What are the Different Types of Network Topology?
Network topology is the physical or logical arrangement of devices and connections in a network. It defines how devices are connected to each other and how data flows through the network. There are mainly two types of computer network topologies: physical and logical. Physical topology provides the layout of computer cables and other network devices, whereas Logical topology provides information about how data flows within a network, regardless of the physical arrangement of the devices.
In this article, we will discuss in detail the different types of network topology, such as Bus, Ring, Star, etc. But, before starting, let’s go through the comparison between physical and logical network topologies.
Best-suited Networking courses for you
Learn Networking with these high-rated online courses
| Topology | Physical Topology | Logical Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Bus Topology | Devices are connected to a single backbone cable. | Data flows through a shared communication line. |
| Ring Topology | Devices are connected in a closed loop, with each connected to two other devices. | Data flows logically in a circular manner. |
| Mesh Topology | Each device is physically connected to every other device. | Logical routes are determined dynamically based on network algorithms. |
| Star Topology | All devices connect to a central hub or switch. | Data flows logically through the central hub. |
| Tree Topology | Devices are connected hierarchically in star topologies branching from a backbone. | Data flows logically from top to bottom or between branches. |
| Hybrid Topology | Combines multiple physical topologies into one network. | Logical data flow varies based on the combination of topologies used. |
Types of Network Topologies
There are mainly six types of network topology in computer network.
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Ring Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
- Hybrid Topology
Let us now go over each of these topology in computer network one after the other.
You can also explore- What is Cybersecurity?
Bus Topology
All devices are connected to a single cable, with terminators at each end.
Bus topology employs a single cable (Bus) to connect all the nodes. The main cable serves as the network’s spine. All nodes in a Bus Topology are linked to the Taps and Drop Lines via the bus. Drop Lines are the connections between the central wire or bus and the nodes in this case. The Taps are the three-way connector that aids in connecting the drop line to the main central cable.
The data travels only in one direction, and when it reaches the far end of the line, the terminator removes it from the line. In a bus topology, one computer acts as a server, and the other computers act as clients. A bus topology example is connecting two floors with a single line.
Advantages of Bus Topology
- Less cabling: A common wire connects all nodes in a bus topology.
- Less Expensive: Bus topology is less expensive because it uses a common wire.
- Small network: This is best suited for situations where only a few computers are required for connection establishment.
- Upgradeable: A new node can be added or removed in this topology without affecting the other nodes.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
- Reduced signal strength: To connect a more significant number of nodes, we must increase the number of Taps, Drop Lines, and the central cable. And increasing these things will weaken the signal.
- Core failure: If the main central cable becomes damaged or faulty, the entire network will fail.
- Low security: This is a significant security issue because all nodes in the network can hear what data is transmitted to other nodes in the network.
Use Cases of Bus Topology
- Small networks: Ideal for small networks with limited data transmission needs.
- Temporary networks: Useful for temporary setups, like in conferences or events.
- Cost-effective solutions: Suited for organizations looking for economical networking options with minimal cabling.
For more information regarding the bus topology, read What is a Bus Topology article.
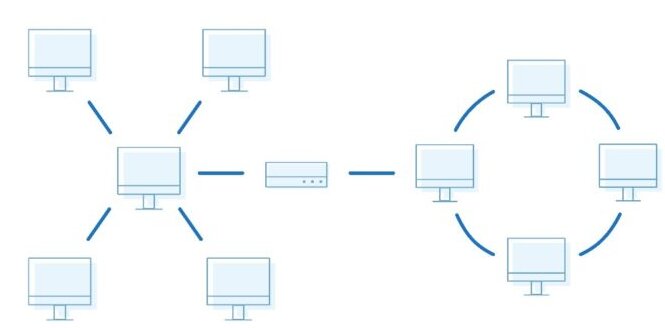
Star Topology
All devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
A hub connects all computers in this type of network topology. A central node connects all other nodes. You can use this type of network topology on LAN networks due to its low cost and ease of setup.
Advantages of Star Topology
- Network failure prevention: Only the affected nodes will fail, while the remaining nodes will continue to function.
- Performance: High performance with a small number of nodes and very little network traffic.
- Upgradation: This topology makes adding, deleting, and moving devices simple.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- Expensive: The cost of installing star topology is high.
- Slow connection: Heavy network traffic can sometimes significantly slow the bus.
Use Cases of Star Topology
- Office environments: Common in office buildings where several workstations connect to a central hub or switch.
- Flexible configurations: Suitable for networks that may require frequent additions or removals of devices.
- Centralized management: Useful in environments where centralized control and management of network devices is required.
For more information regarding the star topology, read What is a Star Topology article. And if you are intrested in learning how Bus and Star topology differ, read the Difference Between Star and Bus Topology article.
Ring Topology
Devices are connected in a closed loop, with each device connected to two other devices.
Ring Topology is a topology in which each computer is linked to another on both sides. The last computer is linked to the first, forming a ring. This topology enables each computer to have exactly two neighbours.
For example, if Node A wishes to send data to Node D, Node A has two options for doing so. That is to say –
- Node A > Node F > Node E > Node D
- Node A > Node B > Node C > Node D
The central computer in this topology is the monitor station, which is in charge of all operations. Devices use tokens for data transmission between them. The computer station must have the token to transmit data. The token is released when the transmission ends, and other computer stations can use it to send data.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- Token system: Only nodes that have tokens can transfer data.
- Less Cabling: As every node manages the cable to its closest neighbour, it requires less cabling.
- Easier troubleshooting: It is less challenging to manage and install because the nodes or cable flaws are easily discernible.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
- Difficult to upgrade: Adding or removing nodes is problematic because it disrupts network activity.
- Failure of a network: When one system crashes, it disturbs the overall network activity.
Use Cases of Ring Topology
- Token ring networks: Historically used in networks using token ring technology for orderly data transmission.
- Local area networks (LANs): Can be used in small LANs where predictable network management is necessary.
- Video conferencing: Suitable for applications where consistent bandwidth and data transfer rates are critical.
For more information regarding the ring topology, read What is a Ring Topology article.
Mesh Topology
Each device is connected to every other device on the network.
Mesh technology is a network configuration in which you link the computers via various redundant connections. There are numerous routes from one computer to another. It lacks the switch, hub, or any central computer that serves as a point of communication.
The Internet is a mesh topology example. Mesh topology is only suitable for wireless networks, and can you can create it using the formula:
(n*(n-1))/2, where n denotes the number of network nodes.
There are two types of Mesh topology: fully connected mesh topology and partially-connected mesh topology. Each computer in a full mesh topology is linked to all other computers in the network. In contrast, in a partial mesh topology, only specific computers are connected to those with whom they frequently communicate.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
- Consistent: Mesh topology networks are reliable because any link failure does not disrupt interaction among connected computers.
- High-speed information exchange: Communication between nodes is extremely fast.
- Easier reconfiguration: Adding new devices would not interfere with the communication of existing devices.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cost: A mesh topology has more connected devices, such as a router, and uses more transmission media than other topologies.
- High-maintenance: Mesh topology networks are extensive and challenging to maintain and manage.
- Efficiency: The number of redundant connections in this topology is high, reducing network efficiency.
Use Cases of Mesh Topology
- Highly reliable networks: Ideal for critical applications requiring high availability and redundancy.
- Wireless networks: Often used in wireless local area networks (WLANs) to ensure connectivity despite physical obstructions.
- Large scale networks: Beneficial for larger setups where multiple connections between nodes improve data transfer reliability and speed.
For more information regarding the mesh topology, read What is a Mesh Topology article.
You can also explore- What are Different Types of Cryptography?
Tree Topology
Devices are connected in a hierarchical structure, with a central hub or switch at the top and sub-hubs or switches below it.
Tree topologies are also known as hierarchical topology, as the root node connects all other nodes to form a hierarchy. This topology is known as a Star Bus topology because it combines several star topologies into a single bus. Tree topology is a standard network topology similar to bus and star topologies.
Data flows from top to bottom in this network topology, from the central hub to the secondary hub and then to the devices, or from bottom to top, from the devices to the secondary hub, which then connects to the central hub. It is a multi-point connection with a non-robust topology because the topology crashes if the backbone fails.
Advantages of Tree Topology
- Structuring: It aids in structuring as the tree-like shape allows any node to hold its child. And this can make it much easier to structure the entire network.
- Interconnection: All nodes can connect to the large and intermediate networks.
- Expansion of nodes: An increase of nodes is possible and easily achievable in this network structure.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
- Expensive: Managing each node in its child may be inefficient. Cabling costs will rise as well.
- Network failure: If the primary central node or another wire fails, all other nodes may become disconnected.
Use Cases of Tree Topology
- Hierarchical systems: Perfect for hierarchical data organization, such as in organizations or university networks.
- Scalable networks: Useful for networks that anticipate future expansion, as it allows for the addition of new nodes without affecting existing ones.
- Telecommunications: Common in various telecommunications infrastructures due to its structured nature.
For more information regarding the tree topology, read What is a Tree Topology article.
Hybrid Topology
It is a combination of two or more of the basic topologies. For example, a star-bus topology is a hybrid topology that combines the star and bus topologies.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- Multiple advantages: These types of network topology combine the advantages of various topologies into a single topology.
- Scalable: Hybrid networks are easily scalable as you can easily integrate the new hardware components.
- Traffic: These types of network topology can handle a high traffic volume while remaining extremely flexible and dependable.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
- Expensive: Because it combines the benefits of multiple topologies into a single topology, this type of topology is quite expensive.
- Complex design: Creating a hybrid topology is a difficult task.
Use Cases of Hybrid Topology
- Diverse environment needs: Suitable for areas requiring different topologies for varying applications (e.g., combining star and bus).
- Large enterprises: Ideal for large organizations that need custom networking solutions based on different departments or locations.
- Flexible configuration: Perfect for networks that need to adapt quickly to changing requirements or technologies.
For more information regarding the hybrid topology, read What is a Hybrid Topology article.
Which Type of Network Topology is Best for You?
The type of network topology that is best for you depends on your specific needs and requirements. Some factors to consider include:
- Cost: Some topologies are more expensive to implement and maintain than others.
- Scalability: How easily can the network be expanded?
- Performance: How well does the network perform under load?
- Reliability: How fault-tolerant is the network?
Conclusion
Apart from the commonly used network topologies mentioned above, there are other topologies that are less frequently used, such as - Daisy Chain Topology and Point to Point (P2P) Topology.
There is no universally correct answer to the question of which type of network topology is best. The ideal topology always depends on your specific needs and requirements. So, when choosing the type of network topology to use, always consider factors such as - cost, scalability, performance, and reliability.
FAQs
How many different types of topology are used in a network?
The study of network topology identifies six fundamental topologies: bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid.
Which network topology is best for a small business?
The star topology is the best network topology for a small business. It is easy to implement and troubleshoot, and it is scalable enough for most small businesses.
Which Network Topology is the most reliable?
The mesh topology is the most reliable network topology, as data can take multiple paths to its destination. However, it is also the most expensive and complex topology to implement.
What is the most common network topology?
The star topology is the most common network topology. It is easy to implement and troubleshoot, and devices can be added or removed without disrupting the network.
What is a network topology?
The term network topology refers to the logical or physical configurations of nodes and connections within a network.
Which network topology is the most scalable?
The tree topology is the most scalable network topology. It can be easily expanded by adding more hubs or switches to the network.
Which network topology is the best for performance?
The mesh topology offers the best performance, as data can take the shortest path to its destination. However, it is also the most expensive and complex topology to implement.
Which network topology is best for a large enterprise?
The tree topology is the best network topology for a large enterprise. It is scalable and reliable, and it can be used to create a high-performance network.
How do I choose the right network topology for my needs?
The best network topology for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Some factors to consider include the size of your network, the type of applications that you will be using, and your budget. You should also consult with a network engineer to get expert advice.
What is LAN topology in computer network?
LAN topology in computer networks refers to how devices on a LAN are arranged and how they communicate. It defines the layout of cables, devices, and their interconnections within the local network (LAN). Common examples of LAN topology are Bus topology, Hybrid topology, Star Topology, Mesh topology, etc. For more information, read the What Is A LAN Topology article.
What is a Point to Point Topology?
Point-to-Point (P2P) topology is a network topology that connects two devices (hub, router, switch, etc.) or nodes directly with a dedicated, private (LAN cable). In this, one of the connected nodes serves as the transmitter, while the other acts as the receiver. To know more about P2P topology, read the What is Point to Point Topology article.
What are the two major categories of network topology?
The two major categories of network topology are:
- Physical Topology: This refers to the physical layout of the network, including the arrangement of cables, devices, and other physical components.
- Logical Topology: This describes how data flows within the network, regardless of its physical layout. It focuses on the way devices communicate with each other and the protocols used.
What protocols are commonly associated with bus and ring topologies?
Common protocols associated with bus and ring topologies are:
- Bus Topology:
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD): This protocol is used in Ethernet networks to manage how network devices respond when two devices attempt to send data simultaneously on the same bus.
- Ring Topology:
- Token Ring Protocol: This protocol uses a token-passing mechanism where a special data packet (the token) circulates around the ring, granting the right to transmit data to the device that holds it.
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI): Although primarily used in LANs, FDDI can also be implemented in a ring topology using optical fiber.
These protocols help regulate data transmission and minimize collisions across the network.
What are the advantages of using a mesh topology?
Mesh topology offers several advantages, such as high reliability and redundancy. Each node is connected to multiple other nodes, ensuring that data can still be routed through different paths if one connection fails. This enhances fault tolerance.
Apart from this, mesh networks can handle high traffic and provide consistent performance, making them suitable for critical applications and environments needing robust connectivity.
How does tree topology differ from star topology?
Tree topology is a hierarchical structure that combines characteristics of both star and bus topologies, featuring a central "root" node and multiple levels of nodes that can branch out. In contrast, star topology has a single central node (like a hub or switch) connected to all peripheral nodes, creating a straightforward layout.
While tree topology allows for more complex, scalable networks, star topology is simpler and easier to manage but can be limited in terms of expansion and redundancy.