What is Reverse Repo Rate – Meaning, Importance, How it Works?
The reverse repo rate, or reverse repurchase, is a significant monetary policy instrument central banks employ to shape and manage an economy's money supply and interest rates. It is pivotal in influencing the overall cost of lending and borrowing funds and, therefore, has a notable impact on economic activities. This article will cover the concept of the reverse repo rate in the Indian context, its significance, and how it works.
What is the Reverse Repo Rate?
The reverse repo rate is the interest rate the central bank (RBI in India) offers commercial banks to park their excess funds for a short period, typically overnight or a few weeks, and earn interest on those funds. It is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from banks and absorbs liquidity from the banking system.
Here's a quick analogy: Imagine the reverse repo rate as a valve controlling the water flow (money) in a tank (the financial system). By adjusting the valve (the rate), the central bank can manage the water level (liquidity) to prevent both overflow (inflation) and drought (lack of economic activity).


Best-suited Capital Markets courses for you
Learn Capital Markets with these high-rated online courses
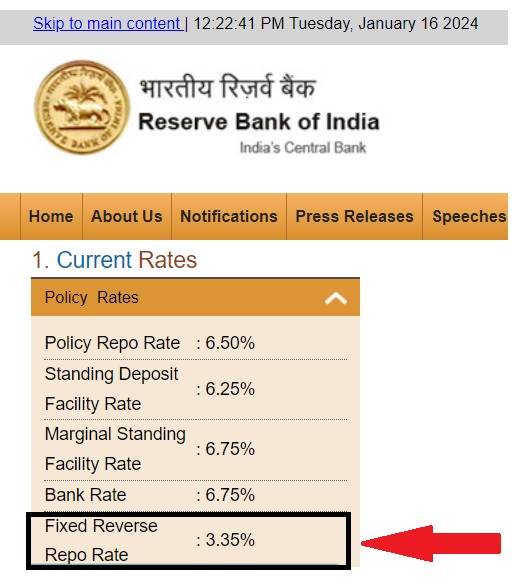
Reverse Repo Rate In India
The reverse repo rate in India is 3.35% as of January 16, 2024.
Source - RBI
How Does Reverse Reporate Work?
The reverse repo rate is a crucial part of monetary policy. Like repo, which stands for 'repurchase option' or 'repurchase agreement,' a reverse repo is a short-term financial transaction.
The Central Bank (RBI) borrows money from commercial banks and other financial institutions in a reverse repurchase agreement. In exchange for its funds, the central bank provides government securities as collateral.
Both parties involved in the transaction agree on two essential things:
- The central bank will repurchase the government securities from the banks at a specified future date.
- The central bank will pay the banks an interest rate, the reverse repo rate, for lending their funds.
Now, how it works:
- Like in a repo, commercial banks and financial institutions have excess funds they want to invest securely.
- They lend these surplus funds to the central bank, earning interest at the reverse repo rate.
- This provides banks with a safe and profitable way to park their extra cash temporarily.
So, the reverse repo rate allows the central bank to borrow money from banks temporarily. It provides banks with a reliable and interest-bearing place to invest their surplus funds while helping the central bank manage monetary policy by controlling liquidity levels in the financial system.


Why is the Reverse Repo Rate Important?
The Reverse Repo Rate plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and stable financial system, making it vital for several reasons -
Manages Liquidity in the Market
The reverse repo rate controls the financial system's liquidity level. Banks with excess funds can deposit them with the central bank at the reverse repo rate mentioned above. This withdrawal of liquidity helps prevent the financial system from becoming flooded with money, which can lead to inflationary pressures and excessive lending.
Stabilises Prices in an Economy
Controlling inflation is a crucial goal of central banks. Central banks can use the reverse repo rate to influence the money supply and overall economic liquidity. Reducing liquidity through the reverse repo rate can help control inflation by limiting the money available for spending and borrowing.
Controls Interest Rates
The reverse repo rate also indirectly affects short-term interest rates in the financial markets. When central banks increase the reverse repo rate, it becomes more attractive for banks to deposit money with the central bank, leading to higher short-term interest rates in the broader financial system. Contrarily, a lower reverse repo rate can lower short-term interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for banks and their customers.
Promotes Responsible Banking Practices
The reverse repo rate influences the behaviour of commercial banks and financial institutions. The attractive reverse repo rate can act as an incentive for banks to prioritise responsible banking practices over excessive lending. It encourages them to strike a balance between maintaining liquidity and making loans.
Monetary Policy Tool
The reverse repo rate helps central banks to fine-tune monetary policy. By adjusting this rate, central banks can influence overall economic conditions, including inflation, economic growth, and financial stability. It allows central banks to respond to changing economic circumstances and achieve policy objectives.


How to Calculate the Reverse Repo Rate?
In India, the RBI determines the reverse repo rate during its monetary policy meetings. Individual investors or banks can't calculate this rate themselves. The RBI announces the reverse repo rate as part of its monetary policy decisions, typically after reviewing various economic factors and conditions.
The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) sets the reverse repo rate after assessing -
- Current economic situation
- Inflationary pressures
- Growth prospects
- Fiscal policy
- Global economic conditions
- Credit conditions
- Other relevant factors are financial stability, exchange rates, liquidity, inflation expectations, monetary aggregates, etc.
The MPC meets regularly (usually every two months) to review these factors and decide on changes to key policy rates, including the reverse repo rate.
Key Takeaways
- The reverse repo rate is a tool for the central bank to manage the amount of money circulating in the financial system.
- Banks can deposit their surplus funds at this rate when they have excess liquidity.
- This deposit process decreases the overall liquidity in the financial system.
- Preventing excessive liquidity is crucial since it can lead to inflation and risky bank lending practices.
Explore these online degree programmes–
FAQs - Reverse Repo Rate
How does the Reverse Repo Rate Differ from the Repo Rate?
While both involve short-term borrowing agreements, the central bank lends money to banks in a repo, while in a reverse repo, banks lend money to the central bank.
What Happens When the Reverse Repo Rate Increases?
An increase in the reverse repo rate incentivizes banks to deposit more funds with the central bank, reducing the money supply and potentially raising short-term interest rates.
How Does the Reverse Repo Rate Affect Inflation?
A higher reverse repo rate can help control inflation by reducing the amount of money in circulation, which can curb rising prices.
How Often Does the Reverse Repo Rate Change?
The reverse repo rate can change after each monetary policy meeting, typically occurring every two months in India.
What are the Effects of a Lower Reverse Repo Rate?
A lower reverse repo rate can encourage banks to lend more funds to businesses and consumers, potentially stimulating economic activity.
Can Individuals or Retail Investors Participate in Reverse Repo Transactions?
Typically, reverse repo transactions are conducted between banks and the central bank, so individual investors do not directly participate in such transactions.

Rashmi is a postgraduate in Biotechnology with a flair for research-oriented work and has an experience of over 13 years in content creation and social media handling. She has a diversified writing portfolio and aim... Read Full Bio