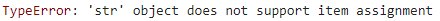Getting started with Python Strings
Python strings are immutable, i.e., you cannot modify the contents of the object. In this article, we will briefly discuss how to create, assign string to a variable, how to access characters in a string and many more.
Any alphabet, numbers, characters you define within single or double quotes in Python becomes a python string. And the variable having a such value becomes a string variable. Python strings are “immutable” in nature, i.e. strings cannot be changed once they are created. This blog will not only tell you what is python string but will also help you learn various string operations in Python.
Table of Contents
- How to Create a String in Python
- Assign String to a Variable
- Declaring Multiline Strings
- Empty String in Python
- How To Access Characters in a String
- Python String Operations
- How to Find the String Length?
- Looping Through a String
- Python Program to Check if the Given String is an Abecedarian Series
- Concatenation of Two or More Strings
- Python Program Demonstrating Concatenation of Strings
- How to Update or Delete a String in Python?
- Deleting a String
- How to Check if the Text is in the String?
- Formatting Strings in Python
- String Formatting Expressions
- String Formatting Method Calls
- Escape Character
- How to Ignore Escape Characters?
- Built-in String Methods
Python strings are made immutable so that programmers cannot modify the contents of the object (accidently). Let’s check this example and see how python strings are immutable in nature.
# Are python strings immutable in nature?# Try changing any character of the string.var = "This a string"print(type(var))var[0] = "K"
Output: var[0] = "K" TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
The typeError as output is generated when you try to modify the existing python string. This error also verifies that strings in python are immutable in nature.
#Example 1: Using single quotes and double quotesstring1 = 'I Love Python'string2 = "I Love Python"print(string1)print(string2)
Assign String to a Variable
You can assign a string to a variable with the variable name followed by an equal sign (=) and the string. Unlike in other programming languages, in Python, you never need to declare variables ahead of time. A variable, in this case, a string is created when you assign it a value.
Now you might be wondering why two kinds of quotes? The main reason is that this allows you to embed a quote character inside a string without having to escape it with a backslash as shown below:
#Example 2: Why two kind of quotesstring1 = "'I love Python' says Jef"string2 = 'She said, "I love Python!"'print(string1)print(string2)
Declaring Multiline Strings
You can actually use triple quotes to create strings when you want to have multiline strings with line breaks. They are commonly used for documentation strings or embed multiline error messages or HTML or XML code in your program code.
Triple strings aren’t really useful for short strings. An example can clarify the picture:
#Example 3: Using three single quotes (''') or three double quotes (""")string3 = '''There was a Young Lady of London,Who loved programming;When asked about her favorite programming language,She exclaimed, "I love Python"That's what she said'''string4 = """\nYou can write the above exampleusing 'three double quotes as well"""print(string3)print(string4)string4
If you see the last line of the code I have not used the print function to display the string4. The output will be different from that using print(). The print function basically strips the quotes, adds a space between each thing that it prints, and then a newline at the end. However, the interpreter prints the string along with the quotes and the escape characters like .
Empty String in Python
At times you might need an empty string, for example, you might want to build a new string from other strings so want to have a placeholder for this yet to be created new string. You can actually create an empty string using any of the string creation methods discussed above.
#Example 4: Empty Stringstring5 = ' 'string5 += 'Hi!!'print(string5)
Best-suited Python courses for you
Learn Python with these high-rated online courses
How to Access Characters in a String?
When you are manipulating sequences, it’s very common to have to access individual characters of string at one precise position. We call this indexing and you can access one character at a time by specifying its offset (position) inside square brackets after the string’s name. So, you get back a one-character string at the specified position, i.e offset.
#Example 5: Accessing String Charactersstring6 = "PYTHON"print(string6)
The expression inside the bracket is referred to as index and it is usually coded as an offset from the beginning of the string. The first offset (leftmost) is 0, the next is 1, 2, 3, and so on. Python also allows you to fetch items of a string using negative offsets. You can think of that as counting the string characters from the end. Basically, positive indexes count from the left, and the negative ones from the right. Let’s try to understand this with the help of a few examples.
Note: Remember that string indices must be integers, not float type
#Example 6: String Indexingstring1 = "I Love Python" print(string1[0])print(string1[4], string1[5])print(string1[-1], string1[-3])#print(string1[20])
The points that we can infer from the above example are:
- The first offset of a string is at 0
- string1[0] fetches the first item of the string, in our example ‘I’
- Negative indexing can be considered as counting backward from the end or right
- string1[-3] fetches the third item from the end (like string1[len(string1)−2]), in our example ‘h’
- If you specify an offset that is the length of the string or longer you will get an exception, in our example the commented line string1[20] raises exception
In the examples that we have worked on till now, we did encounter a few unknowns like + operator, or len() function, etc. Therefore, let us take a look at a few common string operations that you will frequently come accross.



Python String Operations
How to Find the String Length?
Let’s begin by calculating the length of the string. Strings like any other Python sequence have a length. You can easily get the length of the string using the built-in function len as shown below. len is a built-in function in Python that returns the number of characters in a string.
#Example 7: String length using len functionstring1 = "I Love Python"print(len(string1))#print(string1[len(string1)])
Like I mentioned earlier, while indexing if we use the offset that is the length of the string, we get IndexError. That is because since we start indexing from 0, the last letter of the string will be at position one less than string (length-1). If you ask me, you can always use negative indices. Alternatively, you can also find the length of the string by looping through a string. Let’s take a look
Looping Through a String
Looping means being able to execute a block of code more than once. Python provides different looping constructs such as for and while, which serve different purposes. Often, a lot of string operations involve processing a string one character at a time and we call this traversal. Here;s an example demonstrating who to traverse through a string:
#Example 8: Looping through a string"""Finding the length of a string using for loop"""string1 = "I Love Python"def calculatelen(string): count = 0 for i in string: count = count + 1 return count print(calculatelen(string1))
In the above example, we are calculating the length of the string using for loop and in operator. Each time the loop traverses the string, the variable count is increased by 1. The loop continues until we reach the end of the string. Let’s now look at a more interesting example.
Python Program to Check if the Given String is an Abecedarian Series
Write a Python program to check if the given string is an abecedarian series. Abecedarian series refers to a sequence or list in which the elements appear in alphabetical order. Example: “ABCDEFGH” is an abecedarian series, while “BOB” is not.
#Example 9: Abecedarian Seriesdef is_abecedarian(string): previous = string[0] for i in string: if i < previous: return False previous = i return True print(is_abecedarian('BCDEFGH'))print(is_abecedarian('BOB'))
In the above example, you should notice that the relational operators work on strings. In the fourth line of the code, if i < previous, we are comparing two string characters using < operator. Now let us consider an example using a while loop construct. Try writing a Python program that prints each character of each item of string in a new line using a while loop.
#Example 10: Print each character of a string in new line using while loop"""Finding the length of a string using for loop"""string1 = "I Love Python"def displaystring(string): count = 0 while count < len(string): print(string[count]) count = count + 1 displaystring(string1)
This is a pretty simple example. The loop iterates until the variable count is less than the length of the string. When the count equals the length of the string, the condition evaluates to False, and the body of the loop is not executed anymore.
Concatenation of Two or More Strings
You can concatenate two or more strings using + operator and repeat a string using * operator like shown below.
#Example 11: Concatenation and repetition of stringsstring1 = 'abc' + 'def' string2 = 'xyz'string3 = string1 + string2 #concatenationstring4 = string2 * 4 #repetitionprint(string3)print(string4)
Python Program Demonstrating Concatenation of Strings
Here’s a simple exercise. In Robert McCloskey’s book Make Way for Ducklings, the names of various ducklings goes like this: Jack, Kack, Lack, Mack, Nack, Ouack, Pack, and Quack. Given prefixes “JKLMNOPQ” and suffix “ack”, write a python program that generates these names using loop constructs and concatenation operators
#Example: For loop and + operatorprefix = "JKLMNOPQ"suffix = 'ack'for i in prefix: if (i == 'Q' or i == 'O'): print(i + "u" + suffix) else: print(i + suffix)
Let us now look at how to change or delete a string in Python. Is that even possible? What’s your answer: Yes or No?
How to Update or Delete a String in Python?
Updating a String
If you have guessed it ‘Yes’, then you are wrong. Python does not allow you to update or delete a character of a string. That’s because strings are immutable sequence types of Python, which means you can’t change an existing string in-place. The best you can do is to create a new string to achieve the variation.
#Example 13: Updating or Deleting a String"""Strings are immutable data types"""string1 = "I love python"string1[0] = "Y"print(string1)
Trying to update a string will give you the TypeError as shown above. So how can you modify a string in Python? You can do so using string tools like concatenation or slicing and then assigning all this to a new string variable with the same name as that of the original string. We will look at slicing operations in the next part of the article.
#Example 13: Updating or Deleting a String"""Strings are immutable data types"""string1 = "I love python"string1[0] = "Y"print(string1)
Deleting a String
You can delete an entire string using the del keyword in Python. However, you can delete a character of a string as shown below.
#Example 15: Deleting a character of stringstring1 = "I love python"print("Original string:", string1)del(string1[3])print("Deleting the string item at 3rd offset:", string1) #Example 16: Deleting entire stringstring2 = "I Love Python"print("Original String:", string2)del(string2)print("Deleted String:", string2)
Example 15 will give you a TypeError and Example 16 will give you NameError. Let us now move on to the next query.
How to Check if the Text is in the String?
There are multiple ways to search a string for a particular substring or a character. The simplest way to check if a string contains a substring in Python is using in operator.
#Example 17: Method 1, Searching using in operatorstring1 = "I Love Python"word = "Love"if word in string1: print("Word Found!")else: print("Not found what you are looking for in the string") word1 = "love"#For case-insensitivity you can use 'if word1 in string1.lower():'if word1 in string1: print("Word Found!")else: print("Not found what you are looking for in the string")
Beware of case-sensitivity. If you want to do a case-insensitive search you can normalize the strings using lower() or upper() built-in functions of Python as shown above. You should keep in mind that the above method works fine for sequences of characters, but not necessarily a whole word. For example, “word” in “sword” is True. If you want to match the entire word then you should use regular expressions.
Now let see how to search if a particular character is present in a string
#Example 18: Using find() methodstring1 = "I Love Python"word = "kove"if string1.find(word) != -1: print("Word Found!")else: print("Not found!")
The find() method searches for the word or a character and returns the position of the substring in the original string if the substring is present. Else, returns -1 if the substring is not found.
Moving on, let’s explore how to format Python strings.
Formatting Strings in Python
Proper text formatting makes code and data much easier to read and understand. Python offers a rich variety of string formatting methods. String formatting allows you to perform multiple type-specific substitutions on a given string in a single step. In Python, string formatting is available in two ways:
- String formatting expressions: ‘…%s…’ % (values)
- String formatting method calls: …{}…’.format(values)
Let us explore each of these in detail.
String Formatting Expressions
This formatting technique has been there since Python’s inception and loosely based on printf statement of C language. Python provides the binary operator %, which can be applied on strings to format them in a very simple manner. Using %, you can write code to perform multiple string substitutions all at once rather than doing it in parts. Let’s look at that with the help of an example:
#Example 19: string formatting expressions: ‘…%s…’ % (values) print(“%d %s %s %0.1f” % (1, ‘use’, ‘Python’, 3.0 ))
Doesn’t that make sense? No problem! String formatting examples might look a little strange until you understand the syntax or what is actually being done there. So, let’s dive in. To format strings:
- On the left side of the % operator, you need to provide a format string containing one or more conversion targets, each of which starts with %
- On the right, you need to provide a Python object that you want to be inserted in the format string
For instance, in the above example we have %d, %s, %f as our conversion targets and to the right of the % operator we have the integer 1 that replaces %d, the strings ‘use’ and ‘Python’ that replace the two %s, and finally 3.0 that replaces %0.1f. The general format of the conversion targets looks something like this:
%[(keyname)][(flags)][(.precision)]typecode
Output:
You can learn more about this printf style string formatting in the official Python Documentation.
String Formatting Method Calls
Python 2.0 7 Python 3.0 introduced a new way of string formatting that provided a large degree of flexibility and customization compared to C printf style formatting.
Python String format() Method
Python’s str.format() can be used to perform string formatting operations. It’s more like a normal function call rather than an expression. The format string contains substitution targets (replacement fields) and arguments to be inserted either by position (e.g., {2}) or keyword (e.g., {sam}). Just like you would pass arguments to functions and methods by position or keyword. Here’s an example to clear the picture.
#Example 20: str.format methodstr1 = “I”str2 = “Love”str3 = “Python”print(‘{} {} and {}’.format(str1, str2, str3))print(‘{0} {1}, {0} {2}’.format(str3, 2.0, 3.0))print(“{0} {ver2}. {0} {ver1}”.format(str3, ver1=2.0, ver2=3.0))
- In the line (‘{} {} and {}’.format(str1, str2, str3), you can see that bracket pairs are replaced with the arguments in the order in which you pass arguments.
- Like shown in the next line of the code, (‘{0} {1}, {0} {2}’.format(str3, 2.0, 3.0, indexes can be specified inside the brackets.
- You can also use named arguments like in the last line of the code, (“{0} {ver2}. {0} {ver1}”.format(str3, ver1=2.0, ver2=3.0)
Let us now look at more examples to get to know a few key points about string formatting.
#Example 21: String Formatting Examplesstr3 = “Python”template = ‘{0} {1} {2}’ # By positionprint(template.format(‘I’, ‘Love’, str3))print(‘{0:f}, {1:.3e}, {2:g}’.format(3.14159, 3.14159, 3.14159))print(‘{0}:{ver}’.format(str3, ver=[2.0, 3.0])) tuple1 = (334, 45, 23456, 103, 66)print(‘{0} {2} {1} {2} {3} {2} {1} {2}’.format(*tuple1)) #Alignment & paddingprint(‘{:~^30s}’.format(‘Python’))print(‘{:~>30}’.format(‘Python’))print(‘{:0=8d}’.format(–1234))
The points that can be inferred from the above example are as follows:
- You can pass arguments by position or keyword name
- format() methods creates and returns a new string object
- You can use the format method just % operator by adding extra syntax in the format string. Ex: ‘{0:f}, {1:.3e}, {2:g}’.format(3.14159, 3.14159, 3.14159)
- Unlike %, format allows repetition of arguments as shown in the above example, ‘{0} {2} {1} {2} {3} {2} {1} {2}’.format(*tuple1)
- Note that, you can use pass dictionary keys, tuples, lists, and other objects as arguments to format method
- The format method also allows you to change the alignment of the string using the syntax :[fill_char][align_operator][width]. The align_operator can be:
- <, for left-alignment within the given width
- >, for right-alignment within the given width
- ^, for center alignment
- =, to place the padding after the sign
(Refer to the last three line of the code)
Escape Character
In Python, you can escape the meaning of some characters within the strings to achieve your requirement. Python allows you to do that by using a backslash (). Backslash and the character immediately following it together from an escape sequence. The most common escape sequence that you might have come across would be , which indicates to begin a new line.
#Example 22: Escape Charactersprint(‘Welcome\nto\n\nPython Tuorial!\n‘)print(‘a bc’)print(‘”I love Python!”‘)print(‘Today we are learning: \Python\‘)
| Escape Sequence | Description |
| Inserts a new line | |
| Inserts a horizontal tab | |
| \ | Inserts a literal backslash in a string |
| ’ & ” | Insert a single quote or double quote in a string |
That’s great! But what if you want to ignore escape characters? How to do that?
How to Ignore Escape Characters?
You can ignore escape sequences in Python, by passing the string as raw string. This can be done by placing ‘r’ or ‘R’ before the string that you are working on. ‘r’ stands for raw and it interprets the string as and preserves the escape sequences as literals.
#Example 23: Ignoring Escape Sequenceprint(r‘Welcome\nto\n\nPython Tuorial!\n‘)str2 = r“”Hello world”“print(str2)
#Example 24: String Methodsstr1 = ‘ \n This is a Python Tutorial. \n‘print(str1.strip()) #Striiping Whitespacestr2 = “XßΣ”str3 = ‘python’str4 = ‘THIS is python’print(str2.lower()) #converts to lowercaseprint(str3.upper()) #converts to uppercaseprint(str2.casefold()) #creates lowercase string(might cause strings to grow in length)print(str3.capitalize()) #returns capitalized version of stringprint(str4.swapcase()) #swaps the case str6 = ‘1s’str7 = ” “str8 = ‘this is python’print(str6.isdigit())print(”.join(reversed(str3))) #takes a string & returns an iterator in reverse order;print(str4.replace(‘python’, ‘java’)) #replace one sub-string with another sub-string # Methods to evaluate the contents of a stringprint(str4.isalpha()) print(str3.islower())print(str3.isupper())print(str6.startswith(“1”)) print(str7.join([“python”,“and”,“java”])) #join a list of strings using another string as separatorprint(str8.count(“th”)) #count number of occurrences of a sub-string
| Method | Description |
| str.strip([chars] | Removes (strips) any leading or trailing characters contained in the argument chars. By default removes all white spaces. |
| str.rstrip & str.lstrip | Strip characters from the end of the string and the from the start of the string respectively |
| str.lower() | Converts every character to its lowercase equivalent |
| str.upper() | Converts every character to its uppercase equivalent |
| str.casefold() | Creates a lowercase string but is more aggressive than str.lower and cause strings to grow in length |
| str.capitalize() | Capitalize the string, i.e makes first character capital and rest small |
| str.swapcase() | Swaps lowercase character with uppercase and vice versa |
| str.title() | Returns title case version of the string |
| str.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) | Returns list of substrings based on the separator argument sep |
| str.replace(old, new[ , count]) | Replaces the old string with the new string. Optional argument specifies number of occurrences to be replaced |
| str.isupper(), str.islower(), str.istitle(), str.isalpha(), str.isalnum(), str.isspace() | These methods can be used to evaluate the contents of the string |
| str.join(‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘ …) | A string separator can used to join a list of strings together into a single string |
| str.count(sub[ , start[ , end]]) | Counts the number of occurrences of a substring. You can also specify the starting & ending positions |
| str.startswith(prefix[ , start[ , end]]) & str.endswith(prefix[ , start[ , end]]) | These methods can be used to test the beginning and the ending of the string respectively |
So, folks, these are just a few string methods. I suggest you go through official Python documentation to learn about these string methods and others in detail.
Top Trending Article
Top Online Python Compiler | How to Check if a Python String is Palindrome | Feature Selection Technique | Conditional Statement in Python | How to Find Armstrong Number in Python | Data Types in Python | How to Find Second Occurrence of Sub-String in Python String | For Loop in Python |Prime Number | Inheritance in Python | Validating Password using Python Regex | Python List |Market Basket Analysis in Python | Python Dictionary | Python While Loop | Python Split Function | Rock Paper Scissor Game in Python | Python String | How to Generate Random Number in Python | Python Program to Check Leap Year | Slicing in Python
Interview Questions
Data Science Interview Questions | Machine Learning Interview Questions | Statistics Interview Question | Coding Interview Questions | SQL Interview Questions | SQL Query Interview Questions | Data Engineering Interview Questions | Data Structure Interview Questions | Database Interview Questions | Data Modeling Interview Questions | Deep Learning Interview Questions |
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio