Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization in cloud computing can be defined as a technique that enables various consumers and organizations to share a single physical instance of a service/resource.
In cloud computing, virtualization is described as the development of a virtual desktop, storage device, operating system, as well as network resources.
It can also be defined as a technique that enables various consumers and organizations to share a single physical instance of a service/resource. It accomplishes this by giving a logical name to a physical resource and giving a pointer to that physical resource on demand.
Multiple operating systems and applications can run on the same machine and hardware with the help of this technique. Furthermore, this technology provides a virtual environment not only for application execution but also for storage, memory, and networking.
In this article, let’s understand the virtualization technique in the following order:
- Concept behind virtualization
- Virtualization architecture
- Difference between Type 1 and 2 hypervisors
- Types of virtualization in cloud computing
- Working of virtualization in cloud computing
- Advantages/Benefits
- Disadvantages/Drawbacks
Concept behind virtualization
Hardware virtualization is the process of creating a virtual machine on top of an existing operating system and hardware. A virtual machine provides a logically separate environment from the underlying hardware.
The Host Machine is the machine on which the virtual machine will be created and the virtual machine itself is known as the Guest Machine.
Best-suited AWS Certification courses for you
Learn AWS Certification with these high-rated online courses
Virtualization architecture
The conceptual model of virtualization is referred to as virtual architecture. Hypervisors are commonly used in this.
The hypervisor decouples operating systems and applications from the underlying computer hardware. This allows the host machine to run multiple virtual machines as guests that share the system’s physical computer resources. They are classified into two types:
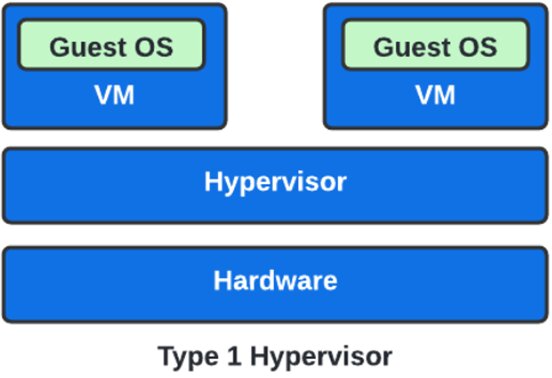
Type 1 Hypervisor
This type of hypervisor runs on the bare system hence, it is also known as a bare-metal hypervisor. It lacks a host operating system because it is installed on a bare system.
They provide high availability as well as resource management. It allows for direct access to the system hardware and thus improves ease of use, stability, and performance.
Type 1 hypervisors include LynxSecure, Oracle VM, VirtualLogic VLX, etc. The Type 1 hypervisor is depicted in the diagram below:
Type 2 Hypervisor
This type of hypervisor runs on the hosted systems hence, it is also known as a hosted hypervisor. It is installed on the top of the host operating system.
It facilitates system configuration while also simplifying management tasks.
The addition of the host operating system limits performance and exposes security flaws. Type 2 hypervisors include Containers, VMWare Fusion, VMWare workstation 6.0, etc. The Type 2 hypervisor is depicted in the diagram below:
Difference between Type 1 and 2 hypervisors
| Benchmark | Type 1 Hypervisor | Type 2 Hypervisor |
| Another name | Bare-metal | Hosted |
| Definition | Runs directly on the system with virtual machines (VMs) running on top of it. | Runs on a conventional OS |
| Virtualization | Hardware | Operating System |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Performance | High | Low |
| Security | More secure | Less Secure |
| Example | LynxSecure, Oracle VM, etc | Containers, VMWare Fusion, etc |
Types of virtualization in cloud computing
There are various types of virtualization techniques. Some of those are described below:
Application Virtualization
This type enables a user to access an application from a server remotely. All of the application’s personal information and other characteristics are stored on the server. But all this information can still be run on a local workstation via the internet. As an example, you could virtualize Microsoft PowerPoint and run it on Ubuntu via the Opera browser.
Network Virtualization
This type enables a user to run multiple virtual networks, each with its own control and data plan. They coexist on top of the same physical network. It can be managed by individuals who are potentially unfamiliar with one another.
The idea is that the technology conceals the true complexity of the network by segmenting it into manageable parts. Similar to how your segmented hard drive makes it easier for you to manage files.
This type has the following subtypes:
- Internal network: Allows a single system to operate as a network
- External network: Collection of various networks into a single network, or separation of a single network into several.
Desktop Virtualization
This type allows a user’s operating system to be stored remotely on a server in the data center. The user can virtually access their desktop from almost anywhere using a different computer.
Users who require specific operating systems, other than Windows, will require a virtual desktop. Its main advantages are user mobility, easy software installation management, patches, and updates.
Storage Virtualization
In this type, a virtual storage system manages an array of servers. The servers have no idea where their data is stored and instead function more like workers in a hive. It allows storage from multiple sources to be managed and used as a single repository.
Despite changes and breakdowns in the underlying equipment, storage virtualization software maintains smooth operations, consistent performance, and a continuous suite of advanced functions.
This type has the following subtypes:
- Block: In this subtype, multiple storage devices are merged as one.
- File: In this subtype, the storage system grants access to files stored on multiple hosts.
Data Virtualization
In this type, data is collected from various sources and managed in a single location. This is done without understanding more about the technical details such as how data is collected, stored, formatted, and arranged logically.
Many large corporations, such as Oracle, At scale, Cdata, and others, offer their services.
Server Virtualization
In this type, masking of server resources takes place. It enables the user to tailor their hardware to the current workload. This is referred to as elasticity.
It enables businesses to expand their own data centers without the hassle of purchasing new hardware. This is also known as hardware virtualization.
This type has the following subtypes:
- Full: Because the underlying hardware is fully simulated, guest software does not need to be modified.
- Emulation: The virtual machine simulates hardware and becomes independent of it. The guest operating system does not need any changes.
- Para: The hardware is not simulated and the guest software operates in its own isolated domains.
Working of virtualization in cloud computing
Virtualization is very important in cloud computing technology. Normally, in cloud computing, users share the data present in the clouds, such as applications, but with virtualization, users share the infrastructure. The main application of this technology is to provide standard versions of applications to their cloud users.
For example, if the next version of that application is released, the cloud provider must provide the latest version to their cloud users. But, providing the latest version will be expensive.
To address this issue, we primarily employ virtualization technology. With this, all servers and software applications required by other cloud providers are maintained by third-party individuals. The cloud providers must pay the money on a monthly or annual basis.
Check Out the Best Online Courses
Advantages/Benefits
There are various benefits of this technique. Some of those are:
- Increases development productivity
- It lowers the cost of acquiring IT infrastructure.
- Allows for rapid scaling and remote access
- More adjustable.
- Enables the users to run various operating systems concurrently
- Special hardware and utility requirements are no longer required.
- Resource management that is effective
- Employee productivity has increased as a result of improved access.
- Data loss is reduced because data is backed up across multiple storage locations.
Disadvantages/Drawbacks
Some of the drawbacks of this technique are listed below:
- Implementation is expensive.
- It is also a security risk.
- Time-consuming.
- The absence of availability.
Explore Free Online Courses with Certificates
Conclusion
Virtualization essentially means running numerous operating systems on a single machine while sharing all hardware resources. And it assists us in providing a pool of IT resources so that we can share these IT resources to benefit the business.
If you are looking for a comprehensive course in Cloud Computing, then these cloud courses may be useful. This program assists interested students in becoming fully-fledged Cloud professionals.
Top Trending Tech Articles:Career Opportunities after BTech Online Python Compiler What is Coding Queue Data Structure Top Programming Language Trending DevOps Tools Highest Paid IT Jobs Most In Demand IT Skills Networking Interview Questions Features of Java Basic Linux Commands Amazon Interview Questions
Recently completed any professional course/certification from the market? Tell us what liked or disliked in the course for more curated content.
Click here to submit its review with Shiksha Online.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio