Is Blockchain Security Strong Enough For Banks?
Can we trust blockchain protection for a crucial and significant industry like Banking and Finance? Even if we can, exactly how secure is blockchain security for the banking sector? Let’s dig in to find out the answers to the above questions.
- Introduction
- How can Blockchain security protect Banks?
- What is Blockchain Technology?
- Is Blockchain only a Public Ledger?
- What is Blockchain security?
- What does cryptographically secured mean?
- The impact of Blockchain security on the Banking Sector
Introduction
The immense potential of digitization relieved workers. Moreover, it enhanced the working standards today. Digital tools and services made our lives more comfortable than ever before. From ordering groceries online to making financial transactions, every essential task has become effortless now.
However, ease sometimes compromises security, ownership, and privacy. With the growing usage of the online ecosystem, for instance, social media platforms for payments and transactions have unconsciously invited more cybercrimes.
- According to Allianz, with the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic. The number of cyberattacks rose by 200%.
- In the financial sector specifically, cyberattacks have increased by 238% globally since February 2020.
- According to the Business Standard reports, India crossed over 2.9L cyber security incidents related to digital banking in 2020.
The above alarming reports not only state the facts but also raise the concerns about strengthening the current security measures.
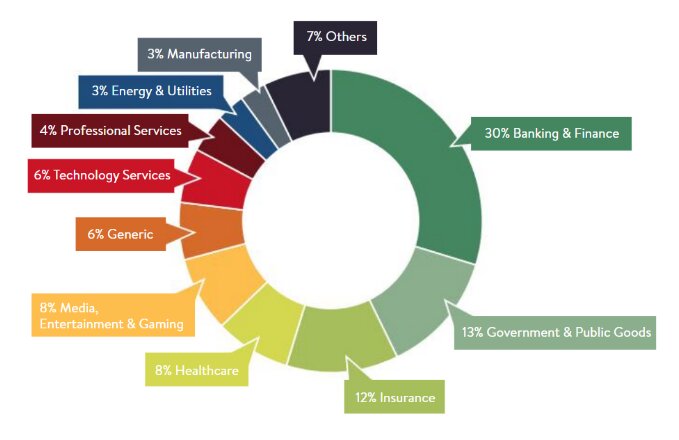
However, according to the Report by Global Blockchain Benchmark Study. The Finance and Banking sector uses blockchain the most among other sectors.
Best-suited Blockchain courses for you
Learn Blockchain with these high-rated online courses
How can Blockchain security protect Banks?
Almost every bank maintains a centralized system to store massive customer information and transaction records. Hence, it becomes easy to tamper, steal or corrupt the data files. With hackers being more resilient than ever. The banking sector needs a robust and highly secured solution.
We require a decentralized tamper-proof solution for the banking industry. Hence, Blockchain technology steps in as a potential solution to security issues. Let’s begin by understanding how Blockchain security could become a reliable remedy for cybersecurity attacks?
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain helps create a decentralized database with a Peer-to-Peer (P2P) connection. This means there will be no centralized party to control the database. Blockchain is basically a public registry of who owns what and who transacts what to whom? It provides an efficient way to work with several parties without trusting each other. The term distributed ledger technology (DLT) underpins blockchain can enable financial institutions to regulate governance around data sharing.

Moreover, The decentralized ledgers in blockchain are immutable. This means records can’t be changed or modified later. The network stores each transaction as history data. It supports an append-only ledger of records that will be added to the chain later. Therefore, storing customers’ details and transaction records on a decentralized network makes sharing information among different parties easier and more secure.

Is Blockchain only a Public Ledger?
Let’s dig more into the privacy and security part of blockchain technology adoption. We all heard that blockchain is characterized as a public ledger commonly. However, not all blockchain networks are necessarily public.
Blockchain infrastructures are broadly categorized into three types: Public, Private, and Consortium.
- Public blockchain as the name suggests is open and permission-less like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- In contrast, a Private blockchain is a closed, trusted, and permissioned system that stays among a few institutions which don’t allow external members. For instance, private organizations and Banks use a private blockchain.
- Consortium blockchain on other hand is shared permissioned. This means external members require permission to join the network like companies and government regulators together.
What is Blockchain Security?

The connection between blocks makes transactions traceable and verifiable using backtracking. It also ensures non-repudiation. This means by the concept of digital signing no one can deny their transactions.
In Addition, as blockchain is a distributed network, each node or system in the network stores the exact same copy of the data record. So, even if someone tries to tamper with the records on one copy. There will be numerous other copies to mark down the tampered data. This consistent behavior among nodes instantly checks and corrects the tampered record.
Coming back to blockchain security, even when we say blockchain is a public network. It requires high computation to forge a block in the network. Each block requires proving its worth to the network. That means it has to cross the threshold Validity level to achieve the approval of the network.
Above all, the mechanism to keep the distributed network aligned, connected, and collectively decide on calling a block valid is called Consensus. It ensures the synchronization of the network. A few of the popular consensus protocols are Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake(PoS), and Proof-of-History (PoH). Blockchain has a random “difficulty level” setting managed by their consensus protocol. This signifies how hard it is to mine or forge a block in the network.
What does Cryptographically Secured Mean?

For instance, if a hash function produces N bits of output. An attacker needs to compute 2^(N/2) hash operations on random input to search for the second match of the output. Hence, for every 256 hash functions, the attacker needs to compute 2^128 hash operations. Even if one computation takes 1 microsecond, it will require approximately 10^25 years to match the output. This is the level of difficulty and complexity which ensures the security of blockchain as a network.

The impact of Blockchain Security on the Banking Sector
- Blockchain solutions eliminate middle parties which result in cost reduction and high transaction speed.
- Immutability feature of blockchain reduces the fraud attacks and enables transparency.
- The distributed ledger and consensus mechanism ensures data consistency across the network.
- Reduces manual processing for data validation and reconciliation.
- Maintains automated audit trails for the transactions.
- Enhance the customer experience with real-time trade settlements.
- Doesn’t rely on trusting another party, which increases the trust and transparency in the system.
- Smart contracts allow parties to process automated constraints and business rules, which maintain authenticity.
- Help banks to automate financial reporting and raise compliance actions.
Therefore, These are a few of the assessments to establish grounds for Blockchain applications in the Finance and Banking sector.

In Conclusion
Blockchain is moving forward to disrupt and revolutionize the banking sector. Moreover, the technology seems confident and promising to resolve the current banking issues and limitations. Blockchain worldwide enthusiasm has even motivated the government to acknowledge its use cases. Also, to establish new regulations in favor of the technology. Let’s see how this technology can improve cross-border payments, trade finance, and capital markets in the future.
Recently completed any professional courses/certification from the market? Tell us what you liked or disliked in the course for more curated content.
Click here to submit its review with Shiksha Online.
FAQs
What are other the Consensus mechanisms used for Blockchain Security?
1. Proof-of-Work (PoW) 2. Proof-of-Stake (PoS) 3. Proof-of-Elapsed Time (PoET) 4. Proof-of-History (PoH) 5. Proof-of-Activity (PoA) 6. Proof-of-Burn (PoB)
Is Blockchain security 100% tamper-proof?
No technology can assure 100% solution to the security problem. Blockchain is one of the stepping stones to make the system or network as secure as possible.
What are the possible scenarios where Blockchain security can be hacked?
1. A 51% Attack 2. Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks 3. Bugs in the Smart Contract 4. Sybil Attack 5. Routing attack 6. Wormhole attack
What does non-repudiation mean in Blockchain Security?
It means by the concept of digital signing no one can deny their transactions.
This is a collection of insightful articles from domain experts in the fields of Cloud Computing, DevOps, AWS, Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, and Natural Language Processing. The range of topics caters to upski... Read Full Bio