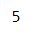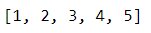Python Eval: Exploring the Pros, Cons, and Best Practices for Safe and Secure Usage
In this article, we will learn how to use python eval function, its advantages and limitations. Later in the article, we will also discuss some best practices of using eval function.
Python eval() is a built-in function in Python that evaluates a string as a Python expression and returns the result. The purpose of eval is to allow the dynamic execution of Python code at runtime. It can perform mathematical calculations, manipulate data structures, and execute code dynamically. However, using eval cautiously is important, as it can pose security risks if used improperly. With proper usage and best practices, eval can be a powerful tool for creating dynamic and flexible Python applications. In this article, we will learn how to use eval in Python with the help of examples.
Table of Content
Best-suited Python courses for you
Learn Python with these high-rated online courses
What is Python Eval?
Python eval is a built-in function that evaluates the specified expression (if the expression is a legal python statement) and returns the result. The eval() function takes a string as input and returns the result of the expression evaluated. It can dynamically execute Python code at runtime, allowing for flexible and dynamic application development.
Syntax
eval(expression, globals, locals)
Parameter
expression: A string that you want to evaluate.
globals: A dictionary to specify the available global methods and variables.
locals: A dictionary to specify the available local methods and variables.
Return Value
The eval() method returns the result evaluated from the expression.
Now, let’s take some examples to get a better understanding of eval() function
How eval() works in Python?
Step-1: Takes a string as input, which should contain a valid Python expression.
Step-2:
- Evaluates the expression and return the result.
- The result can be of any data type – a number, a string, a list, a tuple, a dictionary, or even a function.
Step-3: It would raise a Syntax Error if the string passed to eval() contains syntactically incorrect expression.
Till now, we have a clear understanding of eval function and its working, so let’s take some examples to get handier of using eval function.
Example-1: Evaluating a simple mathematical expression
# Evaluating the expression "2 + 3"result = eval("2 + 3")print(result)
Output
In this example, we pass the string “2 + 3” to the eval() function, which evaluates the expression and returns the result 5 and print it.
Example-2: Evaluating a string as a list
# Evaluating the string "[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]" as a listmy_list = eval("[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]")print(my_list)
Output
In this example, we pass the string “[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]” to the eval() function, which evaluates the string as a list and returns the list [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. We then assign the list to the variable my_list and print it.
Example-3: Using eval() to create a calculator program
# Creating a calculator program using eval()while True: expression = input("Enter an expression to evaluate: ") if expression == "exit": break try: result = eval(expression) print(result) except: print("Invalid expression")
Output
We use the eval() function in this example to create a simple calculator program. The program uses a while loop to prompt the user to enter an expression to evaluate repeatedly and then uses eval() to evaluate the expression and print the result.
If the user enters the string “exit,” the program exits the loop and terminates. If the expression the user enters is not a valid Python expression, the program catches the resulting exception and prints an error message.
| Programming Online Courses and Certification | Python Online Courses and Certifications |
| Data Science Online Courses and Certifications | Machine Learning Online Courses and Certifications |
Advantages of Python Eval
Dynamic Code Evaluation
It means that you can execute code that is not known at compile-time but only at runtime. It can be used to build complex applications that require a high degree of flexibility, such as custom scripting languages, plugins, and extensions.
Code Testing and Debugging
Eval can also be used for testing and debugging purposes. For example, if you have a complex function or expression, you can use eval() to test it with different inputs and see the output without having to re-run the entire program. This can help you catch bugs and errors quickly and efficiently.
Programmatic Code Generation
It means, using eval function you can dynamically create python code and execute it. This can be useful in scenarios where you need to generate code based on user input or generate code for use in other applications.
Despite its advantages, eval can also be a significant security risk if used improperly. Now, we will see the limitations and restrictions of the eval function in Python.
Limitations and Restrictions of Python Eval
Access to Sensitive Data
If the eval function is used improperly, it can provide access to sensitive data or functions. For example, if eval is used to evaluate an expression that includes the open() function, an attacker could use it to read or modify files on the system. Similarly, if eval is used to execute system commands, an attacker could use it to run arbitrary commands on the system.
Must Read: File Handling in Python: Open, Read, Write, and Close
Must Read: How to Read and Write Files using Pandas
Code Injection Attacks
One of the most significant risks of using eval is the potential for code injection attacks. If the input to eval comes from an untrusted source, an attacker can inject malicious code into the expression, leading to unauthorized access or damage to your system. Code injection attacks can be difficult to detect and mitigate, making it crucial to validate any input.\
Performances Overhead
Another risk of using eval is the potential for performance overhead. Since eval evaluates code at runtime, it can be slower than compiling code at compile-time, resulting in reduced performance and slower execution times, which can be problematic in certain scenarios.
Best Practices for using Python Eval Safely and Securely
To minimize the risks associated with eval, following best practices for using eval safely and securely is essential. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Avoid using eval with untrusted input.
- In case you need to use eval with untrusted input, validate and sanitize it to ensure that it only contains safe expressions.
- If you need to use eval with untrusted input, consider using a sandboxed environment like the RestrictedPython module, which provides a restricted execution environment that limits the capabilities of the evaluated code.
- Use alternative methods where possible. In spite of using the eval() function, you can use alternative methods such as exec() or ast.literal_eval(). These methods can provide similar functionality without the same security risks.
- Limit the scope of eval. You can limit the scope of the evaluated expression by providing restricted global and local dictionaries, which can help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and functions.
Alternative Methods to Eval in Python
While eval can be useful in certain scenarios, it’s not always the best choice. Here are some alternative methods to eval in Python:
- exec() function: exec() is a built-in Python function similar to eval, but it can execute arbitrary Python code as a block instead of just evaluating a single expression. It will be helpful when you need more control over the evaluated code.
- ast.literal_eval() function: ast.literal_eval() is a secure version of eval that can only evaluate a restricted set of expressions, such as strings, numbers, tuples, lists, dictionaries, and Booleans which makes it much safer to use with untrusted input.
- compile() function: compile () is a built-in Python function that compiles Python code at runtime. It can provide a performance boost over using eval. The function compiles code only once that can run multiple times.
Conclusion
Python eval is a powerful feature that can provide a high degree of flexibility and functionality in Python applications. However, it can also be a significant security risk if used improperly. To use eval safely and securely, it’s essential to follow best practices, limit the scope of evaluated expressions, and use alternative methods where possible. By following these guidelines, you can leverage the power of eval while minimizing the risks associated with its use.
Top Trending Article
Top Online Python Compiler | How to Check if a Python String is Palindrome | Feature Selection Technique | Conditional Statement in Python | How to Find Armstrong Number in Python | Data Types in Python | How to Find Second Occurrence of Sub-String in Python String | For Loop in Python |Prime Number | Inheritance in Python | Validating Password using Python Regex | Python List |Market Basket Analysis in Python | Python Dictionary | Python While Loop | Python Split Function | Rock Paper Scissor Game in Python | Python String | How to Generate Random Number in Python | Python Program to Check Leap Year | Slicing in Python