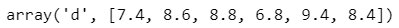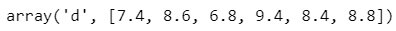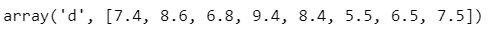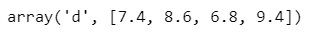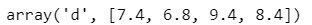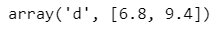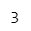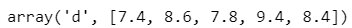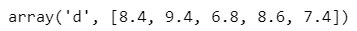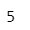How to use Python Array
Python arrays are linear-ordered data structures that store the elements of the same data type at contiguous memory locations. In this article, we will discuss how to use python arrays.
Arrays are fundamental data structures that are used to store the elements of the same data type at contiguous memory allocations. This article will briefly discuss what an array is in Python and how to use them in Python.
Arrays are very similar to the List in Python, but you can store the elements of different data types in the list.
Also Read: Data Types in Python
Also Read: Python List Practice Programs for Beginners
Must Check: Python Online Courses and Certifications
Table of Content
Best-suited Python courses for you
Learn Python with these high-rated online courses
What is Array in Python?
Python arrays are linear-ordered data structures that store the elements of the same data type at contiguous memory locations.
- Arrays are not-built into a data structure
- Array in Python is mutable.
- The index value in the Array goes from 0 to n-1 (where n is the Array’s length).
- Arrays are size efficient
- As they are very compact and take less memory space
- Mathematical operations over NumPy are performed using NumPy
Also Read: NumPy array in Python.
Also Read: What is Python
How to declare Arrays in Python
In Python, you can directly use Array. To use Array, we have to import the array module, i.e.
import array as arr
Once you have imported the array module, you can define your Array.
Syntax:
variable_name = Array (typecode, [elements])
Parameters in Syntax:
- variable_name: name of the variable
- typecode: specifies the data type of elements
- elements: the data you want to store
- Elements in the Array are stored inside square brackets and separated by commas.
Note: For typecode, you can refer to the below table
| Type Code | C Type | Python Type | Size |
| ‘b’ | signed char | int | 1 |
| ‘B’ | unsigned char | int | 1 |
| ‘u’ | wchar_t | Unicode Character | 2 |
| ‘h’ | signed short | int | 2 |
| ‘H’ | unsigned short | int | 2 |
| ‘i’ | signed int | int | 2 |
| ‘I’ | unsigned int | int | 2 |
| ‘I’ | signed long | int | 4 |
| ‘L’ | unsigned long | int | 4 |
| ‘q’ | signed long long | int | 8 |
| ‘Q’ | unsigned long long | int | 8 |
| ‘f’ | float | float | 4 |
| ‘d’ | double | float | 8 |
How to use Arrays in Python
Before starting how to use an array in Python, we will create an array that we will use further in our examples.
Example – 1: Create an array of grades for students.
#create a python array#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
grade
Output
Accessing elements from an Array
Elements in arrays can only be accessed through their indexes.
- Variable_name[index] is used to access the element in an array
- An index must be an integer
Example 2: Access the grade of the third student’s example -1.
#access the third elementgrade[2]
Output
Adding elements to an array
Elements in Arrays can be added using three methods:
- insert ()
insert () is a built-in function that adds one or more elements to an array’s index position.
Example -3: Insert the grade 8.8 at the third position (index = 2)
#import array
import array as arr
#define variable
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
#insert 8.8 at index 2
grade.insert(2, 8.8)grade
Output
- append ()
append (), add only one element at a time at the end of the Array.
Example 4: Add 8.8 at the end of the array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
#add 8.8 at the end of arraygrade.append(8.8)grade
Output
- extend ()
It is quite similar to the append () function but using extend (), you can add an array to the existing Array. The new Array will be merged with the existing Array at the end.
Example 5: Add the grade of three more students
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
grade.extend([5.5, 6.5, 7.5])grade
Output
Removing elements from an Array
Elements in Array can be removed using the:
- pop ()
It will delete the element at any index position. By default, it will delete the last element of the Array.
Example 6: Remove the last element from the array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
grade.pop()grade
Output
- remove ()
It will delete the specified elements from the arrays as it takes an element as a parameter.
- If there are repeated elements, it will delete the first element of the Array.
- remove () function will raise an error if the given element is not present in the Array.
Example 7: Remove 8.6 from the array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
grade.remove(8.6)grade
Output
- del ()
It is used to remove (or delete) more than one element at a time.
Example 8: Remove the third element from the array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])
grade.del(2)grade
Output
Slicing an array
Slicing in Python is used to print an array’s specified range of elements.
- The slicing operation is performed using (:)
Example 9: Access the third and fourth element only
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])grade[2:4]
Output
Searching elements in an Array
We can access the elements in the Array using varibale_name[index], but what if you don’t know the index and want to find the index of any particular elements of an array? Then in that case:
- index () is used to find the index of that element
- For duplicate elements in the Array, then the index () will return the index of the first occurrence of that element.
Example 10: Search the index of the value 9.4
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])grade.index(9.4)
Output
Updating Elements in an Array
If you want to update any existing value in an array, you only have to re-assign a new value.
Example 11: Update the value at the index position 2
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])grade[2]=7.8grade
Output
Reverse an Array
To reverse an array, Python allows using the built-in function name reverse ().
Example 12: Reverse the array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])grade.reverse()grade
Output
How to find the length of an Array in Python
To find the number of elements in the Array, we use a built-in function len (array_name), that returns an integer value.
Example 13: Find the length of an array
#import arrayimport array as arr
#define variable/create Array
grade = arr.array('d', [7.4, 8.6, 6.8, 9.4, 8.4])len(grade)
Output
Application of Arrays:
- Post office boxes
- Contacts on Cell Phones
- Chess Board: Used to store the possible moves
- Matrices: Matrices are simple 2D arrays that are used for image processing.
- A Restaurant menu
Advantages and Disadvantages of Arrays in Python
- Arrays are mutable in nature.
- i.e., we can easily add new elements, delete or update the existing elements.
- Easy access to elements
- The order of Accessing doesn’t matter.
- No issue of overflow or shortage of memory
- As the elements are allocated on contiguous memory locations.
- Stores the elements of the same data type only.
- It doesn’t support random access, i.e., to access any element, you need to know the index of that element.
Conclusion
In this article, we have briefly discussed how to use Python arrays with the help of examples.
Hope you will like the article.
Keep Learning!!
Keep Sharing!!