What is ERP? A Beginner's Guide to ERP in 2024
Businesses are increasingly digitizing their operations and have shifted to solutions that can provide them with efficient results at lesser costs and higher efficiency. ERP or Enterprise resource planning solutions is one such effective solution helping businesses manage business operations and processes more efficiently. ERP solutions are now being implemented across organizations, from planning operations to integrating business processes, thereby contributing to better decision-making. Wondering what is ERP? Read our blog to learn more about it.

What is ERP? Definition and Scope
ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning refers to a suite or collection of integrated business management software that organizations use across industries. It is used to collect, store, manage and interpret data from a number of business activities like product planning, manufacturing, purchases, and service delivery.
ERP systems are complete, integrated platforms. They manage all aspects of a production-based or distribution business. With your core accounting function, these systems also support all aspects of financial management, HR, supply chain management, and manufacturing.
Enterprise Resource Planning systems will also provide transparency into your complete business process by tracking all production, logistics, and financial aspects. These integrated systems act as a business's central hub for end-to-end workflow and data, allowing a variety of departments to access them.
Technology service providers and vendors offer these ERP software solutions based on the size and business requirements of the organizations. ERP helps different technologies to connect with the business as well as individuals and eliminate any costly duplicate and incompatible or irrelevant technology.
Must Read - Key Phases of ERP Implementation and Best Practices to Follow
Best-suited Human Resources courses for you
Learn Human Resources with these high-rated online courses
Types of ERP
Boradly, there are three types of ERP.
- On-premise ERP: This ERP system is installed on a company's servers and managed by its IT department.
- Cloud-based ERP: Also known as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) ERP, this system is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet.
- Hybrid ERP: This type of system combines both on-premise and cloud-based ERP solutions, allowing companies to take advantage of both benefits.
Must Explore - ERP courses
Core Components of ERP
There are four main components of ERP, which areas follows -
Finance and Accounting
This module manages financial transactions, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting. It helps streamline financial processes, improves accuracy in financial data, and enables better financial analysis and decision-making.
Human Resource Management
The HR Management module handles employee-related processes, including employee records, payroll, benefits administration, recruitment, training, and performance management. It helps automate HR tasks, improves employee data management, enhances workforce planning, and facilitates efficient HR operations.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management module covers the entire supply chain, from procurement to production to distribution. It includes inventory management, demand forecasting, order management, supplier relationship management, and logistics coordination. This module helps optimize the supply chain, reduces costs, improves inventory control, enhances demand planning, and ensures timely delivery.
Customer Relationship Management
The CRM module manages customer interactions, sales processes, and marketing activities. It tracks customer data, manages leads and opportunities, facilitates sales forecasting, and supports marketing campaigns. CRM enables businesses to improve customer satisfaction, increase sales efficiency, personalize marketing efforts, and build stronger customer relationships.
Must Read - Difference Between CRM And ERP
ERP systems' core components/modules work together to integrate and streamline various aspects of business operations, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and overall performance.
Related - 4 Types of Planning in Management that Every Manager Must Know
Features of an ERP
An ERP system is usually directly associated with the following characteristics :
- Modularity: The ERP system incorporates different functional modules responsible for controlling and operating a department's functions. The advantage of a module structure is that the modules can work separately without any problem. At the same time, they can integrate perfectly to ensure the flow of information and operational transparency.
- Flexibility: Given the dynamic nature of business and the need to innovate continuously, organizations require solutions capable of adapting to a constantly changing environment. The ERP structure provides flexibility based on the ability to interconnect with other tools and on the operation of each module separately.
- Scalability: In the business world, development and growth are generally associated, and as companies evolve, they need tools capable of accompanying them in this process. ERP providers can base their service on functionalities adapted to the specific needs of each company.
Related - Management Planning Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Ideal ERP System
An ideal ERP system is a single database containing all the data from different software modules. These software modules may include the following:
- Manufacturing: Some of the functions include engineering, capacity, workflow management, quality control, bills of material, manufacturing process, etc.
- Finance: Accounts payable, accounts receivable, fixed assets, general ledger and treasury management, etc.
- Human Resources: Benefits, training, payroll, hours and attendance, etc.
- Supply Chain Management: Inventory, supply chain planning, vendor scheduling, claims processing, order entry, purchasing, etc.
- Projects: costs, billing, management activity, time and expenses, etc.
- Customer Management: sales and marketing, services, commissions, customer contact, support call center, etc.
- Data Warehouse: Generally, this module can be accessed by customers, suppliers and employees.
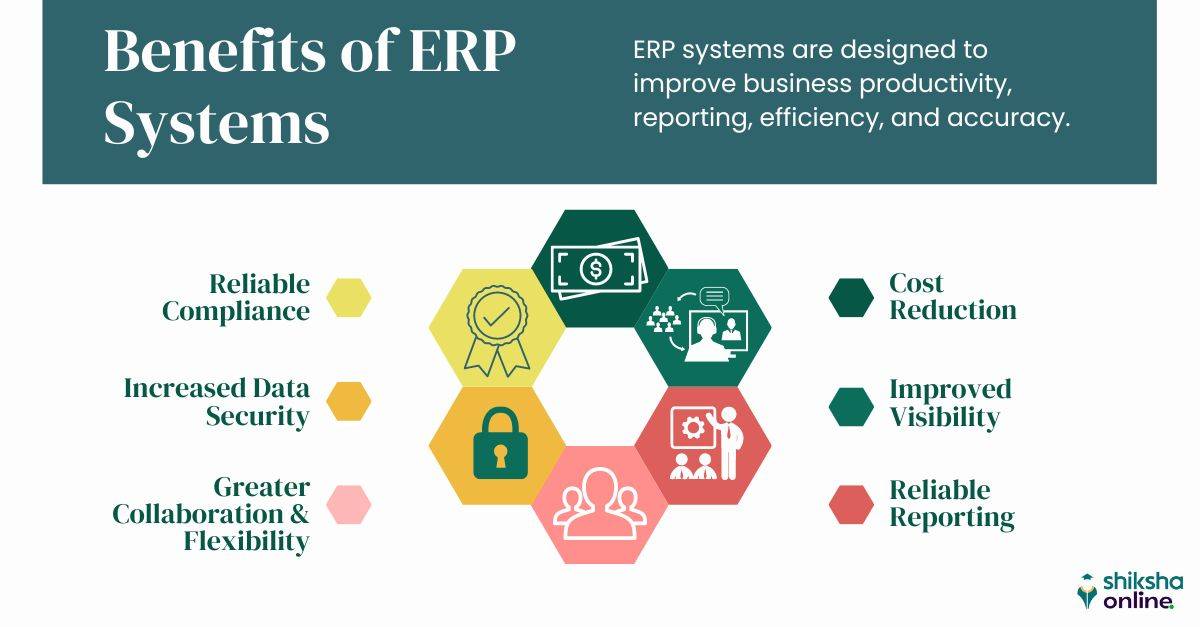
What Are the Benefits of ERP?
Here are some of the most remarkable benefits of an effective ERP:
- Cost Reduction: The main benefit of ERP is the ability to reduce costs throughout the organization. Improved visibility into processes helps administrators identify and eliminate inefficiencies. Automation allows departments to reduce human errors from manual data entry while allowing them to focus more on other essential tasks. Improved security reduces the potential costs and damage associated with cyberattacks and other threats. In each case, cost savings is the bottom line.
- Improved Visibility: ERP systems combine workflows and other process information, providing authorized employees and administrators with an overview of all relevant projects and functions. It allows accessing project updates with a single click and keeps important documentation secure.
- Reliable Reporting: Integrated ERP monitoring tools capture relevant data and present it in a fully comprehensive and easy-to-follow manner. This allows for more accurate reporting and real-time views of critical resources.
- Feasible Ideas: Reporting on captured data is a big step, but it's not everything; integrated ERP analytics solutions help extract key insights from raw data, enabling companies to make more informed decisions and identify important trends. Additionally, because ERP systems are coordinated across departments, business leaders can now easily identify how changes in one area of the organization affect other areas.
- Reliable Compliance: As financial reporting, data security, and other regulations become more stringent—and the penalties for failing to meet regulatory standards are more severe—a proper ERP can help organizations stay compliant. Cloud and hybrid ERP solutions are designed to keep up with all regulatory standards, and ERP audit trails make it easy to demonstrate compliance or identify potential problem areas.
- Increased Data Security: Integrated security protocols provide an additional layer of data security. These defenses are designed to work across all business processes and protect the shared database from threats. This helps reduce the likelihood of attackers breaking in through bypassed systems.
- Greater Collaboration: Since ERP solutions can also function as effective centers for collaboration and communication, users can share files, access customer support records, set up meetings, view relevant data, and more.
- Greater Flexibility: The ERP systems are designed to be flexible to manage the full range of business processes. This means that they can typically perform important tasks and can be customized to support individual tasks. Modern ERP systems also come with advanced automation and other resource-saving tools, allowing companies to scale to meet increased demand easily.
- Better Customer And Partner Management: ERP solutions not only benefit internal processes and communications, but they are also effective in improving customer and partner relationships. ERP systems can provide information related to vendors and service providers and facilitate optimal information sharing. In addition, these systems allow tracking of customer responses, ensuring that every customer is supervised.
- IT Simplification: The main goal of ERP systems is to simplify and aggregate IT processes. This further simplifies other employee tasks, such as improving data accuracy, increasing productivity, and creating a happier workforce.
Also Read - Difference Between ERP and SAP
Future of ERP
Businesses have continually integrated ERP systems for several decades. These systems have been evolving with the business demands. In future, we are more likely to see several trends and developments in this domain:
- Cloud-based ERP: Integrating ERP systems with cloud-based platforms has helped businesses with advantages like lower costs, easier scalability, and improved accessibility.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: ERP systems will increasingly incorporate disrupting technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to improve decision-making and automate routine tasks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): ERP systems must incorporate IoT data to provide more accurate and timely insights into operations.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technologies can improve ERP systems' security and transparency, especially in supply chain management and financial transactions.
- Integration with other systems: ERP systems are increasingly being integrated with other business systems, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Human Resources Management (HRM) systems, to provide a more comprehensive view of organizational data.
Cloud-Based ERP Software Market is expected to grow at a +15% CAGR during the forecast period 2023-2030. The future of ERP will be characterized by increased flexibility, intelligence, and connectivity, as organizations seek to leverage these technologies to gain a competitive advantage.

Rashmi is a postgraduate in Biotechnology with a flair for research-oriented work and has an experience of over 13 years in content creation and social media handling. She has a diversified writing portfolio and aim... Read Full Bio