Difference between ASP and ASP.NET
Have you ever wondered about the core differences between ASP and ASP.NET? While ASP is an initial server-side script engine for dynamic web pages, relying on interpreted scripts like VBScript, ASP.NET is a strong web application framework that utilizes compiled code, supports multiple programming languages like C# and VB.NET, and offers advanced features for modern web development. Let's understand more!
Table of Content
- Difference Between ASP and ASP.NET
- What is ASP?
- What is ASP.NET?
- Similarities Between ASP and ASP.NET
Best-suited Web Development courses for you
Learn Web Development with these high-rated online courses
Difference Between ASP and ASP.NET
Below is a table of differences between ASP and ASP.NET
| Feature |
ASP (Classic ASP) |
ASP.NET |
| Development Model |
Interpreted |
Compiled |
| Language Support |
Primarily VBScript and JScript |
Supports any .NET language, including C#, VB.NET, and F# |
| State Management |
Limited support for session and application state |
Advanced state management features, including view state, session state, application state, and cache |
| Runtime Execution |
Interpreted at runtime |
Compiled to Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) and executed on the .NET Framework |
| Separation of Concerns |
Limited; code and HTML are often mixed |
Clear separation through code-behind files, MVC, and Web Forms |
| Components |
Uses COM-based components |
Uses .NET components and libraries |
| Debugging |
Basic debugging features |
Advanced debugging support in Visual Studio, including breakpoints, watch windows, and detailed error information |
| Error Handling |
Basic error handling with On Error Resume Next |
Structured exception handling with try-catch blocks |
| Security |
Basic security features |
Comprehensive security features, including authentication, authorization, and secure communication (SSL) |
| Performance |
Generally slower due to interpreted scripts |
Faster execution due to compiled code and optimizations in the .NET Framework |
| Scalability |
Less scalable due to limited application and session management features |
Highly scalable with advanced caching, session management, and application deployment options |
| Development Tools |
Primarily developed using text editors and limited IDE support |
Extensive IDE support with Visual Studio, including IntelliSense, server controls, and a rich designer environment |
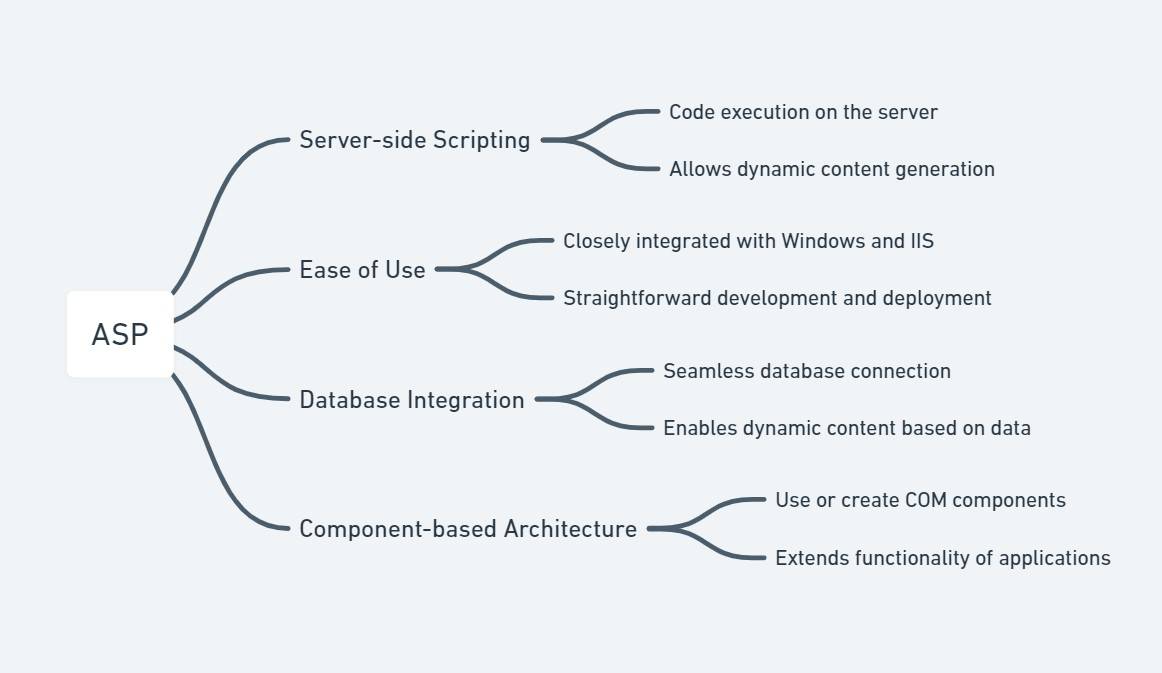
What is ASP?
ASP stands for Active Server Pages. It is Microsoft's first server-side script engine for dynamically generated web pages. Introduced in 1996 as an add-on to Internet Information Services (IIS) via the Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack, it marked a significant advancement in web development technology by allowing for the creation of dynamic, interactive, and database-driven web applications.
ASP files are executed on the server, and the output is sent to the user's web browser. This server-side technology enables developers to combine HTML pages, script commands, and COM components to create interactive web pages and powerful web-based applications. ASP uses scripting languages such as VBScript (Visual Basic Scripting Edition) or JScript (Microsoft's version of JavaScript) for its programming logic.
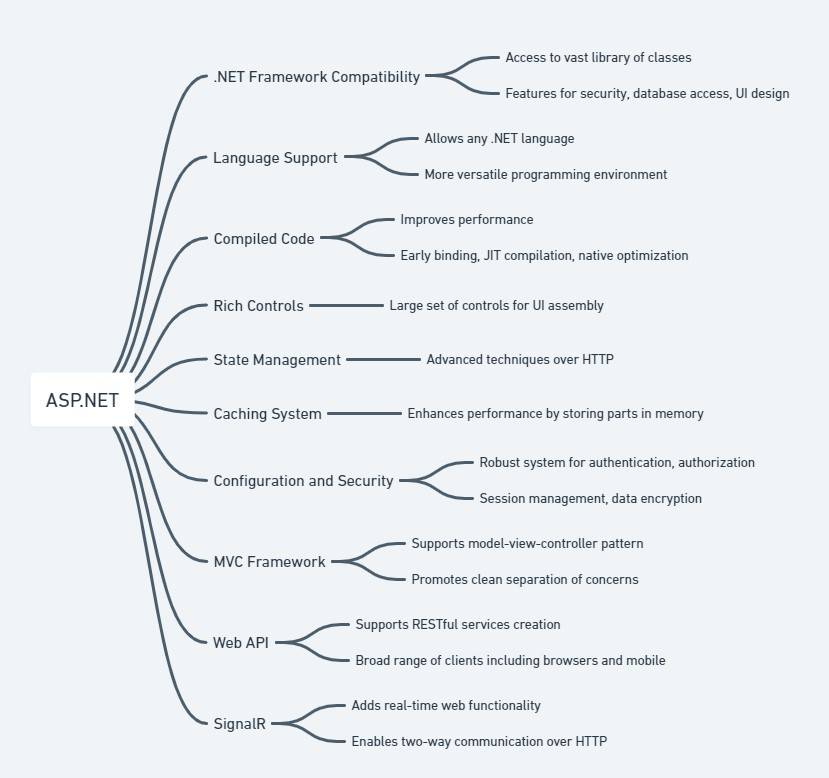
ASP.NET is a web application framework developed by Microsoft to allow programmers to build dynamic websites, applications, and services. It is part of the .NET Framework, enabling developers to use a full-featured programming language such as C#, VB.NET, or F# to build web applications easily. ASP.NET extends the .NET platform with tools and libraries specifically for web development.
Key Features:
Similarities Between ASP and ASP.NET
Below is a table highlighting the similarities between ASP and ASP.NET
| Aspect |
Similarity |
| Core Purpose |
Both are used for building dynamic web pages and web applications. |
| Server-side Execution |
Execution of code occurs on the server side, generating HTML that is sent to the client. |
| Integration with IIS |
Integrated with Microsoft's Internet Information Services (IIS) for web hosting. |
| Support for Custom Components |
Both can utilize custom components to extend functionality: COM components in ASP and managed .NET components in ASP.NET. |
| Scripting Language Support |
Support scripting languages, though the specific languages differ (VBScript, JScript for ASP; C#, VB.NET for ASP.NET). |
| Microsoft Technology |
Part of the Microsoft technology ecosystem for web development. |
| Access to Database |
Provide capabilities for connecting to databases for data-driven web applications. |
| State Management |
Offer state management features, though ASP.NET's capabilities are more advanced. |
| Development Environment |
It can be developed and debugged in Visual Studio or other compatible IDEs from Microsoft. |
| Security Features |
Include built-in security features, with ASP.NET offering more comprehensive options. |
Thus, the primary difference between ASP (Active Server Pages) and ASP.NET comes from their architectural foundation, programming model, and the era of web development they represent.


Check out Web Development courses here!
FAQs
What is the main architectural difference between ASP and ASP.NET?
The primary architectural difference lies in how they process requests and execute code. ASP uses an interpreted script model, primarily with languages like VBScript, meaning the code is interpreted on-the-fly with each request. ASP.NET, on the other hand, operates on a compiled model, where code (written in languages such as C# or VB.NET) is compiled into a .NET assembly before execution. This fundamental difference makes ASP.NET applications generally faster and more efficient, as the overhead of interpreting code is eliminated.
Can ASP and ASP.NET applications run side by side on the same server?
Yes, ASP and ASP.NET applications can run side by side on the same server. Since they are processed by different engines—ASP by the Classic ASP engine and ASP.NET by the .NET runtime—they can coexist without interfering with each other. This compatibility is beneficial for organizations transitioning from ASP to ASP.NET, allowing them to migrate applications gradually.
How do ASP and ASP.NET differ in terms of state management?
State management in ASP is relatively primitive, relying on cookies, the Session object, and the Application object to maintain state across requests in a stateless HTTP protocol. ASP.NET provides a more sophisticated and flexible state management system, including the View State, Control State, Session State, Application State, and Cache mechanisms. ASP.NET's state management is designed to be more configurable and efficient, offering better support for large-scale, distributed, and high-performance web applications.