Difference between Internal and External Business Environment
The internal business environment includes factors within the company, like employees, culture, and management. The external business environment consists of external forces such as market trends, competition, and regulations. Both environments significantly impact a company's operations and success.
Explore marketing courses
Table of Content
- Difference Between Internal and External Business Environment
- What is Internal Environment?
- What is External Environment?
- Key Differences Between Internal and External Business Environment
Difference Between Internal and External Business Environment
Both business environments, internal and external, are essential to building a successful venture and coping with changing conditions. Let's understand the significant differences between both.
Best-suited General Management courses for you
Learn General Management with these high-rated online courses
| Aspect | Internal Environment | External Environment |
| Control | The organization has control over internal factors. | The organization has limited control over external factors. |
| Influence | Internal factors directly impact the organization’s operations and outcomes. | External factors indirectly affect the organization’s operations and outcomes. |
| Examples | Organizational structure, culture, resources, policies, leadership, and management. | Market conditions, economic, legal, regulatory, technological advancements, and social and cultural factors. |
| Controllability | Relatively controllable by the organization. | Often beyond the organization’s direct control. |
| Adaptability | Can be shaped and adapted by the organization to achieve its objectives. | Requires monitoring and adaptation by the organization to navigate challenges and changes. |
| Decision-making | Internal factors inform and influence the organization’s decision-making processes. | External factors provide insights and considerations for the organization’s decision-making processes. |
| Focus | Primarily focuses on factors within the organization. | Primarily focuses on factors outside the organization. |
| Impact on Performance | It can directly impact the organization’s performance and outcomes. | It can indirectly impact the organization’s performance and outcomes. |
| Control over Resources | The organization has control over its internal resources and capabilities. | The organization may have limited control over external resources and capabilities. |


What is Internal Environment?
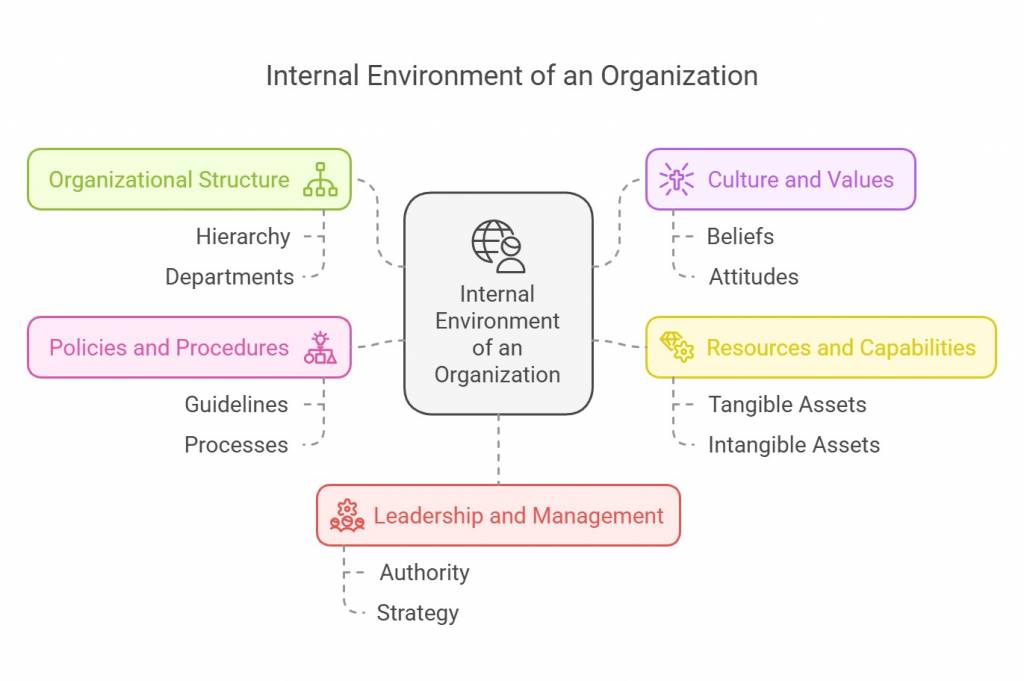
The internal environment encompasses all the factors and conditions within an organization that directly impact its operations and outcomes. These factors are generally under the control or influence of the organization’s management.
Unleash your potential in Environmental Studies! Find top colleges, engaging programs, flexible online courses, and a world of career possibilities!
Key aspects of the internal environment include:
Organizational Structure: This refers to how the organization is designed, including its hierarchy, departments, and reporting relationships.
Culture and Values: The shared beliefs, attitudes, and behaviours shape the organization’s work environment and interactions.
Resources and Capabilities: The organization’s tangible and intangible assets, such as financial resources, human resources, technology, and intellectual property.
Policies and Procedures: The established guidelines, rules, and processes that govern the organization’s operations and decision-making.
Leadership and Management: The individuals who hold authority and influence within the organization, guiding its direction and implementing strategies.
Craft Your Career Path: Find Courses After 12th That Lead to Jobs and Free Online Courses!


What is External Environment?
The external environment refers to the factors and conditions outside the organization that affect its operations but are beyond its direct control. These factors often pose uncertainties and challenges that organizations must navigate.
Key aspects of the external environment include:
The external environment refers to the factors and conditions outside the organization that affect its operations but are beyond its direct control. These factors often pose uncertainties and challenges that organizations must navigate. Key aspects of the external environment include:
Market conditions: The state of the industry, competition, customer preferences, and market trends that impact the demand and supply of goods or services.
Economic factors: External economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, economic growth, and fluctuations in consumer spending affect the overall business environment.
Legal and regulatory factors: Laws, regulations, and government policies that organizations must comply with and which can have implications for their operations and strategies.
Technological advancements: Changes in technology, innovation, and digital transformations can disrupt industries and create new opportunities or challenges.
Social and cultural factors: Social trends, demographic shifts, cultural norms, and societal values influence consumer behaviour and market dynamics.


Key Differences Between Internal and External Business Environment
- Control: The organisation controls the internal environment, allowing it to shape and modify internal factors. In contrast, the external environment is beyond the organization’s direct control.
- Influence: The internal environment directly influences the organization’s operations and outcomes. Conversely, the external environment indirectly affects the organization by creating opportunities or challenges that must be addressed.
- Focus: The internal environment primarily focuses on organisational factors, such as structure, culture, and resources. The external environment, however, concentrates on factors outside the organization, such as market conditions, regulations, and societal trends.
- Controllability: The organisation’s internal environment is relatively controllable, as it can adapt and shape its internal factors. On the other hand, the external environment is often beyond the organization’s direct control and requires monitoring and adaptation.
- Scope of Influence: The internal environment’s influence is limited to the organization’s boundaries and internal dynamics. In contrast, the external environment extends beyond the organization and encompasses various external factors and stakeholders.
- Impact on Decision-making: The internal environment informs and influences internal decision-making processes within the organization. The external environment provides insights and considerations for external factors that impact decision-making, such as market conditions and regulatory requirements.


Conclusion
The business environment is a complex and ever-changing landscape. Businesses that understand the internal and external environments are more likely to succeed. By continuously checking internal and external business environments, businesses can make informed decisions and eliminate situations that adversely affect their business.
FAQs
What is the difference between the internal and external business environment?
The internal business environment comprises factors within an organization's control, such as structure and culture. The external environment includes external factors beyond the organization's control, like market conditions and regulations.
Can you give examples of the internal business environment?
Internal factors include company culture, employee skills, management structure, and internal policies. These elements directly influence how a business operates and its overall effectiveness. Understanding these factors helps in optimizing performance and employee satisfaction.
What are some examples of the external business environment?
The external business environment includes market conditions, economic factors, technological advancements, legal and regulatory factors, and social and cultural trends.
How does the internal environment differ from the external environment in terms of control?
The internal environment is controllable by the organization, allowing it to shape and adapt internal factors. In contrast, the external environment is beyond direct control and requires monitoring and adaptation.
How do external business environment factors impact a company?
External factors such as economic conditions, competition, regulations, and technological advancements can significantly affect a company's strategy and operations. Businesses must adapt to these changes to remain competitive and ensure long-term sustainability.
Can internal and external environments change simultaneously?
Yes, both environments can change at the same time. For instance, a new regulation (external) may require a company to alter its internal processes. Companies must be agile and responsive to changes in both environments to thrive.
How can businesses analyze their internal and external environments?
Businesses can use tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to evaluate internal capabilities and external challenges. This analysis helps in strategic planning and decision-making.

Chanchal is a creative and enthusiastic content creator who enjoys writing research-driven, audience-specific and engaging content. Her curiosity for learning and exploring makes her a suitable writer for a variety ... Read Full Bio





Comments
(1)
S
7 months ago
Report
Reply to Sneha Gupta