Logical Function in Tableau
In Tableau, many functions are used in Tableau Calculation. This article will discuss Logical Functions and how to create them in Tableau.
Table of Content
Best-suited Tableau courses for you
Learn Tableau with these high-rated online courses
Why use Logical Function?
Logical functions in tableau allow finding whether the given condition is True or False (Boolean Function).
Let’s understand with the help of an example:
From the Sample Superstore data, list all the subcategories whether they are profitable or loss-making. The subcategories are classified as profitable if the Profit > 0.
Then we can use the formula:
Tableau offers various logical functions like IN, AND, IF, ELSE, OR, etc.
Now, we will see how to create a logical calculation in Tableau.



Must Check: What is Tableau?
Must Check: Tableau Online Courses & Certifications
Create a Logical Calculation
We will understand how to create logical calculations with the help of an example using Sample Superstore data.
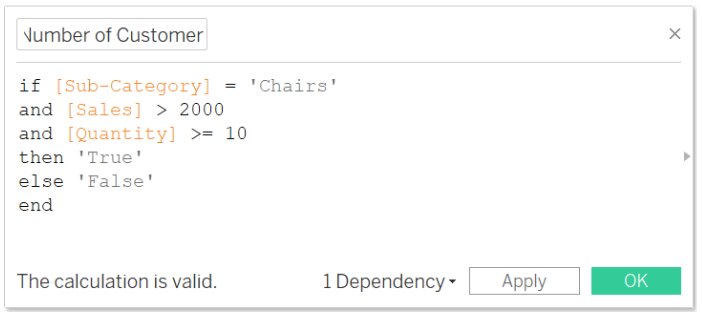
Problem Statement: Find the number of customers who spend $2000 on the ‘Chair’ Subcategory and purchased more than 10 items.
Steps to Create:
- Connect the Sample Superstore data
- Select Analysis -> Create Calculated Fields
- Enter the name “Number of Customers”
- Write the formula
Note: In the above formula we used the IF-ELSE condition with AND condition. In True we get the number of customers who are satisfying the given condition while in False we will get the number of customers who are not satisfying the above condition.
The formula will show the number of customers who satisfies the above conditions as True
- Click OK
- The new calculated field (Number of Customers) appears in Data Pane under the dimension
- Drag and Drop Number of Customers in Row shelf
- Drag and Drop Customer Name to Text in the Mark Pane
- Right-click on Customer Name in the Mark Pane
- Select Measure -> Select Count Distinct
- Right-click on Customer Name in the Mark Pane
From the above, we get the number of customers who are satisfying the given condition is only 2.
Logical Function available in Tableau
IN
- It will return the TRUE if any value in the first expression is in the second expression
- Syntax: <expression 1> IN <expression 2>
- Example
This expression return TRUE, if SUM(Sales) matches value.
AND
- It is used to perform logical conjunction between two expressions
- Similar to the intersection in mathematics
- It will return TRUE if both the conditions (expressions) are TRUE otherwise return FALSE
- Syntax: <expression 1> AND <expression 2>
- Example:
This expression will return TRUE if both the conditions are satisfied otherwise return FALSE.
OR
- It is used to perform logical disjunction between two expression
- Similar to the union in mathematics
- It will return TRUE if one of the expressions is TRUE otherwise FALSE
- Syntax: <expression 1> OR <expression 2>
- Example:
This expression will return TRUE if either of the conditions are satisfied otherwise return FALSE.
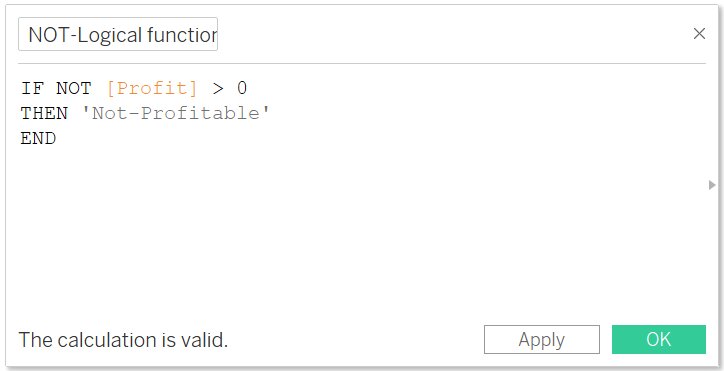
NOT
- It will return the opposite of the given expression
- It will return FALSE if we input TRUE and will return TRUE if we input FALSE
- Syntax: NOT (expression)
- Example:
This expression will return Not-Profitable, if profit is less than zero.
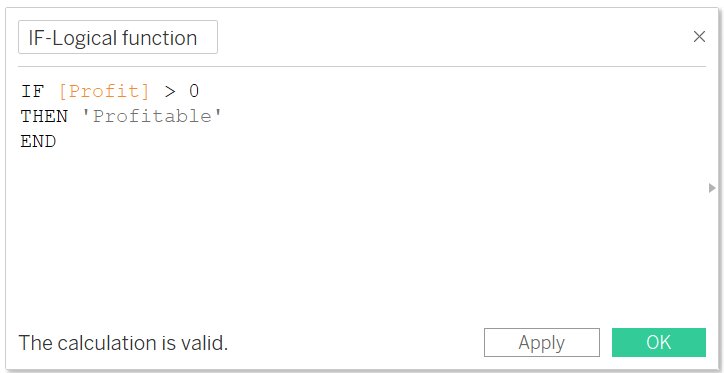
IF
- It is used to test the series of expressions returning then value for the first TRUE expression
- It is one of the useful decision-making function
- Syntax: IF <expr> THEN <expr> END
- Example:
The above expression return TRUE, if the profit is greater than zero.
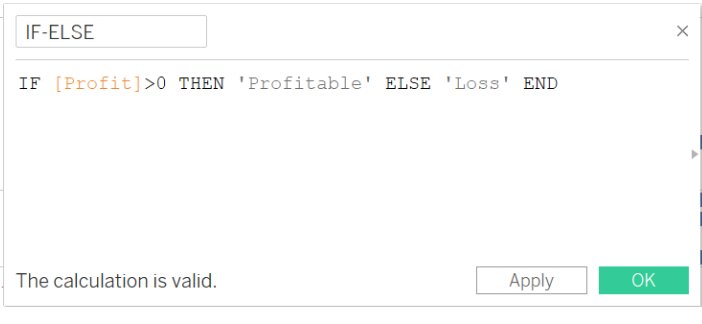
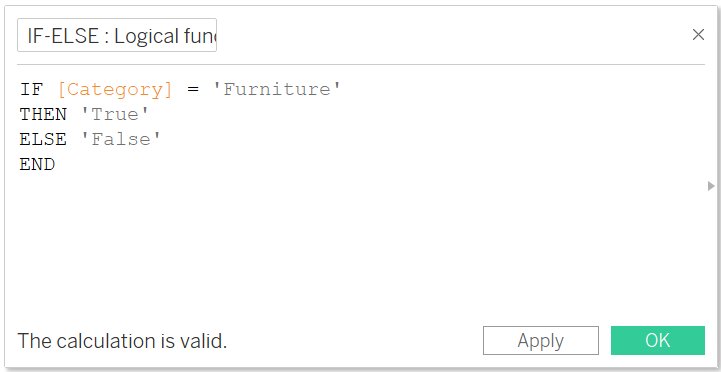
IF-ELSE
- It is used with the IF and will return the expression if the condition under IF is not satisfied
- Syntax: IF <expression> THEN <statement> ELSE <statement> END
- Example:
The above expression will return TRUE if category is Furniture otherwise will return FALSE.
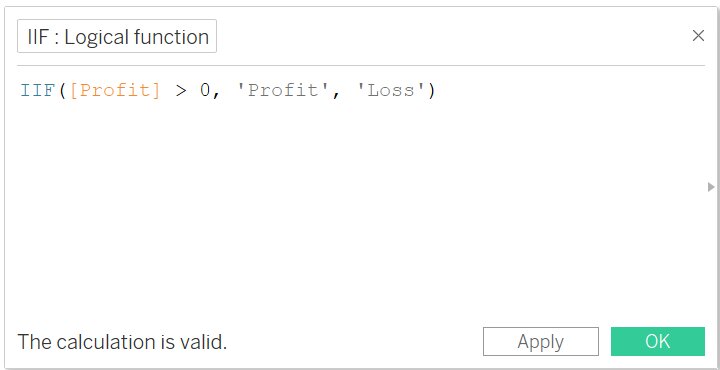
IIF
- It is a simple version of IF-ELSE function
- If both the conditions are TRUE, it will return the first statement otherwise the second function
- Syntax: IIF (expression, TRUE_statement, FALSE statement)
- Example:
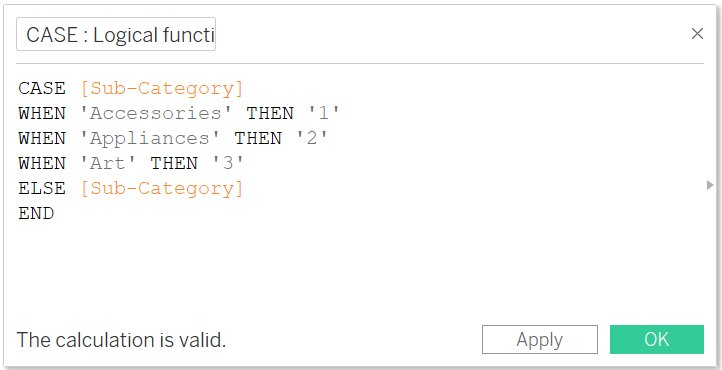
CASE
- It is used to perform to perform logical tests and will return the required value, when the test expression is TRUE
- Syntax:
CASE [<expression>]
WHEN <value 1> THEN <return 1 >
WHEN <value 2> THEN <return 2>
……….
ELSE <retrun>
END
- Example:
The above function will return 1, 2, and 3 when the corresponding entries from sub-categories are mentioned.
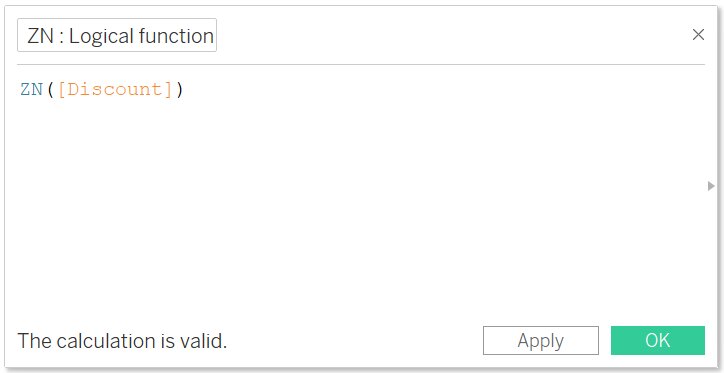
ZN
- It will return the expression if it is not NULL, otherwise, it will return zero
- Syntax: ZN (expression)
- Example:
The above expression will change the null value to zero if we have any null entry in discount.



Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed different logical functions in tableau with the help of examples. We also discussed how to create Logical Function in Tableau.
Hope this article, will help you in your data analytics journey.
Top Trending Articles:
Introduction To Tableau | Products Of Tableau | Data Types In Tableau | Change Data Type In Tableau | File Type In Tableau | Data Aggregation | Connecting Data In Tableau | Dimension And Measure | Tableau Show Me | Joins In Tableau | Union In Tableau | Operators In Tableau | Number Functions In Tableau | String Functions In Tableau | Filter In Tableau | Context Filter In Tableau | Filters In Tableau | Types Of Charts In Tableau | Bar And Line Chart In Tableau | Pareto Chart In Tableau | Gantt Chart In Tableau | Box And Whisker Chart In Tableau | Waterfall Chart In Tableau | Donut Chart In Tableau | Funnel Chart In Tableau | Dual Axis Chart In Tableau | Sort Data In Tableau | Tableau Sets | Groups In Tableau | Tableau Hierarchy | Tableau Forecasting | Highlighting In Tableau | Word Cloud In Tableau | Cohort Analysis In Tableau