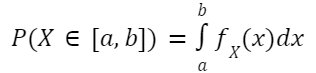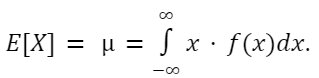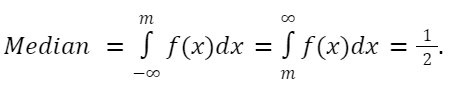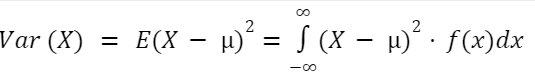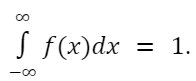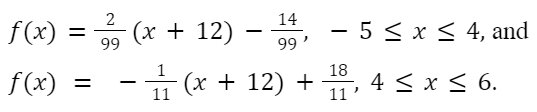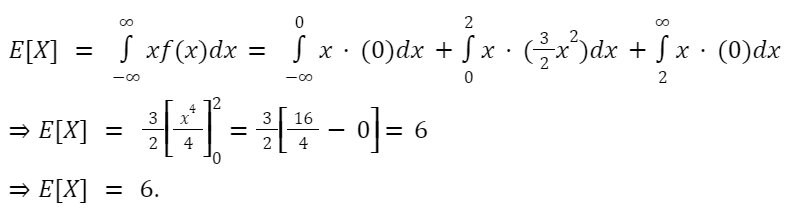Probability Density Function: Definition, Properties, and Application
Probability Density function describes the probability distribution of the continuous random variable. In this article, we will briefly discuss what is probability density function, its properties, its application, and how to calculate it.
Probability distribution represents all the possible values that a random variable can take, and we know there are two random variables: Discrete and Continuous random variables. The probability density function and probability mass function describes continuous and discrete probability distributions, respectively. This article will briefly discuss the probability density function, its properties, how to calculate it, and its application.
Table of Content
Best-suited Machine Learning courses for you
Learn Machine Learning with these high-rated online courses
What is Probability Density Function (PDF)
The probability Density Function or PDF describes a probability distribution of a continuous random variable.
The PDF of any continuous random variable X is a function fX: R -> [0, inf) such that,
for any interval [a, b] in R.
- It takes the values in a given interval, i.e., is equal to the integral of its PDF over the given interval.
- The PDF function is like a bell-shaped curve, and the probability of the outcome lies below the curve.
- Distribution Functions using PDF: Weibull Distribution, Lognormal Distribution, Exponential Distribution, Gamma Distribution, Uniform Distribution, and Beta Distribution.
Mean, Median, and Variance of PDF
Mean
The mean of the probability distribution function of a continuous random variable is given by:
Median
Median divides the PDF curve into two equals halve, let the PDF has a median at x = m, then:
Variance
Variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean.
Related Read – Probability and Non Probability Sampling
Properties of Probability Density Function
- It is the differentiation of the cumulative distribution function.
- The value of PDF is always greater than or equal to zero for all real numbers i.e., f(x) >= 0.
- Total area under the PDF curve is always equal to one.
- PDF curve is always continuous over the entire range.
- Median divides the PDF curve into two halves.
Example – 1: Let X be a continuous random variable with the PDF given by:
Find the probability between 3 and 5.
Answer:
Example – 2: Let X be a continuous random variable and the following PDF:
fX(x) = ce-x, x >= 0, otherwise 0
where c is any positive constant.
Answer – 2: As we know the total area under the curve is equal to one (from property – 3), i.e.,
Example – 3: Find the mean of the given PDF.
f(x) = (3/2)x2, 0 <= x< = 2, and 0 otherwise.
Answer – 3:
| Programming Online Courses and Certification | Python Online Courses and Certifications |
| Data Science Online Courses and Certifications | Machine Learning Online Courses and Certifications |
Joint Probability Distribution Function
The joint probability distribution is nothing but denotes the probability distribution of two or more continuous random variables that together form a continuous random vector.
- For a joint PDF, both the random variables are jointly continuous.
- Calculation of joint PDF involves multiple integrals.
Application of Probability Density Function
- Use to simulate the combustion of a diesel engine.
- It is used to represent the annual data of atmospheric NOx temporal concentration.
- It is used in machine learning algorithms, analytics, probability theory, neural networks, etc.
Conclusion
Probability Density function describes the probability distribution of the continuous random variable. In this article, we have briefly discussed what is probability density function, its properties, its application, and how to calculate it.
Hope this article, help you to clear your all doubts regarding Probability Density Function.
Top Trending Article
Top Online Python Compiler | How to Check if a Python String is Palindrome | Feature Selection Technique | Conditional Statement in Python | How to Find Armstrong Number in Python | Data Types in Python | How to Find Second Occurrence of Sub-String in Python String | For Loop in Python |Prime Number | Inheritance in Python | Validating Password using Python Regex | Python List |Market Basket Analysis in Python | Python Dictionary | Python While Loop | Python Split Function | Rock Paper Scissor Game in Python | Python String | How to Generate Random Number in Python | Python Program to Check Leap Year | Slicing in Python
Interview Questions
Data Science Interview Questions | Machine Learning Interview Questions | Statistics Interview Question | Coding Interview Questions | SQL Interview Questions | SQL Query Interview Questions | Data Engineering Interview Questions | Data Structure Interview Questions | Database Interview Questions | Data Modeling Interview Questions | Deep Learning Interview Questions |