What is a Flowchart? (With Examples)
A flowchart graphically represents the sequences of a process with logical steps represented through symbols. Learn more about flowcharts in this article.
A flowchart is a graphical representation of a process. Each process step is represented by a different symbol that contains a brief description of the process step. The flowchart provides a visual description of the activities involved in a process. It shows their sequential relationship, facilitating a quick understanding of each activity and its relationship with the others.
Content
The process flow is represented through graphic symbols linked together with arrows to indicate the flow direction. A flowchart also expresses the flow of information and materials, derivations of the process, the number of steps in the process, and interdepartmental operations. It makes it possible to identify repetitive loops, which is essential for redesign and improvement actions.
The flowchart also facilitates the selection of process indicators, which are essential to carry out their control and evaluate their performance and effectiveness.
Flowcharts and Process Management: Benefits
Organizations constitute process systems. Therefore, it is essential to identify the processes and relationships between them, plan the flow of activities to analyze the processes, and ensure their documentation. Thus, flow charts are essential to understand how a process works and determining its improvement points. In this sense, there are many benefits of using the flowchart, which are –
Provides a transparent view of the process
First, it improves understanding of the process. A process’s activities, relationships, and incidents are not easily discernible a priori. Diagramming makes it possible to grasp this set and go further, focusing on specific aspects of it, and appreciating the interrelationships that are part of the process and those that occur with other processes and sub-processes.
Facilitates customer identification
It is easier to determine your needs and adjust the process to meet your needs and expectations.
Stimulates analytical thinking
At the time of studying a process, flowcharts make it more feasible to generate valuable alternatives.
Provides a more effective method of communication
We can process visuals 60,000 times faster than text. Hence it gets straightforward to communicate our data in flowcharts. The data in flowcharts may look identical, but how data is addressed in the charts may be vastly different.
Allows establishing the added value
The flow chart allows you to analyze the value activity contributing to the process. Therefore, it allows identifying those that are unnecessary, reducing time and costs.
Helps to establish control mechanisms
Similarly, the flowchart is an excellent tool for controlling and improving processes. At the same time, it makes it easier to establish the objectives for the different operations and activities carried out.
Saves time and costs
It facilitates the study and application of actions that improve the variables of time and activity costs and, therefore, influence the improvement of effectiveness and efficiency.
Finally, it constitutes the essential starting point for improvement, redesign, or reengineering actions.
Best-suited Project Management courses for you
Learn Project Management with these high-rated online courses
Types of Flowcharts
We can categorize the types of flowcharts basis orientation and application –
Types of flowcharts basis orientation
There are four types of flowcharts based on the orientation of their representation:
- Horizontal – According to the reading order, the flow of operations goes from right to left. It is the most common model.
- Vertical – The flow and sequence of operations are from the top down. This is an ordered list of operations according to their purpose.
- Panoramic – They represent the entire process on a single chart, using both the vertical and horizontal models.
- Architectural – Describes a person’s work itinerary or a form about their work area.
Types of flowchart basis application
Process Flowchart – A process flow diagram is probably the most versatile of the four flowchart types because it can apply to just about anything. A process flow diagram is used to –
- Map out roles and responsibilities within an organization for clarity.
- Prepare a proposal for a new process or project to understand its scope and steps.
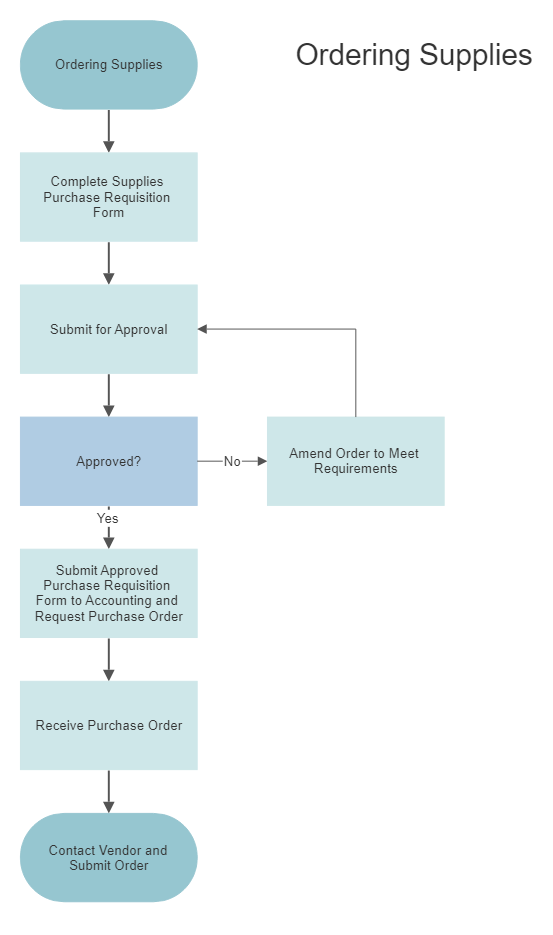
Workflow Diagram – It suggests how data and documents flow within your organization. A workflow diagram shows how a business or process works. This type of workflow diagram can be used to:
- Train new employees
- Uncover potential problem areas
- Clarify business operations by displaying a high-level overview
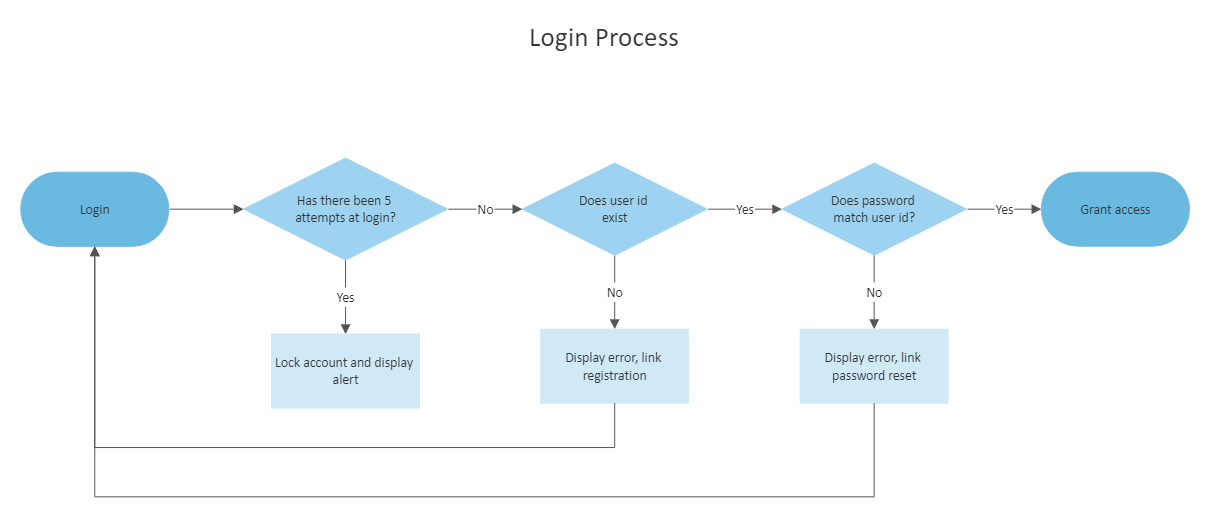
Swimlane Flowchart – Describes how different departments, processes, or employees interact. Swimlane flowchart is helpful to show how multiple information flows side by side. They are similar to a workflow diagram, but the key here is that it allows you to create different categories where the activity takes place. A flowchart or swimlane diagram is excellent for documenting an entire process that interacts with different segments of an organization or requires collaboration between different teams.
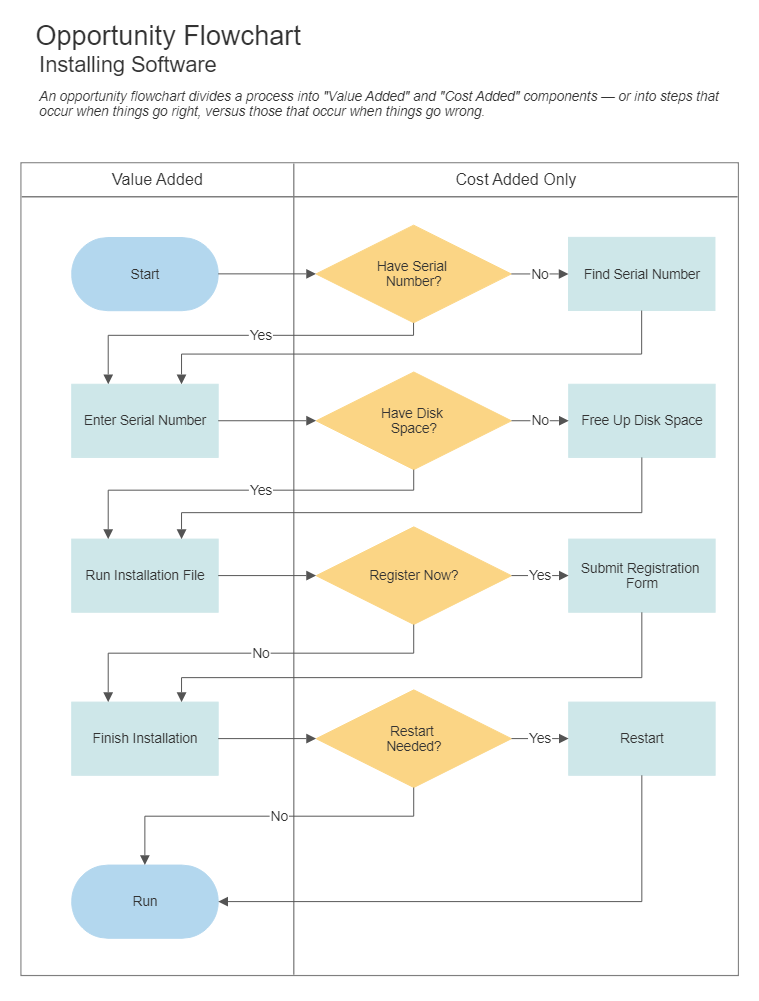
Data Flow Diagram– You can see where data enters and leaves an information system. A data flow diagram shows how data is processed. It is useful when you want to design or analyze a system. Although it is most often used for software development and design, it can be used to analyze any information flow, such as how information moves through a business.
Types of Boxes Used In A Flowchart
A flowchart makes use of several boxes that represent the flow of information. Arrows connect these boxes to each other and display the flow of control. Let’s learn about each box in detail.
1. Terminal
A terminal shape is an oval-shaped box indicating the program’s start or end. In every flowchart, you will notice a start of an algorithm and the end of the algorithm presented in an oval-shaped box.
2. Data
In a flowchart, data is represented in a parallelogram-shaped box. This box includes the inputs or outputs and mainly depicts the input data and output information.
3. Process
A process is presented in a rectangular box within a flowchart.
This rectangular box is where you can write the codes and logic or a program or run the main course of action of the algorithm.
4. Decision
A diamond box represents decision or control statements like if, or conditions like a > 0, etc. The result of the logic run in the previous step can be either a “yes” or a “no.”
5. Flow
The Arrow line depicts the direction of the process flow. Every flowchart displays the process flow from start to end, with the algorithms presented in between in different boxes. Arrows present the information in a neat and presentable way.
6. On-Page Reference
On-Page References are presented in a circular figure. These circles suggest that the flowchart is in continuation with the further steps. You can use such reference if you have less space and the flowchart is long.
Any numerical symbol can be present inside this circle. That same numerical symbol should depict before the continuation to make the user understand the continuation.
Flow Chart Samples – SmartDraw









Rashmi Karan is a writer and editor with more than 15 years of exp., focusing on educational content.
Education: M.Sc. Biotechnology
Experience: 15+ years creating informative and educational content
Spe