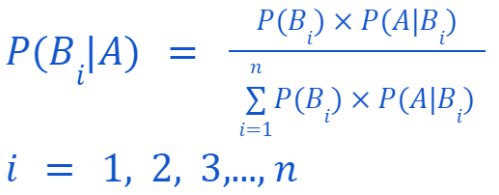Introduction to Bayes’ Theorem
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss one of the most important theorems Bayes’ Theorem which is used in data science and machine learning algorithms like Naive Bayes’ Classifier.
To know about the random variable (continuous and discrete random variables), distributions, read the article on Probability.
Best-suited Machine Learning courses for you
Learn Machine Learning with these high-rated online courses
Table of Content
- Joint Probability
- Marginal Probability
- Conditional Probability
- Bayes’ Theorem
- Generalization of Bayes’ Theorem
- Application of Bayes’ Theorem
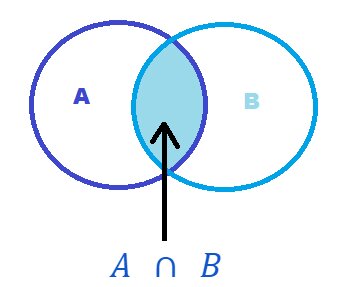
Joint Probability:
Joint probability is the probability of two events A and B, occurring at the same time.
It is given as the probability of intersection of event A and event B.
Let’s understand the joint probability with an example,
Problem Statement:
Probability that number 6 will appear twice when two dice are rolled at the same time.
Solution:
Marginal Probability:
Marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable.
Example:
Conditional Probability:
Let there are two events A and B of any random experiment,
then the probability of occurrence of event A, such that event B has already occurred is known as Conditional Probability.
Mathematical formula of conditional probability is:
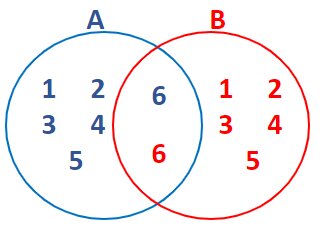
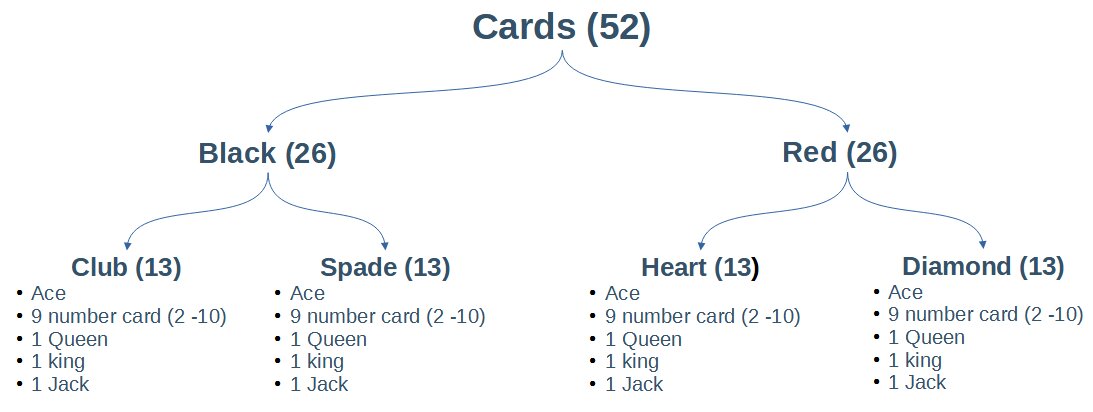
Let’s understand the conditional probability by an example:
Problem Statement: Given that you drew a black card, what is the probability that it is ace.
Solution:
A = drawing ace card
B = drawing black card
Now, we have to find probability of ace, when black card is drawn i.e.
P ( A | B)
Bayes’ Theorem:
Bayes’ theorem is an extension of Conditional Probability.
It includes two conditional probabilities.
It gives the relation between conditional probability and its reverse form.
Let’s understand the formula by an example:
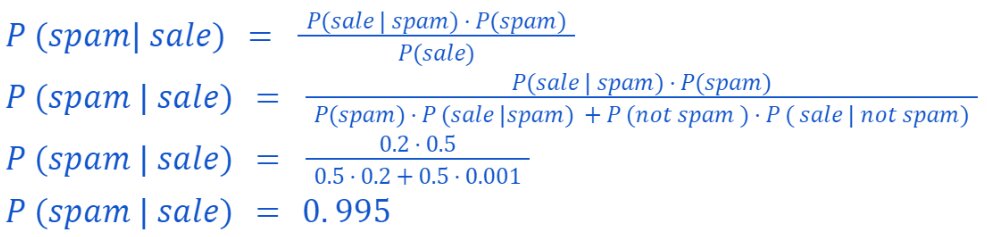
Problem Statement:
A company trained a model to detect the pattern in the words in spam mails.
If model learn a word “sale” which appears 20% of all spam mails.
Assuming 0.1% of non-spam mails include the word sale, and 50% of all mails received by user is spam.
Find the probability that a mail is spam if the word “sale” appears in it.
Solution:
We have:
Now, we have to find the probability that a mail is spam if the word “sale” appears in it
i.e. P (spam | sale)
Now, using Bayes’ Theorem, we get
Before going for Generalization of Bayes’ theorem, let’s understand the “Theorem of Total Probability”
Theorem of Total Probability:
If there is B1, B2, …., Bn be a set of exhaustive and mutually exclusive events and
A is another event associated with Bi, then:
Generalization of Bayes’ Theorem:
If there is B1, B2, …., Bn be a set of exhaustive and mutually exclusive events and
A is another event associated with Bi, then:
Now, let’s use this complicated-looking formula to solve a problem,
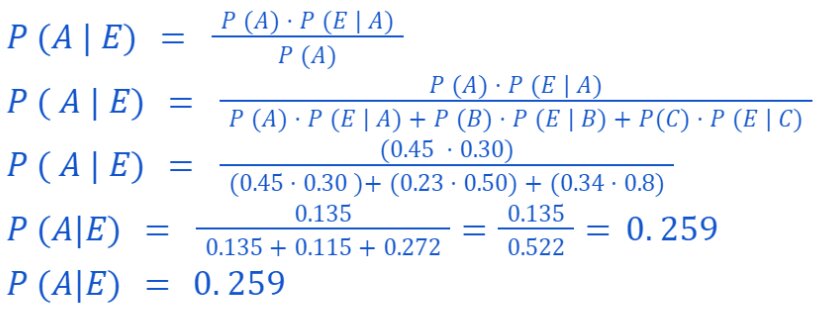
Problem Statement:
There are 3 employees A, B, and C in race to be managers.
Probability of A, B, and D to be managers are 4/9, 2/9 and ⅓ respectively.
Probability that bonus scheme will be introduced if A, B, and C become managers are 3/10, ½, and ⅘ respectively.
If the bonus is introduced, what is the probability that A became manager.
Solution:
We have:
Now, if the bonus has been introduced then the probability that A became manager, i.e. P ( A | E)
Application of Bayes’ Theorem:
- Naive Bayes’ Classifier
- Discriminant Function and Decision Surface
- Bayesian Parameter Estimation
Conclusion:
In this article you will learn about the conditional probability, Bayes’ theorem with examples.
As it has use in most prominent learning techniques today.
Hope this article will help you in data science and machine learning journey.
Frequently Ask Question (FAQ)
Ques 1. What is Joint and Marginal Probability?
Ans 1. Joint Probability
Joint probability is the probability of two events A and B, occurring at the same time.
It is given as the probability of intersection of event A and event B.
Marginal Probability
Marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable.
Ques 2. What is Conditional Probability?
Ans 2: Let there are two events A and B of any random experiment,
then the probability of occurrence of event A, such that event B has already occurred is known as Conditional Probability.
Ques 3. What is Bayes’ Theorem?
Ans 3: Bayes’ theorem is an extension of Conditional Probability.
It includes two conditional probabilities.
It gives the relation between conditional probability and its reverse form.
Top Trending Articles in Statistics:
Skewness In Statistics | Statistics Interview Question | Basics Of Statistics | Measure Of Central Tendency | Probability Distribution | Inferential Statistics | Measure Of Dispersion | Introduction To Probability | Bayes Theorem | P-Value | Z-Test | T-Test | Chi-Square Test | Outliers In Python | Sampling and Resampling | Regression Analysis In Machine Learning | Gradient Descent | Normal Distribution | Poisson Distribution | Binomial Distribution | Covariance And Correlation | Conditional Probability | Central Limit Theorem
FAQs
What is Joint and Marginal Probability?
Joint probability is the probability of two events A and B, occurring at the same time. It is given as the probability of intersection of event A and event B whereas Marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable.
What is Conditional Probability?
Let there are two events A and B of any random experiment, then the probability of occurrence of event A, such that event B has already occurred is known as Conditional Probability.
What is Bayes' Theorem?
Bayesu2019 theorem is an extension of Conditional Probability. It includes two conditional probabilities. It gives the relation between conditional probability and its reverse form.

Vikram has a Postgraduate degree in Applied Mathematics, with a keen interest in Data Science and Machine Learning. He has experience of 2+ years in content creation in Mathematics, Statistics, Data Science, and Mac... Read Full Bio