An Introduction to Human Resource Accounting (HRA)
This post explores the advantages organizations can gain from implementing human resource accounting, such as improved decision-making, better resource allocation, and increased employee motivation.
The value of an organization’s human capital is not only calculated concerning their salaries and benefits. Human resource accounting (HRA) also considers how much money is spent on hiring and training an employee and the employee’s future value to the company. Although not foolproof, HRA is still a useful and frequently used tool among HR departments.
Let us learn more about HRA.
Must read- What is Human Resources?
Content
- What is HRA?
- HRA Definitions
- HRA Methods
- Objectives of HRA
- Importance of HRA
- HRA Models
- Limitations of HRA
Explore HR Courses
What is Human Resource Accounting?
Human resource accounting (HRA) is a type of accounting that seeks to determine the cost and value of the people, also known as human capital, working in an organization.
HRA is an economic indicator of what an organization spends on its human capital. It indicates money spent on recruiting, training, salary and benefits of existing employees in previous months and years.
Best-suited Human Resources courses for you
Learn Human Resources with these high-rated online courses
Human Resource Accounting Definitions
American Accounting Society Committee (1973)
“Human Resource Accounting is the process of identifying and measuring data about HR and communicating this information to interested parties.”
Davidson and Roman L Weil
“HRA describes a variety of proposals that seek to report and emphasize the importance of human resources – knowledgeable, trained and loyal employees in a company earning process and total assets.”
Eric Flamholtz, University of California (1974)
“Human resource accounting is the measurement of the cost and value of the people for the organisation.”
Stephen Knauf (1983)
“HRA is the measurement and quantification of human organizational inputs such as recruiting, training, experience and commitment.”
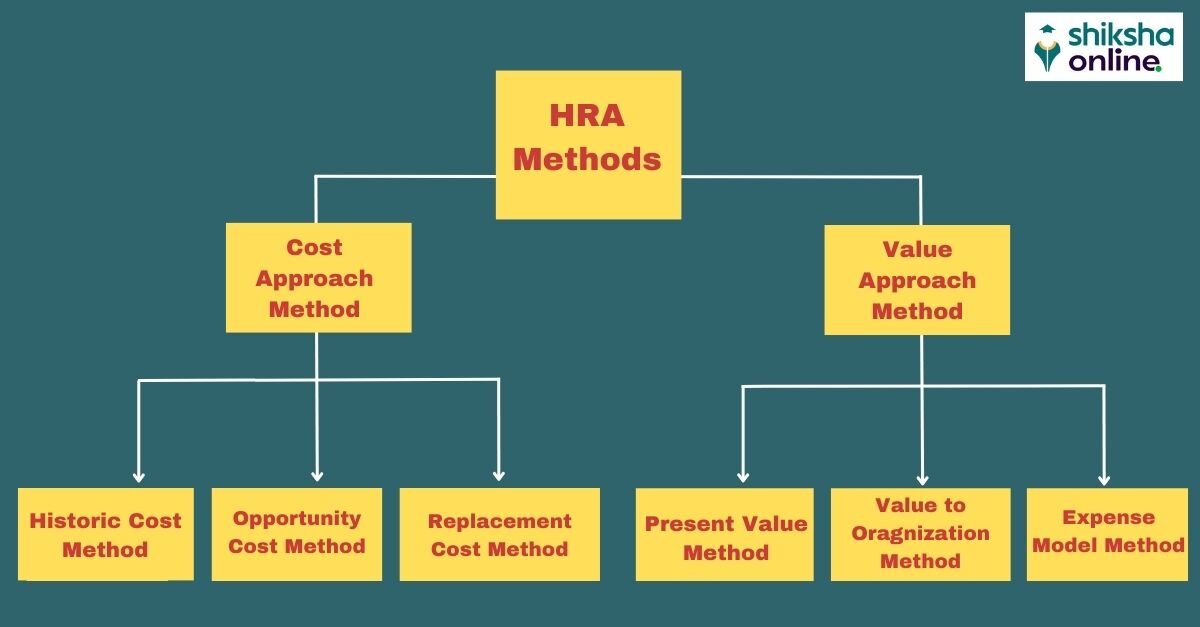
Human Resource Accounting Methods
1. Cost Approach Method
The cost approaches involve the computation of the cost of human resources to the organization. Different cost approach methods include –
- Historical Cost Method – The historical cost method involves calculating the cost incurred by the company in recruiting, training, and developing its employees. This approach is easy to apply but does not reflect human assets’ true value.
- Replacement Cost Method – This method involves estimating the cost of replacing an employee with a similar level of skill and experience.
- Opportunity Cost Method – The opportunity cost method estimates the potential earnings an employee could have earned if they pursued a different career.


2. Value Approach Method
The value of human resources is measured based on the contribution they are likely to make to the organizations during their employment. Different value approach methods include –
- Present Value Method – This method estimates the present value of the future cash flows an employee must generate for the company.
- Value to the Organization Method – In this method, the most valuable employee of the organization is determined and measured whether the organization is earning premium profits from the services of that employee and helps in finding the value of that employee.
- Expense Model Method – This method divides the employees into two categories: Decision-making and decision-execution. It then determines the actual cost incurred in both categories and whether it benefits the organization.


Objectives of Human Resource Accounting
The basic objectives of human resources accounting are:
- Facilitate people management.
- Help management make decisions about acquiring, assigning, developing, and maintaining human resources.
- Provide information to management about the cost and value of human resources.
- Ensure the effective use of human resources.
- Eee if HR produces a return on investment from interested people in the organization.
- Provide accounting details of human resources to people outside the company, such as bankers, financial institutions and creditors, etc.
Check out Free HR Management Online Courses & Certifications
Importance of Human Resource Accounting
Human resource accounting is a good measurement tool to base future hiring, firing, and other changes in staffing needs. It allows forecasting the anticipated value of existing employees and potential future employees. Below are some reasons why human resource accounting is important –
- Facilitates employment management.
- Helps decide transfers, promotion, training and termination of human resources.
- Provides a basis for planning physical assets for human resources.
- Aids in evaluating the expenses made to provide continuous training to employees.
- It helps to identify the causes of high staff turnover at various levels and to take preventive measures to contain it.
- Helps locate the real cause of the poor return on investment, such as inadequate or insufficient utilization of physical assets or human resources.
- It enables understanding and assessing an organization’s internal strength and helps management run the company in the most adverse and unfavourable circumstances.
- Provides valuable information for people interested in long-term company investments.
- Help employees improve their performance and bargaining power.
Related Read – Difference Between Human Capital And Physical Capital
Models of Human Resource Accounting
There are five main HRA models –
The Lev and Schwartz Model
Eugene Lev and Arieh Schwartz developed the Lev and Schwartz Model in 1971, also known as the LS model. The LS model provides a useful framework for understanding the trade-offs in a company’s capital structure decisions. By considering the costs and benefits of debt and equity financing, companies can make informed decisions about financing their operations and investments to maximize shareholder value.
The Eric Flamholtz Model
The Eric Flamholtz Model was developed by Eric Flamholtz in 1996. This model provides a useful framework for organizations to assess the value of their human capital investments and develop strategies for maximizing their ROI. Organizations can leverage their human capital to achieve greater performance and success by aligning human capital investments with business goals and creating a conducive organizational culture.
Morse Model
Richard Morse, a professor of accounting at the University of Southern California, developed the Morse model. It is a theoretical framework to assess the value of an organization’s human capital and develop strategies for maximizing its potential.
Likert Model
The Likert model helps to assess the value of human capital by measuring the degree to which employees are aligned with the organization’s goals and values. The model suggests four key factors influencing employee alignment: job satisfaction, motivation, leadership, and communication.
Ogan’s Model
The Ogan model was developed by Pekin Ogan (1976) and is based on two components: individual knowledge and organizational knowledge within a business. According to the Ogan model, the value of human capital can be assessed by measuring the contribution of individual and organizational knowledge to the organization’s performance and success.


Limitations of Human Resource Accounting
While human resource accounting has numerous advantages, there are also limitations to this approach –
- Subjectivity: HRA relies on subjective assessments of employees, which can lead to consistency in measuring human capital. Personal biases can influence these assessments, which can affect the accuracy of the data collected.
- Difficulty in measuring intangible factors: HRA sometimes does not measure intangible factors such as employee motivation, job satisfaction, and organizational culture. These factors play a significant role in the productivity and success of an organization, but they are difficult to quantify.
- Time-consuming: Measuring and evaluating human resources can be time-consuming, requiring extensive data collection and analysis, particularly for organizations with limited resources.
- High cost: Human Resource Accounting requires specialized software and trained professionals, which can be expensive for SMEs.
- Lack of universal standards: There are no universal standards for Human Resource Accounting, which can make it challenging to compare the results of different organizations.
- Focus on short-term benefits: HRA often focuses on short-term benefits, such as productivity and profitability, rather than long-term benefits, such as employee development and retention.
FAQs
How is human capital measured in Human Resource Accounting?
Human capital is typically measured in terms of the costs incurred in recruiting, training, and developing employees and their current and potential future contributions to the organization.
Can Human Resource Accounting be used for financial reporting?
While HRA is not a standard financial reporting method, some organizations include human capital information in their annual reports to provide stakeholders with insights into the value of their workforce.
What are the benefits of implementing Human Resource Accounting?
Benefits of Human Resource Accounting include improved resource allocation, enhanced talent management, better workforce planning, and a more accurate assessment of an organization's overall worth.
Are there any limitations to Human Resource Accounting?
Limitations of Human Resource Accounting include the difficulty of accurately quantifying the value of human capital, the subjectivity involved, and the challenges of predicting future contributions.
Can Human Resource Accounting help measure HR initiatives' return on investment (ROI)?
Yes, HRA can help calculate the ROI for various HR initiatives, such as training programs or talent acquisition efforts, by quantifying the costs and benefits associated with these initiatives.

Rashmi is a postgraduate in Biotechnology with a flair for research-oriented work and has an experience of over 13 years in content creation and social media handling. She has a diversified writing portfolio and aim... Read Full Bio