Colleges offering Python Courses in India
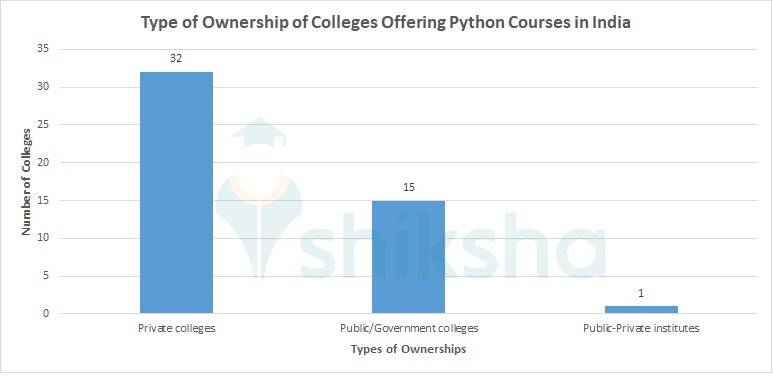
There are a total of over 83 colleges offering Python courses in India. Out of the total colleges, 67% are Private colleges, 31% are Public/Government colleges and 2% are Public-Private institutes.
Colleges offering Python Courses in India Highlights
| Parameters | Particulars |
|---|---|
| No. of colleges offering Python courses in India | 83 (Approximately) |
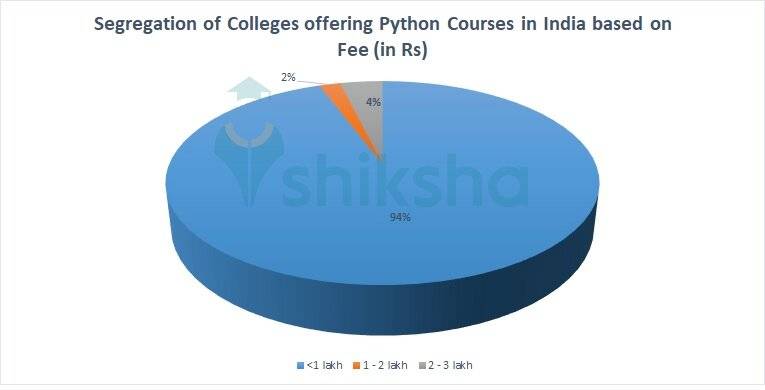
| Fees | Annual fee <1 lakh - 94% Annual fee 1 - 2 lakh - 2% Annual fee 2 - 3 lakh - 4% |
| Admission Process | Merit-Based and Entrance Exams such as NIMSEE |
| Top colleges offering Python courses in India | Parul University, UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited, NIELIT Lucknow, National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh |
| Top cities offering Python courses in India | Delhi/NCR, Mumbai, Kolkata, Pune, Bangalore |
Python is a rising popular specialisation opted by students who wish to learn more about data analysis. Since Python is required in software engineering jobs, game development, database management and more, the number of students applying for the course is increasing every year.
Python Eligibility Criteria
Students should meet the basic eligibility criteria to be eligible for admissions into Python courses. However, it should be noted that the eligibility criteria may differ from institute to institute.
- Should have qualified 10+2 (or equivalent) examination) from a recognized board.
- Students should have studied Mathematics and
There are a total of over 83 colleges offering Python courses in India. Out of the total colleges, 67% are Private colleges, 31% are Public/Government colleges and 2% are Public-Private institutes.
Colleges offering Python Courses in India Highlights
| Parameters | Particulars |
|---|---|
| No. of colleges offering Python courses in India | 83 (Approximately) |
| Fees | Annual fee <1 lakh - 94% Annual fee 1 - 2 lakh - 2% Annual fee 2 - 3 lakh - 4% |
| Admission Process | Merit-Based and Entrance Exams such as NIMSEE |
| Top colleges offering Python courses in India | Parul University, UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited, NIELIT Lucknow, National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh |
| Top cities offering Python courses in India | Delhi/NCR, Mumbai, Kolkata, Pune, Bangalore |
Python is a rising popular specialisation opted by students who wish to learn more about data analysis. Since Python is required in software engineering jobs, game development, database management and more, the number of students applying for the course is increasing every year.
Python Eligibility Criteria
Students should meet the basic eligibility criteria to be eligible for admissions into Python courses. However, it should be noted that the eligibility criteria may differ from institute to institute.
- Should have qualified 10+2 (or equivalent) examination) from a recognized board.
- Students should have studied Mathematics and English as compulsory subjects.
- Should have secured a minimum of 50% in the 10+2th (or equivalent) qualifying examination.
- Admissions will be offered on the basis of their 10+2th standard marks or scores secured in the entrance exam.
Top Colleges offering Python Courses in India with Shiksha Aggregate (Aggregate)
Top Private and Government Colleges offering Python Courses in India
Private Colleges offering Python Courses in India
| Private Colleges | Course Fee (in Rs) |
|---|---|
| Parul University | 7.5 K |
| UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited | 11 K |
| Institute of Computer Science and Information Technology, NIMS University | 1.8 L |
| Manipal ProLearn, Bangalore | 3.7 K - 20.32 K |
| GRV Business Management Academy | 10 K - 18 K |
Government Colleges offering Python Courses in India
| Public Colleges | Course Fee (in Rs) |
|---|---|
| NIELIT Lucknow | 1.4 K - 6 K |
| National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh | 2.2 K - 4.2 K |
| NIELIT Delhi | 1.18 K - 8.5 K |
| National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Ropar | 8.4 K |
Check the detailed infographic for more information
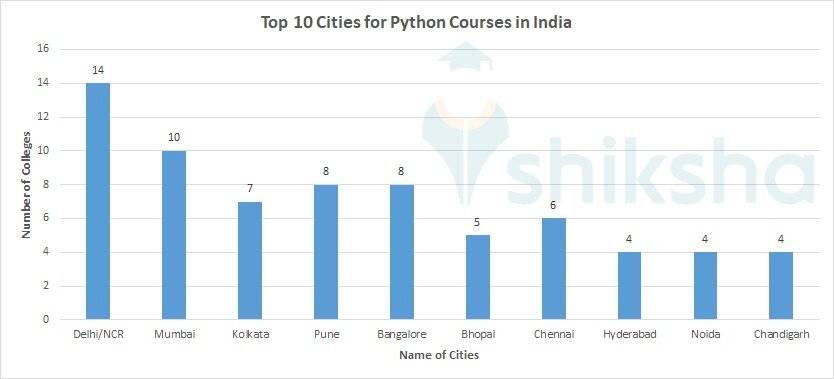
Location Wise Colleges Offering Python Courses in India
There are many cities in India that are popular destinations for Python courses. Among all of the cities, the top 10 cities have been listed out which offers Python courses in India.
ROI of Top Colleges offering Python Courses in India
The comparison between the fee that has been invested by the student while pursuing his/her course and the return he/she gets during placement is the ROI or Return of Investment. While selecting a college or university, the students are advised to check the ROI factor. Among the colleges offering Python courses in India, UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited is the top institute ROI-wise.
The best colleges offering Python courses in India with the average annual fee and average placement package are tabulated below:
| Name of the College | Average Annual Fee (in Rs) | Average Placement Package (in Rs) |
|---|---|---|
| UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited | 11 K | 3.6 LPA |
Note: Above statistics are based on the latest available data
Read More:
| Colleges offering Python courses in Delhi/NCR | Colleges offering Python courses in Mumbai |
| Colleges offering Python courses in Kolkata | Colleges offering Python courses in Pune |
Top Recruiters for Python Course Graduates
Students will be able to opt for various career opportunities after graduating with a Python course. Listed below are a few top companies that recruit Python course graduates in India along with their placement ratings:
| Name of the College | Placement Ratings | Top Recruiters |
|---|---|---|
| Skybird Aviation, Bengaluru | 4.7 | |
| Click Labs Institute | 4.7 | |
| National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Ropar | 4,0 | |
| NIELIT Srinagar | 4.0 | BQE Software, ICI computer Education, NICT, Hazratbal, A-One Technologies, Masterpro, J&K Bank, Green Valley College of Education |
| National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh | 4.0 | ACCENTURE, Dell, Infosys, Quark, RBS (Royal Bank of Scotland), Satyam, Sonata Software, TCS, WNS GlobalServices |
| NIELIT Lucknow | 4.0 | Intel, HCL, Wipro, Quest, Microsemi, TATA, Tech Mahindra |
| GRV Business Management Academy | 4.0 | Udaan Logistics, Resource Pro, GoRupee InfinTech Services, Finnovation Tech Solutions Pvt Ltd, Clarks Exotica Resort Spa, Aegis BPO, 247 Customer |
| G H Raisoni Institute of Business Management, Jalgaon | 3.8 | Accenture, Anglo-Eastern, Deloitte, FIS Solutions, IBM, JP Morgan Chase, L&T Infotech, TCS, Wipro |
| Parul University | 3.8 | Capegemeni, Jaro Education, Indian Navy, Genpact, TATA Motors and Knoldus |
How affordable is studying Python Course in India?
Based on the below pie chart, it can be estimated that pursuing Python courses in India is economical as approximately 96% of colleges have annual fees ranging below Rs. 1 lakh. Some of these colleges are:
- UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited
- Parul University
- NIELIT Lucknow
- National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh
- NIELIT Delhi
- National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Srinagar
Approximately 2% of the colleges have course/annual fees ranging from Rs 1-2 lakh. Some of these colleges are
- Institute of Computer Science and Information Technology, NIMS University
Approximately 2% of the colleges have course/annual fees ranging from Rs 2-3 lakh. Some of these colleges are
Refer to the infographic below to get a detailed overview of the break-up of colleges offering Python courses in India based on fees:
Read More
| Colleges offering Python Courses Accepting NIMSEE |
Top Colleges offering Python Courses in India: Cutoff
Colleges prepare their own admission cutoff after considering various factors during the admission process. Those students who score within the cutoff in the entrance exams have a higher chance of admission. The cutoff of the colleges offering Python courses in India can be checked through the table given below.
| College Cutoff | College Cutoff |
|---|---|
| Parul University Cutoff | G H Raisoni Institute of Business Management, Jalgaon Cutoff |
| IIIT Bhagalpur Cutoff | Indus University Cutoff |
 All FiltersClear All
All FiltersClear AllColleges offering Python Courses in India

FAQs
Q. Are admissions into college offering Python courses entrance exam or merit-based?
A. Colleges can offer admissions into Python courses based on entrance exam or merit as per their eligibility.
Q. Which cities are the best for Python courses?
A. According to statistics, cities such as Delhi/NCR, Mumbai, Kolkata and Pune are the best for Python courses.
Q. How many colleges in India offer Python courses?
A. There are approximately 76 colleges in India that offer Python courses,
Q. Which are the top colleges in India that offer Python courses?
A. Some of the top colleges in India that offer Python courses are - Parul University, UPTEC Computer Consultancy Limited, NIELIT Lucknow, National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Chandigarh.
Q. What is the average fee to study Python courses in India?
A. The average fee to study Python courses in India is less than 1 lakh.
Q. Which are the top recruiters for Python course graduates?
A. The top recruiters for Python course graduates are – ACCENTURE, Dell, HCL, TATA, Tech Mahindra and more.