Introduction to Inheritance in C++
In this blog, we will explore the concept of inheritance in C++ and its access. We will also discuss different types of inheritance, such as single inheritance, multiple inheritance, and hierarchical inheritance, and how they can be used in different scenarios. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid understanding of inheritance in C++ and how it can be leveraged to create powerful and flexible programs.
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming that allows a class to inherit properties (data and functions) from another class. This feature is supported by many programming languages, including C++. Inheritance is a powerful mechanism that enables developers to create new classes that build upon existing classes, leading to code reuse and extensibility. In C++, inheritance is implemented using the “class” keyword and the colon (:) symbol to indicate that a class is derived from another class. The derived class gains access to all of the public and protected members of the base class, and can add its own unique properties and functions.
Explore C++ Courses
Table of Content
- What is Inheritance in C++?
- Access Modes in C++ Inheritance
- Types of Inheritance in C++
- Method Overriding in C++
What is Inheritance in C++?
The capacity of a class to derive or “inherit” properties from an existing class, usually referred to as the parent class, is known as inheritance. These characteristics are essentially data (variables) and methods (functions) of the parent class.
Inheritance allows code reusability. Without altering any code, the new class(es) inherits all properties and functions from the pre-existing parent class(es). Parent classes are also referred to as base classes, and the new classes are known as child classes or derived classes.
Let’s look at an example syntax:
class Mother { // eat() function // sleep() function
};
class Baby : public Mother { // cry() function };
Here, the class Baby is derived from the class Mother. So, all the attributes of the class Mother are accessible to the class Baby.
Note how we have used the keyword public while inheriting the class Baby from the class Mother. We can also use keywords private or protected and these are called the modes of inheritance. Let’s understand them in detail:
Best-suited C++ courses for you
Learn C++ with these high-rated online courses
Access Modes in C++ Inheritance
Public Mode
If the subclass is derived from a public base class, the public members of the base class also become public in the derived subclass. Similarly, the protected members of the based class become protected members in the derived class too.
Protected Mode
If the subclass is derived from a protected base class, then both – the public, as well as protected members of the base class, become protected members in the derived class.
Private Mode
If the subclass is derived from a private base class, then both – the public, as well as protected members of the base class, become private members in the derived class.
However, remember that the private members of the base class cannot be directly accessed by the derived class.
You can also explore – Classes and objects in C++
Types of Inheritance in C++
Single Inheritance
A derived class only has one base class from which to inherit its attributes.
Following is the C++ syntax for single inheritance:
class DerivedClass : access_mode BaseClass { // Body of derived class }; OR class B { ... .. ... }; class A: public B { ... .. ... };
C++ Example
Let’s look at a C++ example for single inheritance:
#include using namespace std;
//Base class class Mother { public: void eat() { cout << "Eats.\n"; } void sleep() { cout << "Sleeps.\n"; } }; //Derived class class Baby : public Mother { public: void cry() { cout << "Cries.\n"; } };
//Main function int main() { //Create object of the class baby Baby b; //Calling members of the base class b.eat(); b.sleep(); //Calling member of the derived class b.cry(); return 0; }
Output:
Multiple Inheritance
A derived class has multiple base classes from which it inherits its attributes.
Following is the C++ syntax for multiple inheritances:
class DerivedClass : access_mode BaseClass1, access_mode BaseClass2, .... { // Body of derived class };
OR class B1 { ... .. ... }; class B2 { ... .. ... }; class A: public B1, public B2 { ... ... ... };
#include using namespace std; //first base class class Automobile { public: void automobile() { cout << "This is an automobile.\n"; } }; //second base class class FourWheel { public: void fourwheel() { cout << "This is a Four-wheeler automobile.\n"; } }; //derived class class Car : public Automobile, public FourWheel { }; //Main function int main() { //Create object of the derived class Car car; //Calling members of the base classes car.automobile(); car.fourwheel();
return 0; }
Output:
Multi-level Inheritance
A derived class inherits its attributes from another derived class.
Following is the C++ syntax for multi-level inheritance:
class C { ... .. ... }; class B: public C { ... .. ... }; class A: public B { ... ... ... };
C++ Example
Let’s look at a C++ example for multi-level inheritance:
#include using namespace std; //Base class class Grandmother { public: void bake() { cout << "Bakes.\n"; } }; //Intermediate class class Mother : public Grandmother { public: void eat() { cout << "Eats.\n"; } void sleep() { cout << "Sleeps.\n"; } }; //Derived class class Baby : public Mother { public: void cry() { cout << "Cries.\n"; } };
//Main function int main() { //Create object of the class baby Baby b; //Calling members of the base class b.bake(); //Calling members of the intermediate class b.eat(); b.sleep();
//Calling member of the derived class b.cry(); return 0; }
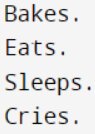
Output:
Hierarchical Inheritance
In this type, multiple derived classes inherit their attributes from a single base class.
Following is the C++ syntax hierarchical inheritance:
class BaseClass { // Body of BaseClass } class DerivedClass1 : public BaseClass { // Body of DerivedClass1 } class DerivedClass2 : public BaseClass { // Body of DerivedClass2 } . . . class DerivedClassN : public BaseClass { // Body of DerivedClassN }
#include using namespace std; //Base class class Mother { public: void eat() { cout << "Eats.\n"; } void sleep() { cout << "Sleeps.\n"; } }; //Derived class 1 class Baby1 : public Mother { public: void cry() { cout << "Cries.\n"; } }; //Derived class 2 class Baby2 : public Mother { public: void laugh() { cout << "Laughs.\n"; } };
//Derived class 3 class Baby3 : public Mother { public: void play() { cout << "Plays.\n"; } };
//Main function int main() { //Create object of the class baby1 Baby1 b1; //Create object of the class baby2 Baby2 b2; //Create object of the class baby3 Baby3 b3; //Calling all public members b1.eat(); b1.sleep(); b1.cry(); b2.eat(); b2.sleep(); b2.laugh(); b3.eat(); b3.sleep(); b3.play(); return 0; }
Output:
Hybrid Inheritance
In this type, we use a combination of more than one form of inheritance – a hybrid inheritance.
C++ Example
Let’s look at a C++ example for hybrid inheritance:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int numA; public: void get_numA() { cout << "Enter the value of the first number: "; cin >> numA; } }; class B : public A { protected: int numB; public: void get_numB() { cout << "Enter the value of the second number: "; cin >> numB; } }; class C { protected: int numC; public: void get_numC() { cout << "Enter the value of the third number: "; cin >> numC; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int val; public: void mul() { get_numA(); get_numB(); get_numC(); cout << "Product of the three numbers is: " << numA*numB*numC; } }; int main() { D val; val.mul(); return 0; }
Output:
You can also explore – OOPs concepts in C++
Method Overriding in C++
The ability of C++ to allow a derived class to provide some specific implementation of a method that has already been specified in one of the base classes is known as method overriding or member function overriding.
For instance, if a function with the same name is defined in both the base class and the derived class, the definition of the derived class will take precedence. The identical naming scheme used by the basic and derived classes causes this disparity.
Also check: Difference Between Overloading And Overriding
Endnotes
Hope this article was helpful for you to understand C++ inheritance and how to implement different types of inheritances. The OOPs concepts such as inheritance are the most commonly asked questions in interviews for developer roles in C++.
If you want to learn more about C++ and solidify your basics, you can explore our articles on the C++ programming language.
FAQs
What is inheritance in C++?
Inheritance is a mechanism in C++ that allows a class to inherit properties (data and functions) from another class. The class that is being inherited from is called the base class or parent class, and the class that inherits from it is called the derived class or child class.
What are the benefits of inheritance in C++?
Inheritance allows for code reuse and extensibility by enabling developers to create new classes that build upon existing classes. This can lead to more efficient and maintainable code, as well as increased flexibility in the design of a program.
How is inheritance implemented in C++?
In C++, inheritance is implemented using the "class" keyword and the colon (:) symbol to indicate that a class is derived from another class. The derived class gains access to all of the public and protected members of the base class, and can add its own unique properties and functions.
What is a base class in C++?
A base class is a class that is inherited from by another class. It contains properties (data and functions) that can be accessed by the derived class.
What is a derived class in C++?
A derived class is a class that inherits properties (data and functions) from a base class. It can also add its own unique properties and functions.
What is the difference between public and private inheritance in C++?
Public inheritance allows the public and protected members of the base class to be inherited by the derived class and be accessible from outside the class, while private inheritance only allows the base class members to be accessible within the derived class.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio