What is Edge Computing, and Why is it Critical?
Edge computing is changing how billions of IoT devices generate, store, process, analyze, and transport data. But what do you understand by the term edge computing? Before we answer that question, let us first define the term “edge” in the context of “edge computing.” In this context, the term edge refers to geographical distribution.
- What is edge computing?
- Why is edge computing critical?
- Real-life applications of edge computing
- Advantages of edge computing
- Disadvantages of edge computing
- Why is edge computing the future?
- Is there any need to connect edge devices to data centers, on-premises or in the cloud?
- Conclusion
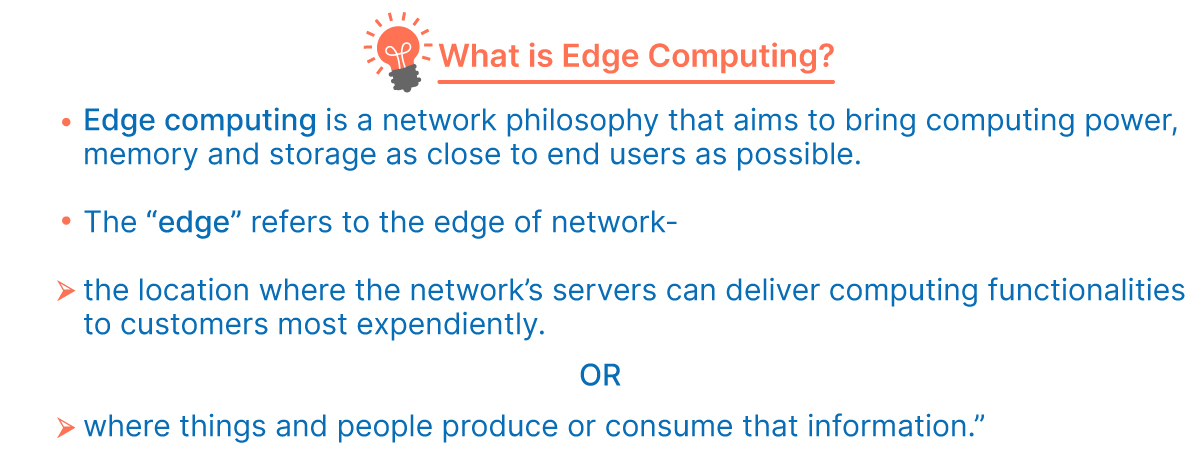
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is exactly what it sounds like: computing at the edge of corporate networks, with “the edge” defined as the location where end devices, such as phones, laptops, industrial robots, sensors, and so on, connect to the rest of the network.
In a simple way: edge computing is the act of delivering computing power as close to the source of data as possible in order to dramatically reduce the communication distance between a client and server, thus reducing latency and bandwidth consumption. Edge computing is one method for a company to use and distribute a shared pool of resources across multiple locations.
You can also explore: Introduction to cloud computing
Best-suited IT & Software courses for you
Learn IT & Software with these high-rated online courses
Why is edge computing critical?
The edge was once a place where these devices could connect to send data, receive data, and download software updates from the cloud or a centrally located data center. With the explosion of IoT devices, that model became flawed. Because of the sheer volume of data collected by IoT devices, larger and more expensive connections to data centers and the cloud are required. With the explosion of the IoT, that model now has flaws. The enormous amount of information collected by IoT devices necessitates larger and more costly connections to data centers and the cloud.
For example, if sensors in a petroleum refinery’s valves detect dangerously high pressure in the pipes, shutoffs must be activated as soon as possible. With the analysis of that pressure data at distant processing centers, the automatic shutoff instructions may arrive too late. However, with edge computing, where processing power is placed closer to the end device, latency is reduced, and roundtrip time can be significantly reduced, potentially saving downtime, property damage, and even lives.
Real-life applications of edge computing
Some of the famous real-life applications of edge computing are:
Autonomous vehicles
Suppose a convoy of trucks travels closely behind one another, saving fuel and reducing congestion. With the help of edge computing, it will be possible to eliminate the need for drivers in all trucks except the front one because the trucks will be able to communicate with each other with ultra-low latency.
Oil and gas industry remote asset monitoring
Oil and gas plants are frequently located in remote locations. Edge computing enables real-time analytics by bringing processing closer to the asset, reducing reliance on high-quality connectivity to a centralized cloud.
Cloud gaming
Cloud gaming, a new type of gaming that streams a live feed of the game directly to devices, is exceptionally latency-sensitive. Edge servers are being built as close to players as possible to decrease delay while providing a fully responsive and highly interactive gaming experience.
Traffic management
Edge computing can help cities manage traffic more effectively by eliminating the need to transport large amounts of traffic data to a centralized cloud, thus lowering the cost of bandwidth and latency.
Virtualized radio networks (vRAN) and 5G
Mobile network operators are increasingly looking to virtualize portions of their networks (vRAN). This has cost and flexibility advantages. The new virtualized RAN hardware must be capable of performing complex processing with low latency. Operators will require edge servers to support virtualizing their RAN close to the cell tower.
Advantages of edge computing
Some of the advantages of edge computing are:
- Reduce latency: As we all know, downtime or latency can cost an organization thousands of dollars. On the other hand, organizations can use edge computing to reduce latency and thus increase network speed.
- Reduce response time: Processing data closer to the source of information reduces the distance it must travel significantly. As a result, the response time is reduced.
- High security: Data stored in the cloud is vulnerable to hacking. This can be avoided because edge computing only sends relevant data to the cloud. Furthermore, edge computing does not always require a network connection. As a result, even if hackers gain access to the cloud, not all user data is at risk.
- Reduce costs: Because of the lower bandwidth, edge computing can result in significant cost savings. Because so much data is processed and stored on localized servers and devices, most data does not need to travel to data centers. As a result, edge computing necessitates less bandwidth in the data center.
Disadvantages of cloud computing
Some of the disadvantages of edge computing are:
- Cost: While cloud storage costs less, there is an additional cost on the local end. Much of this stems from the development of storage capacity for edge devices. Edge computing also has a cost component because old IT network infrastructure must be replaced or upgraded to handle edge devices and storage.
- Data loss: When implementing edge computing, the system must be meticulously planned and programmed to avoid data loss. Many edge computing devices, as they should, discard irrelevant data after collection; however, if the data discarded is relevant, the data is lost, and the analysis in the cloud is flawed.
- Security: It is pointless for a company to have a cloud-based provider with excellent security if their local network is vulnerable. While cloud-based security is improving, most breaches are caused by human error and locally used applications and passwords.
You can also explore: Evolution of cloud computing
Why is edge computing the future?
Edge computing’s future will improve alongside advanced networks such as 5G, satellite mesh, and artificial intelligence. More capacity and power, improved access to fast and widespread networks (5G, satellite), and smarter machines within computers (AI) will open up a world of seriously futuristic possibilities, such as:
- Faster connection: Edge Computing makes your data more relevant, valuable, and actionable, resulting in a faster response time. Every second counts, especially in the case of self-driving cars, where everything can go wrong in a split second. It is also useful in factories for reducing on-site injuries by detecting human flesh.
- Increased reach: Unlike Cloud Computing, which requires internet access to process data, Edge Computing can process data locally without requiring internet access, extending computing to remote and inaccessible locations that were previously inaccessible.
- Improved health care: As medical devices advance, they will be able to sense more about your body and respond appropriately in real time. These healthcare devices require edge computing and powerful AI to function, which are currently unavailable. Expect things like emergency calls and response before heart attacks, vital signs monitoring and response, non-invasive cancer cell monitoring and response, and so on once this technology is available.
- Better climate: We need better and more advanced computing solutions to conserve our finite resources and prevent climate change, and edge computing can help us do so. Let’s look at an example to see what I mean. Assume you need to equip a 1,000-acre farm with sensors and connect them all to a cloud system. It will be quite costly. However, network connectivity isn’t as important in edge computing. These systems can make autonomous decisions that balance ground moisture with available water resources.
Thus, it can be concluded that edge computing will be the next step in the evolution of computing.
Is there any need to connect edge devices to data centers, on-premises or in the cloud?
Yes, even with the emergence of edge computing and storage devices, there will still be a need to connect them to data centers or the cloud. To understand it better, let’s take an example of agriculture. Temperature and humidity sensors in agricultural fields collect valuable data, but that data does not have to be analyzed or stored in real-time. Edge devices can collect, sort, and analyze data before sending it to where it needs to go: to centralized applications or some form of long-term storage, either on-premises or in the cloud.
Because this traffic is unlikely to be time-sensitive, slower, less expensive connections, possibly via the internet, can be used. Furthermore, because the data is presorted, the amount of traffic that must be sent may be reduced. The benefit of edge computing is the faster response time for applications that require it and the slowing growth of costly long-distance connections to processing and storage centers.
Conclusion
The primary distinction between cloud computing and edge computing is the location of data processing. Data is collected, processed, and analyzed at a centralized location in cloud computing. Edge computing, on the other hand, is based on a distributed computing environment in which data is collected, processed, and analyzed locally. There is no need to choose between cloud computing and edge computing for cloud solutions because they do not “compete” with each other but rather complement each other and work together to provide better application performance.
FAQs
Edge computing was created by whom?
Brian Noble, a computer scientist, demonstrated how mobile technology could use edge computing for speech recognition in 1997. This was the first time when the term edge computing came to light.
What are the difficulties of edge computing?
Cost, data loss, and security are some edge computing challenges.
In edge computing, which algorithm is used?
Edge computing employs the ERBS Time Synchronization Algorithm.
Is edge computing safe to use?
Edge computing is not secure because it lacks the physical security safeguards found in data centers.
What role does edge computing play in cloud computing?
Edge computing improves the performance of Internet devices and web applications by pulling computing closer to the data source, thus reducing the need for long-distance communications between client and server and lowering latency and bandwidth consumption.
Is edge computing the way of the future?
Yes, edge computing is the future because it has the potential to protect the environment, improve our health, and eliminate road rage.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio