PaaS in Cloud Computing
This article presents a comprehensive view of PaaS in cloud computing, including what is PaaS, PaaS architecture, the benefits of PaaS, and PaaS providers.
The business world has migrated to the “cloud” over the past ten years. To put it another way, businesses have been implementing cloud-based computing architecture to ease operational burdens, save time, save costs, and boost productivity. Third-party cloud service providers often provide cloud computing services, enabling remote application operability and high internet availability. This is especially accurate when employing a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), one of the many cloud computing service models.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) plays a critical and expanding role in cloud computing, just as cloud infrastructure, cloud migration, and cloud services in general do. PaaS, however, has so many advantages of its own that it’s worth highlighting for both the software development environment and the organizations that employ it.
In the article, we will go through the below pointers to understand PaaS in more detail-
- What is Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)?
- How does PaaS work?
- Architecture of PaaS
- Different types of PaaS
- Benefits of PaaS
- Disadvantages of PaaS
- Popular PaaS providers
What is Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)?
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) is a model for delivering cloud services where a third-party cloud service provider sends users some hardware and software tools over the internet, frequently those required for hosting or developing applications.
Must Read – Introduction to Cloud Computing
Now let me explain some characteristics of PaaS to you-
- It provides a development environment that is browser-based. The developer can use point-and-click tools or an Application Programming Interface to construct databases and change application code.
- Web service interfaces, scalability, and security are all included with PaaS.
- For creating a workflow, approval procedures, and business rules, PaaS offers built-in capabilities.
- On the same platform, PaaS is simple to integrate with other apps.
- Additionally, PaaS offers web service interfaces that let us integrate applications running on different platforms.
To cut this long story, allow me to break this to you for better understanding-
- To support the web application life cycle, PaaS consists of –
– infrastructure (servers, storage, and networking)
– platform (middleware, business intelligence, database management systems, development tools, and more).
- These hardware and software tools are available for pay-per-use from cloud service providers.
- Back-end scalability is handled by the cloud service provider in PaaS, so end users are relieved of the responsibility of maintaining the infrastructure.
From this, we can infer that the PaaS model gives users access to software and hardware that can be used to create and operate applications without them having to buy, set up, and maintain the infrastructure.
You May Like – Load balancing in cloud computing
Best-suited Cloud Computing courses for you
Learn Cloud Computing with these high-rated online courses
How does PaaS work?
Adopting a SaaS solution means a business is choosing to outsource their whole technological stack, along with the maintenance expenditures that go along with it, to a third-party vendor. PaaS in Cloud Computing, in contrast, often does not replace a company’s whole IT infrastructure; instead, it enables companies to access important services with low startup costs and accelerated deployment times.
Users typically use web browsers to access the services. PaaS can be used to supply services like Java development and application hosting through public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Related Read – Evolution of Cloud Computing
Architecture of PaaS in Cloud Computing
The PaaS architecture primarily consists of three elements:
- Virtual computers, firewalls, networking, storage, and the operating system make up the cloud infrastructure. Applications are developed, managed, and deployed using software tools.
- Workload monitoring is made easier by the GUI (Graphical User Interface) across the whole lifecycle of apps.
Using the online GUI within the PaaS architecture, application developers may test, collaborate, create, develop, and roll out programs from anywhere. Teams may expedite operations and work on several development projects at once thanks to the GUI, or Graphic User Interface.
Different types of PaaS in Cloud Computing
PaaS solutions come in a variety of forms, each with a unique set of features. Let’s look at some of the most noteworthy PaaS types-
Public PaaS
This type is frequently the simplest and least expensive method to begin using PaaS. It is frequently pre-built with a large variety of components and services, which makes it perfect for quickly creating and deploying applications.
Private PaaS
Private PaaS is a service provided by a single entity, like a business or university. This kind of PaaS is often more expensive than open-source PaaS, but it offers a number of advantages, such as improved performance, more security and privacy, and control over the features and services provided.
Hybrid PaaS
Hybrid PaaS combines public and private cloud computing services. When you need to develop and deploy applications fast, this kind of PaaS allows you the freedom to utilize both on-premises and off-premises resources.
Communications PaaS-
Developers can include real-time communication functions, including phone and video calls, text messaging, and file sharing, to their applications using the Communications PaaS (CPaaS) or Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS).
Mobile PaaS-
Mobile Platform as a Service (mPaaS) enables developers to create, manage, and deploy mobile applications quickly.
Open PaaS-
Open PaaS is a subset of PaaS that is built on an open-source platform. This kind of PaaS often costs less than other kinds of PaaS and offers a variety of advantages, such as more freedom and control over the features and services provided.
Integration PaaS-
Organizations may rapidly and cheaply interface their applications with other apps and data sources thanks to the integration platform as a service (iPaaS).
Must Read – Cloud Computing Project Ideas
Benefits of PaaS
The following is a summary of some of the most noteworthy benefits of using PaaS.
- Reduced time to market:
PaaS options provide a variety of pre-built parts and services that can hasten the creation of applications.
- Increased developer productivity:
By freeing up their time from managing and configuring the platform infrastructure, developers are better able to concentrate on writing code and creating apps.
- Increased flexibility and scalability:
PaaS solutions are flexible and scalable, making it simple to deploy applications rapidly.
- Cost savings:
Businesses can avoid the up-front costs associated with buying and maintaining their own hardware and software infrastructure by choosing a PaaS solution.
- Instant community:
PaaS vendors typically offere online communities so that developers may acquire ideas, exchange experiences, and get help from others.
Disadvantages of PaaS?
Despite all of its benefits, PaaS software still has some drawbacks that users and enterprises must be aware of before deciding to utilize it.
- Lock-in of vendors:
Application migration to another PaaS vendor would be problematic since one must write applications in accordance with the platform supplied by the PaaS vendor.
- Data Security:
Corporate data is private, regardless of whether it is important or not, so there may be a privacy risk if it is stored outside of the boundaries of the business.
- Integration with the different applications in the system:
Some applications might be local while others might be in the cloud. Therefore, there is a potential that complexity would increase if we want to combine local data with cloud data.
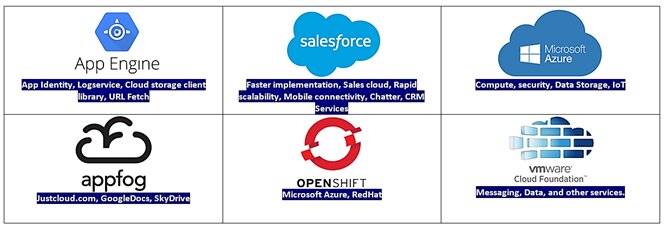
Popular PaaS providers
The PaaS architecture includes tools that enable businesses to access platforms for Business Process Management (BPM), analyze the data, update databases, and add communication features.
Below are of some well-known PaaS providers along with the services they provide.
These are some further PaaS offerings:
- Collaboration within the development team
- application development
- testing, and deployment
- web service integration
- data security, and database integration
In a Nutshell
Fast-moving, highly adaptable settings that can make changes right away are what propel today’s enterprises forward. In such a structure, platform as a service is appropriate. Utilizing cutting-edge tools and software equipment enables businesses to create unique applications and solutions. Fundamentally, adopting a PaaS prevents the need to reinvent the wheel and makes use of already established procedures. This indicates that developers do not need to code everything from scratch. They can simply plug and play with the pre-built, reusable blocks that the PaaS vendor has provided. In the end, this facilitates the deployment and development of apps quickly.
An organization can profit much from leveraging PaaS in Cloud Computing, but they ned to do cloud migration properly. Because moving to the cloud requires controlling movement while preventing data loss, operational disruptions, or expensive models, this is the case. Therefore, it is important to proceed cautiously and ask for assistance when necessary.
Top Trending Tech Articles:
Career Opportunities after BTech | Online Python Compiler | What is Coding | Queue Data Structure | Top Programming Language | Trending DevOps Tools | Highest Paid IT Jobs | Most In Demand IT Skills | Networking Interview Questions | Features of Java | Basic Linux Commands | Amazon Interview Questions

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio