What is Email Spoofing and How to Prevent It?
You’ve almost certainly been a victim of email spoofing at some point in your life. This is because email spoofing affects everyone, from individuals to multibillion-dollar corporations.
Email spoofing is a common form of cybercriminal activity, a type of identity deception used in phishing and spam attacks. In this article, we will cover email spoofing in great detail, but before moving to that, let’s go through the topics that we will be covering in this blog.
Table of Contents (TOC)
- What is email spoofing?
- Real-life examples of email spoofing
- History
- How does email spoofing work?
- Types of email spoofing
- How to prevent email spoofing?
- Difference between spoofing and phishing
What is email spoofing?
Email spoofing is the process of sending emails with a forged sender address. It deceives the recipient into believing that the email is sent by someone they know or trust. It’s usually a phishing tool designed to take over your online accounts, send malware, or steal money.
You can also explore- What is a Salami attack & how to protect against it?
Email spoofing aims to get recipients to open, respond to, and interact with the message. Email spoofing can dramatically enhance the efficacy of phishing and other email-based cyber attacks by deceiving the receiver into trusting the email and its sender.
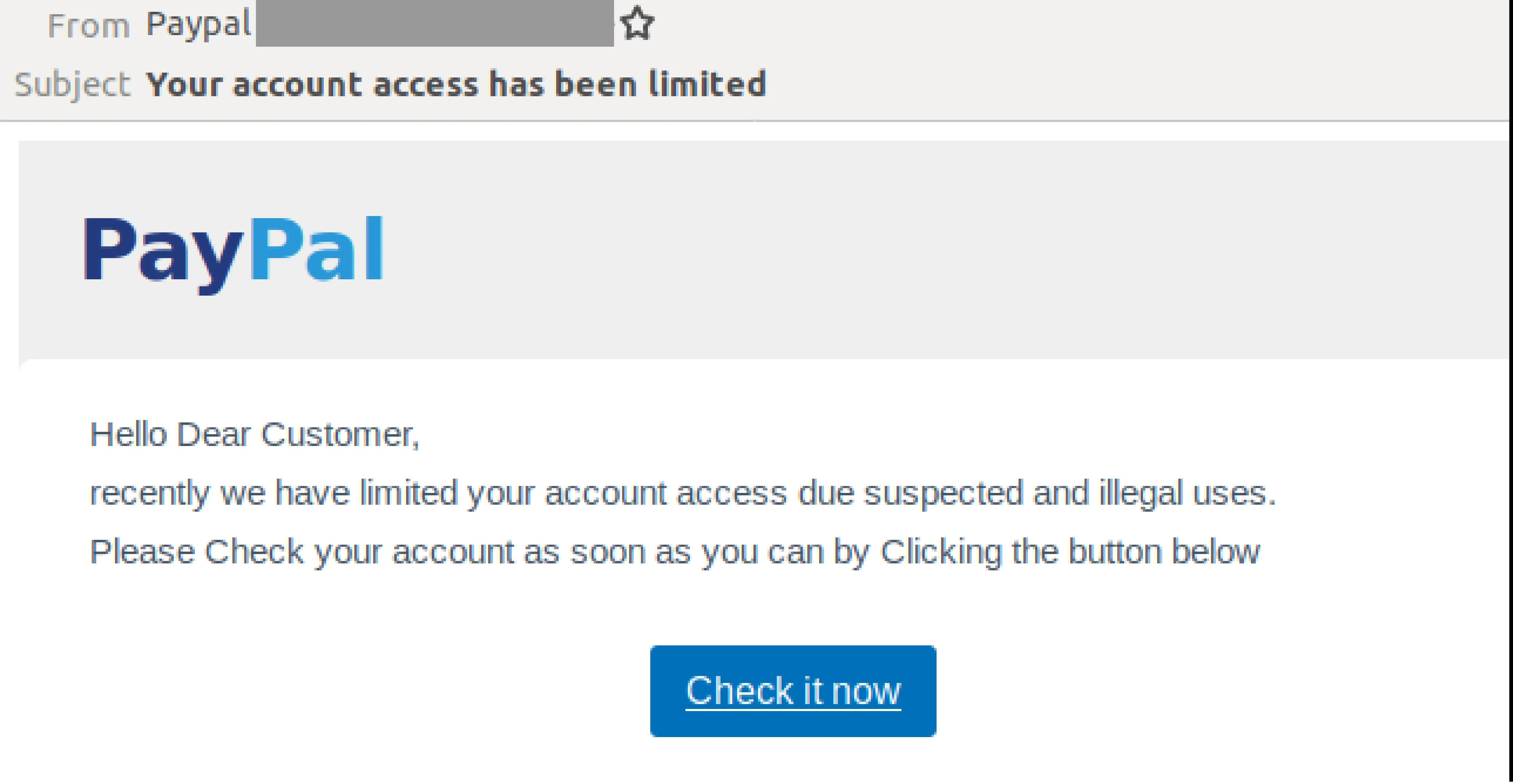
For example, an attacker could send an email that appears to be from PayPal. The message alerts the reader that their account has been limited. And to check the account details, the user should click on the link.
Best-suited Ethical Hacking courses for you
Learn Ethical Hacking with these high-rated online courses
Real-life examples of email spoofing
- A widespread spoofing campaign targeting C-suite executives was discovered in March 2021. The attackers created spoof spear-phishing emails resistant to “Office 365’s native defences and other email security defences.”
- In October 2021, a threat actor was spoofing email domains belonging to the Philippine government. In this attack, the attackers were sending fraudulent emails about COVID-19 to shipping, manufacturing, and energy companies.
You can also explore- What is cybersecurity?
History of email spoofing
Since the 1970s, email spoofing has been a problem. It began with spammers who used it to circumvent email filters. The situation became more prevalent in the 1990s and became a global cybersecurity issue in the 2000s. In 2014, security protocols were implemented to combat this attack. And because of these protocols, many spoofed email messages are now routed to users’ spam folders or are rejected.
You can also explore– What is an Ethical Hacker?
How does email spoofing work?
An attacker can spoof emails with a working Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server and a popular email platform like Outlook or Gmail. When the email arrives in the intended inbox, the email programme reads the contents of these fields and generates the output that the end-reader sees. If certain information is entered into the appropriate fields, what they see will differ from what is true, such as the location of the email’s origin.
This is possible because SMTP does not support the authentication of addresses. Although protocols and methods exist to combat spoofing, their adoption has been slow.
Types of email spoofing
Attackers can spoof email through a variety of methods of varying complexity. They also differ in terms of which part of the email the attacker will forge, for example:
- Via display name: In this, an attacker spoofs only the display name of the email sender. Someone can accomplish this by creating a new Gmail account with the same name as the person they want to impersonate. This type of email will also avoid all anti-spoofing security measures. Because it’s a legitimate email address, it won’t be flagged as spam.
- Via legitimate domains: In this, an attacker may also use the impersonated identity’s actual email address in the From header, such as “Naukri” noreply@naukri.com. This attack does not involve jeopardising the impersonated identity’s account or servers but instead exploits security flaws in the underlying email protocols. Attackers frequently use public cloud infrastructure or third-party email sending services that do not verify domain ownership to send such attacks.
- Via lookalike domains: In this, an attacker attempts to manipulate the receiver by signing up, including using domains similar to the impersonated domain, such as “@doma1n.co” instead of “@domain.co.” This change could be so minor that an inattentive reader would miss it. It worked because when the last time you read an email header was?
You can also explore- What is a Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack?
How to prevent email spoofing?
You can prevent email spoofers from accessing users’ and businesses’ systems in a variety of ways, such as:
- Putting in place an email security gateway
- Using anti-malware software
- Providing cyber awareness training to employees
- Using encryption to safeguard emails
- Evading clicking on unfamiliar links
- Utilizing email security protocols
- Avoiding unusual attachments.
- Using reverse IP lookups to verify senders
Difference between spoofing and phishing
Spoofing occurs when a person steals the details of a legitimate user and pretends to be another user. In contrast, phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which a person steals sensitive information from a user in a fraudulent manner while impersonating a legitimate person.
You can also explore- What is a Phishing attack?
Let’s take a look at the differences in a table:
| Benchmark | Phishing | Spoofing |
| Implementation method | Attackers use social engineering techniques to do phishing. | Spoofing requires the installation of malicious software on the user’s computer. |
| Category | Phishing is not a part of spoofing. | Spoofing is similar to phishing in some ways. |
| Purpose | Attackers do phishing to obtain sensitive information. | Attackers do spoofing to obtain a new identity. |
| Example | Phone Phishing | Email spoofing |
Recently completed any professional course/certification from the market? Tell us what liked or disliked in the course for more curated content.
Click here to submit its review with Shiksha Online.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of email spoofing?
Email spoofing attempts to trick recipients into opening or responding to the message.
What are the dangers of email spoofing?
Phishing and other email-based cyber attacks can benefit significantly from email spoofing.
Is it possible to track down a spoofed email?
An anonymous email cannot be traced to the sender using anything from the sender's name to the IP address and metadata.
How can I tell if an email sender is genuine?
To verify an email's authenticity, ensure the 'From' email address matches the display name.
Is it safer to use text messaging apps or email?
End-to-end encryption is unavailable in popular free email services like Gmail or Yahoo. As a result, it is preferable to use text messaging apps that provide end-to-end encryption.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio