy with both advantages and disadvantages. Let us discuss both.
Advantages
- A moderate rate of inflation is a sign of a healthy economy.
- Theoretically, a higher rate facilitates production, which requires more labour. This leads to more manufacturing opportunities as well as more employment.
- Debtors can easily repay loans with money that holds less value in comparison with the money that they borrowed
Disadvantages
- High inflation rates cause uncertainty which reduces the influx of investment. Usually, countries with higher inflation rates have lower investment rates and, thus, lesser economic growth.
- Higher inflation reduces exports and reduces the current account balance of payments. With higher inflation, unemployment also increases.
- It can also impact people’s lives, such as senior citizens who rely on savings.
Best-suited Banking, Finance & Insurance courses for you
Learn Banking, Finance & Insurance with these high-rated online courses
How is it Calculated?
The basic method for calculating the inflation rate is to find the difference between the indices and divide it by the previous period’s index. Let us understand this with the help of an example.
For example, you want to calculate thecrate for biscuits in March 2021 concerning March 2014. Suppose the price of 100 gm biscuits was 52 rupees in March 2014; in March 2021, it is 60 rupees. Then the rate will be:
Start date: March 2014. Price: ₹ 52 = A
End date: March 2021. Price: ₹ 60 = B
Inflation Rate = ((B – A) / A) x 100 = ((60 – 52) / 52) x 100
= (0.153) x 100
= 15.3%
Worldwide, different indices are used for calculating the inflation rate. Let us discuss the following globally adopted indices:
1. Consumer Price Index
Inflation is measured by the consumer price index (CPI), which is the change in the price of a basket of goods and services purchased by households. Following is the method of calculating CPI:
To calculate the rate using this index, you need to find the difference between CPIs of two time periods. After that, you need to divide it with the CPI of the year for which you need to find the rate. Let us take an example:
Suppose, in January 2007, the CPI of a country was 202.416, and in January 2008, it was 211.080. Now, the rate for the time period will be:
2. Producer Price Indices
It is a price index to measure the average change in the selling prices that the domestic producers receive for the output. It measures the prices of commodities before they reach the customers. Currently, PPI is not used in India. The formula for calculating the PPI is:
You will calculate the inflation rate similar to the method used in CPI.
3. GDP Deflator
It is the measure of prices of domestically produced commodities in a period of one year. The GDP deflator is used for measuring the rate with respect to the base year. It is the ratio of current price (nominal) GDP to the real GDP. The GDP deflator for the base year is equivalent to 100.
Real GDP is calculated on the basis of the base year’s prices. The GDP deflator in India is calculated quarterly but only released annually.
Inflation in India
In India, this rate increased from 4.91% to 5.59% in December 2021, below the market expectations of 5.80%. It is still within the RBI’s 2-6% target range consecutively for the sixth time.
Prices increased at a faster pace, including:
- Food items: from 1.87% to 4.05%
- Clothing and footwear: from 7.94% to 8.30%
Prices went down for:
- Fuel and light: from 13.35% to 10.95% per cent),
- Housing: from 3.66% to 3.61%
- Pan, Tobacco and Intoxicants: from 4.05% to 3.22%
- Miscellaneous items: from 6.75% to 6.65%
- Consumer prices: went down for the first time in 11 months by 0.36% in December
Learn about the power of compounding
Why do you Need to Learn About Inflation?
It is an important concept because it affects every aspect of the economy, including the customer. It has a direct impact on your finances since it reduces the purchasing power of your money.
As the rate increases, you must pay more for basic necessities such as groceries and utility bills. When you start understanding the concept, you can set a practical budget for the time period. According to that, you will be able to manage your finances in the long run better.

FAQs
Explain the difference between stagflation and inflation?
Stagflation is a state of inflation in an economy that has either a slow or stagnant growth rate. Such economies also have a higher rate of unemployment. Inflation is the rate at which the prices of goods and services increase within the economy.
Who benefits from inflation?
Usually, borrowers benefit the most from this rate since they can repay the loan with money that has less worth than the value of borrowed amount.
What are the 3 types of inflation?
Demand-pull, cost-push and built-in inflation are the three types of inflation.

Jaya is a writer with an experience of over 5 years in content creation and marketing. Her writing style is versatile since she likes to write as per the requirement of the domain. She has worked on Technology, Fina... Read Full Bio




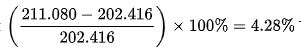
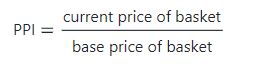
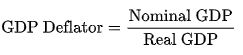
Comments
(1)
A
10 months ago
Report
test
Reply to Aman