What is the OSPF Protocol?
Have you ever considered how network devices, such as routers, can determine the best (shortest) path for data travel from one device to another? It is because of the OSPF protocol.
OSPF full form is Open Shortest Path First protocol. It is a routing protocol used in computer networks to determine the shortest path for data to travel from one device to another. Routers mainly use this protocol in organizations having large networks. OSPF protocol is preferred as it can easily handle different types of network topologies that are quite complex.
You can also explore: What Is A Network Protocol? Working and It’s Type
Before diving deeper into the article, let’s first go through the list of topics under the table of contents (TOC) that we will cover in this article. Here’s the table:
Table of Contents (TOC)
- What is the OSPF Protocol?
- What are OSPF Protocol Areas?
- How Does OSPF Protocol Work?
- Types of Links in OSPF Protocol
- Types of OSPF Protocol Packets
- Types of Open Shortest Path First States
- Conclusion
What is the OSPF Protocol?
OSPF Protocol Definition: It is a routing (Interior Gateway Protocol) protocol used in computer networks to help routers exchange information about the “best” (shortest) paths for data to travel between devices.
The OSPF protocol uses various metrics, such as network traffic, device availability, etc., in order to determine the shortest and most efficient routes. This protocol type is often in large enterprise networks comprising n number of routers and complex network topologies. This protocol is preferred as it can handle these situations well while ensuring that data is delivered quickly and reliably across a network.
Best-suited Networking courses for you
Learn Networking with these high-rated online courses
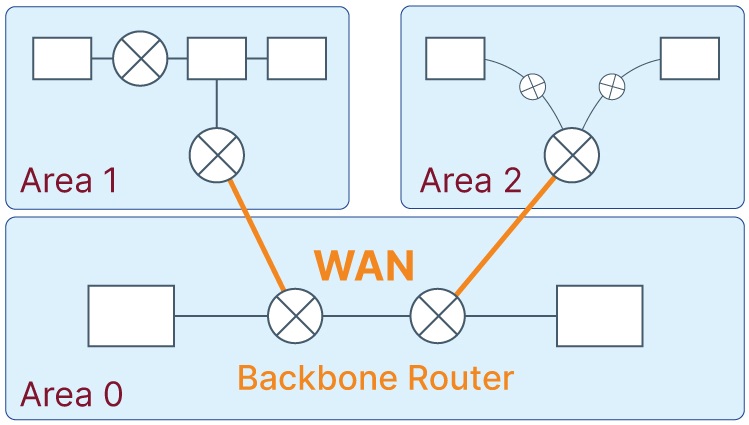
What are OSPF Protocol Areas?
OSPF protocol divides a network’s autonomous system into smaller areas to avoid high traffic caused by flooding. These areas can consist of hosts, routers, and networks.
In a divided area, there are special routers known as Area Border Routers (ABRs), which are located at the borders of an area. These routers summarize the entire information of an area and share it with other areas. Thus, ABRs play an essential role in reducing the amount of traffic that needs to be flooded across the network.
All divided areas of an autonomous system are connected to the backbone router, which acts as a central hub for the entire network. The primary purpose of the backbone is to enable communication between different areas. Without the backbone router, the different areas of the autonomous system would not be able to communicate with each other, and the network would not function correctly.
How Does OSPF Protocol Work?
The working OSPF protocol is not complex to understand. In order to understand them in a better way, let’s divide it’s working into three steps, such as:
- The first step is for two routers connected and running OSPF to become neighbours. This means they establish a relationship that allows them to exchange information about their network topology.
- Once the two routers have become neighbours, they exchange information about their Link State Database (LSDB). The LSDB contains information about the router’s network and the links that connect it to other devices. This information is used to build a map of the network’s topology.
- After exchanging LSDB information, the routers calculate the best route to a destination using the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm. The router selects the best path to add to its routing table and sends the data along that path. This process is repeated for each destination on the network.
Types of Links in OSPF Protocol
OSPF protocol has four types of links that are used to connect routers in a network, such as:
- Point-to-Point Link: This link connects two routers directly without any host or router.
- Transient Link: It is a connection between multiple routers in a network. There are two types of transient links: realistic and unrealistic.
- Unrealistic topology: In this, all routers are connected. This setup is not practical in real-world networks.
- Realistic topology: In this, one router is designated as the main connection point for all the other routers in the network.
- Stub Link: This link connects a router to a network with no other routers. The network has only one router for data entry and exit.
- Virtual Link: This link connects two routers if the link between the two routers is broken. Network administrator between two routers creates this type of link.
You can also explore, these courses:
Types of OSPF Protocol Packets
There are five types of OSPF Packets, such as:
- Hello packet: A Hello packet is used to check if routers can communicate with each other and establish a connection. It’s sent when routers need to become neighbours.
- Database Description: Once routers are connected, a router communicating with another router for the first time sends information about the network to the other router. This helps the other router update its information about the network’s structure.
- Link-state request: When one router needs information about another router’s connection to the network, it sends a link-state request to the other router. The other router responds by sending the requested information.
- Link-state update: A router can use a link-state update to inform other routers about the state of its connections to the network. This is useful when a router wants to broadcast changes to its connections.
- Link-state acknowledgement: Each time a router sends a link-state update to other routers, it waits for a link-state acknowledgement. This helps make the routing more reliable by confirming that other routers received the update.
You can also explore: What Is Data Migration and Its Types?
Types of Open Shortest Path First States
When using the OSPF protocol, a device goes through different states to establish a connection with another router, such as:
- Down: The device is not yet communicating with the other router.
- Init: The device has received a HELLO packet from the other router.
- 2WAY: Both routers have received each other’s HELLO packets, and a connection is established.
- Exstart: The routers begin to exchange information and select a master and slave based on their IDs.
- Exchange: The routers exchange a list of information about the network.
- Loading: The routers exchange more information about the network, such as Link State Advertisements.
- Full: The routers have exchanged all the necessary information and are fully connected.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored what OSPF protocol is in networking. We have also explored its working, types of states, links, packets, etc., in great detail. If you have any queries related to the topic, please feel free to send your queries to us in the form of a comment. We will be happy to help.
Happy Learning!!

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio