What Is Two-Factor Authentication and Why Do We Need It?
Scammers can obtain your sensitive information in a variety of ways. They will use any available method to obtain the information they require to carry out their illegal activities. We’ve all heard of incidents in which hackers steal password and username combinations, resulting in a corporate data breach. Hence, it is best to use two-factor authentication to prevent your login credentials from falling into the hands of a threat actor.
What exactly is two-factor authentication, and why do we need it? Let’s go over the topics we’ll be covering in this blog before we answer these questions:
Table of Content (TOC)
- What is two-factor authentication?
- How does two-factor authentication work?
- Types of 2FA
- Why do we need two-factor authentication?
- Are there any drawbacks of two-factor authentication?
What is two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication, also known as 2FA, is one of the types of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Two-factor authentication is a security process that uses two different forms of identification to cross-verify users. 2FA ensures that people attempting to access an online account are who they claim to be.
You must enter your username and password to confirm your identity. Then, you will be required to provide additional information instead of gaining immediate access. This second factor falls primarily into one of the following categories:
- Something you are familiar with (PIN, password, answers to “secret questions,” specific keystroke pattern, etc.)
- Anything you own (credit card, a smartphone, a small hardware token, etc.)
- Something you are (fingerprint, an iris scan, a voice print, etc.)
Two-factor authentication protects you from various attacks, including phishing, social engineering, and password brute-force attacks. It not only protects you from these attacks, but it also protects your logins from attackers who use weak or stolen credentials.
Let’s try to understand the concept of two-factor authentication with the help of a real-life example. A classic real-world example of two-factor authentication is withdrawing money from an ATM, which requires both an ATM card (something you have) and a PIN (something you know).
Best-suited Cyber Security courses for you
Learn Cyber Security with these high-rated online courses
How does two-factor authentication work?
The process of enabling two-factor authentication varies considerably according to the application or vendor. In general, 2-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your account. This additional security measure requires you to confirm your identity by entering a randomized 4- or 6-digit code that you receive each time you attempt to log in. You can receive your security code or OTP via text, voice call, or email.
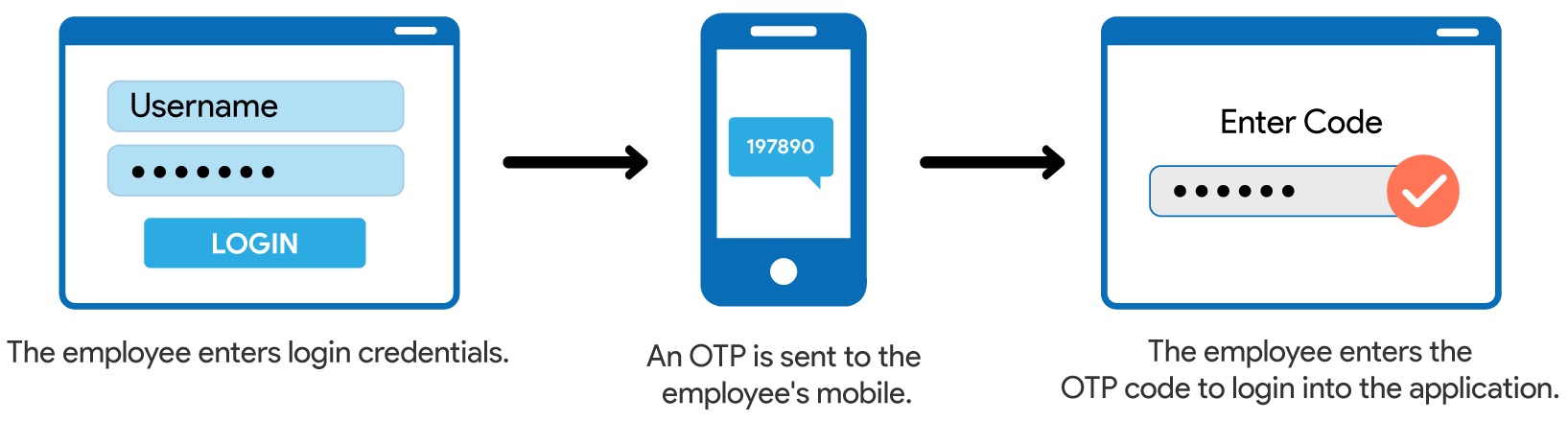
Let’s look at an example of our organization Naukri.com to understand better how it works:
- The application or website prompts the employee to log in.
- After the employee enters their username and password, the site’s server looks for a match and recognizes the user.
- The employee is then prompted to begin the second login step. In this step, the employee must demonstrate that they have something unique to them, such as biometrics, a security token, an Identity card, a mobile phone, and so on.
- In our organization, an OTP is sent to the employee’s phone number in order for him to validate himself. As a result, the employee must enter the OTP.
- After providing both factors, the employee is authenticated and granted access to the application or website.
You should also explore- What is Cybersecurity?
Types of two-factor authentication
There are four main types of 2FA which are:
SMS
When you permit a site’s SMS two-factor authentication option, you’ll frequently be prompted to enter your phone number. When you log in with your login and password the next time, you’ll be prompted to input a unique code (usually 5-6 digits) that will be messaged to your phone. This is one of the most popular options for sites to implement 2FA. Ans is so because several people have SMS-capable phones, and it does not necessarily require the installation of an app.
App authentication
Another alternative for phone-based two-factor authentication is to use an app that creates codes locally, relying on a secret key. If a website supports this type of 2FA, it will display a QR code containing the secret key. You can scan that QR code, and after scanning that QR code, your application will generate a new 6-digit code every 30 seconds. You’ll need to enter one of these codes in addition to your username and password to log in. Google Authenticator is one of the best examples of this service.
Push-based
During login, some systems, such as Apple’s trusted devices, send a prompt to one of your devices. This prompt will imply that somebody is attempting to log in, possibly you, and an estimated location for the login attempt. You can then either approve or reject the attempt.
U2F
Universal Second Factor (U2F) is a newer type of 2FA that typically employs security keys such as small USB, NFC, or Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE) devices. To use it on a website, you must first enroll your U2F device. The site will prompt you to connect your device and tap it to allow the login on subsequent logins.
Why do we need two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication is critical for web security because it eliminates the risks associated with compromised passwords. The goal is to provide more robust protection against unauthorized access to user accounts. Its goal is to make cyber attacks more difficult and to reduce fraud risks.
With 2FA, compromising only one factor will not unlock the account. Even though your passcode is stolen or your mobile is lost, the possibility of someone obtaining your second-factor information is nearly nonexistent. And, if a consumer correctly employs 2FA, applications and websites can become more confident in the user’s identity.
Are there any drawbacks of two-factor authentication?
Yes, just as every coin has two sides, 2FA has its drawbacks. Let’s go over some of the drawbacks that you might encounter if you use 2FA:
Time-consuming
Two-factor authentication adds a step to the verification process, increasing the duration it takes to access accounts. On an individual level, this would appear insignificant. However, applying to a large organization with hundreds of employees adds to thousands of work hours lost yearly.
Expensive
A two-factor authentication system worth hundreds of thousands of rupees would barely register on the balance sheet of a billion-dollar corporation. However, such an expense can mean the difference between profit and loss for a small business.
Failure prone
Two-factor authentication adds two distinct barriers for an attacker in order to overcome in order to gain access. However, doing so increases the complexity and percentage of moving parts in the verification process. As a result, there are more possible causes of verification system failure.
Not completely secure
2FA is far more effective than single-factor controls in preventing unauthorized entry. The level of security will be determined by the type of 2FA used. However, 2FA systems are not immune to simple, low-cost attack methods. An unauthorized person, for example, could steal a user’s phone and thus gain access to the OTP.
Conclusion
Recently, there has been a massive increase in websites that have lost their users’ data. As cybercrime becomes more sophisticated, businesses discover that their outdated security measures are no match for advanced attacks and threats. Fortunately, businesses can easily add an extra layer of security to user accounts through two-factor authentication, also known as 2FA.
FAQs
Is there a problem with two-factor authentication?
Yes. Through phishing attacks, criminals can call users and pose as banks or trusted agents, asking them to confirm the passcode sent to them or provide links to spoofed websites.
What are the three ways in which two-factor authentication can be accomplished?
Two-factor authentication can be accomplished in three ways: Things you know, such as a PIN or password.u00a0 Things you have, such as a smartphone or token.u00a0 Things you are, such as fingerprints or voice recognition.
Is two-factor authentication the same as two-step verification?
No. Two-step verification is the authentication of a single authentication factor twice.
How many different kinds of 2FA are there?
There are four basic types of 2FA: SMS Appu00a0 App authentication Push-based U2F
How do hackers circumvent 2FA?
SIM-Jacking is a technique used by hackers to circumvent 2FA security. SIM-jacking occurs when an attacker obtains control of another person's phone number by duping a mobile phone carrier into transferring the number to their phone.
Why is 2FA insecure?
2FA isu00a0insecure because of social engineering tactics. The hacker contacts your phone company, poses as a victim and activates a new phone with your number.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio