How Does a Customer Journey Map Help Your Business and Customers
For online audiences who hang out on multiple digital channels, marketers work on making a smooth transition across various touchpoints. And that is made possible by mapping the customer journey so that prospects aren’t forced to come across irrelevant, sales-y communication.
Nowadays, customer experience is not just bound to the buying phase or after-purchase feedback. It is necessary to be considered much before the customer comes in contact with the brand. Also, the customer must be provided with apt communication across every touchpoint.
Brands today focus on being consistent in making the customer happy through digital marketing best practices. The reasons are, that the consumer’s online behaviour is trackable, and people consume online media more.
About 65% of respondents said that they can become long-term customers only if a brand provides positive experiences throughout the customer journey (Forbes/Arm Treasure Data survey). This is one of the many reasons why businesses focus on creating a solid customer journey map.
This blog details all about the customer journey map – its definition, how to create one, and more.
- Customer journey map
- Importance of a customer journey map
- Types of customer journey maps
- How to create a customer journey map?
- When to create a customer journey map?
Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a visual outline such as an infographic, illustration or any diagram. It connects all the experiences of anyone who interacts with a brand across channels such as social media, emails, website blogs, chatbots, etc.
This kind of mapping also tells the story of the customer in a visual format. This is how marketing teams and stakeholders are on the same page on what the customer expects and what they do not prefer. They also help spot opportunities to tweak digital marketing strategies.
Basic Elements in a Customer Journey Map
Point of View of Specific Customer Persona – It highlights for whom the customer journey is mapped. Marketing teams create specific buyer personas and based on them, they chart out the customer journey map, across different buying phases, from awareness to conversion.
Marketers create different buyer personas for different purposes. But the crux of audience research remains similar. You may review how to create a buyer persona for keyword research as well.
Scenario – This element covers the sequence of steps a customer takes. It can be the purchasing behaviour, customer feedback, etc. In a nutshell, the scenario defines the past or future actions of the specific customer.
Scope and Opportunities – This element defines which steps should be taken to achieve the business goal.
Mindset and Actions of the Specific Customer – Since the map is a storytelling tool, the data of the customer should reflect their emotions, state of mind, etc. This is where qualitative marketing research methods work.
Touchpoints – Touchpoints can be described as specific moments of the customer when they come across the brand before or after the purchase. By creating a visual representation that has a narrative, a marketing team acts on the pain points and resolves them across all touchpoints.
Let’s focus on touchpoints in more detail in the current online scenario.
Philip Kotler et al. in their bestselling digital marketing book – Marketing 5.0: Technology for Humanity discuss 5A’s customer path. This concept covers 5 phases and applies to customers in every industry who use online means to know about a brand and purchase.
The 5A’s Customer Path comprises
- Aware Phase – The customers are exposed to many competing brands online through search engines and social media.
- Appeal Phase – Then they shortlist the brands that they think will help solve their pain points
- Ask Phase – As they become more curious about the brands, they would research more about the brand
- Act Phase – After being satisfied with the information, they decide to purchase
- Advocacy Phase – Once they purchase, the customers get involved more with the brand and ‘advocate’ on behalf of the brand themselves through word-of-mouth, user-generated content, etc.
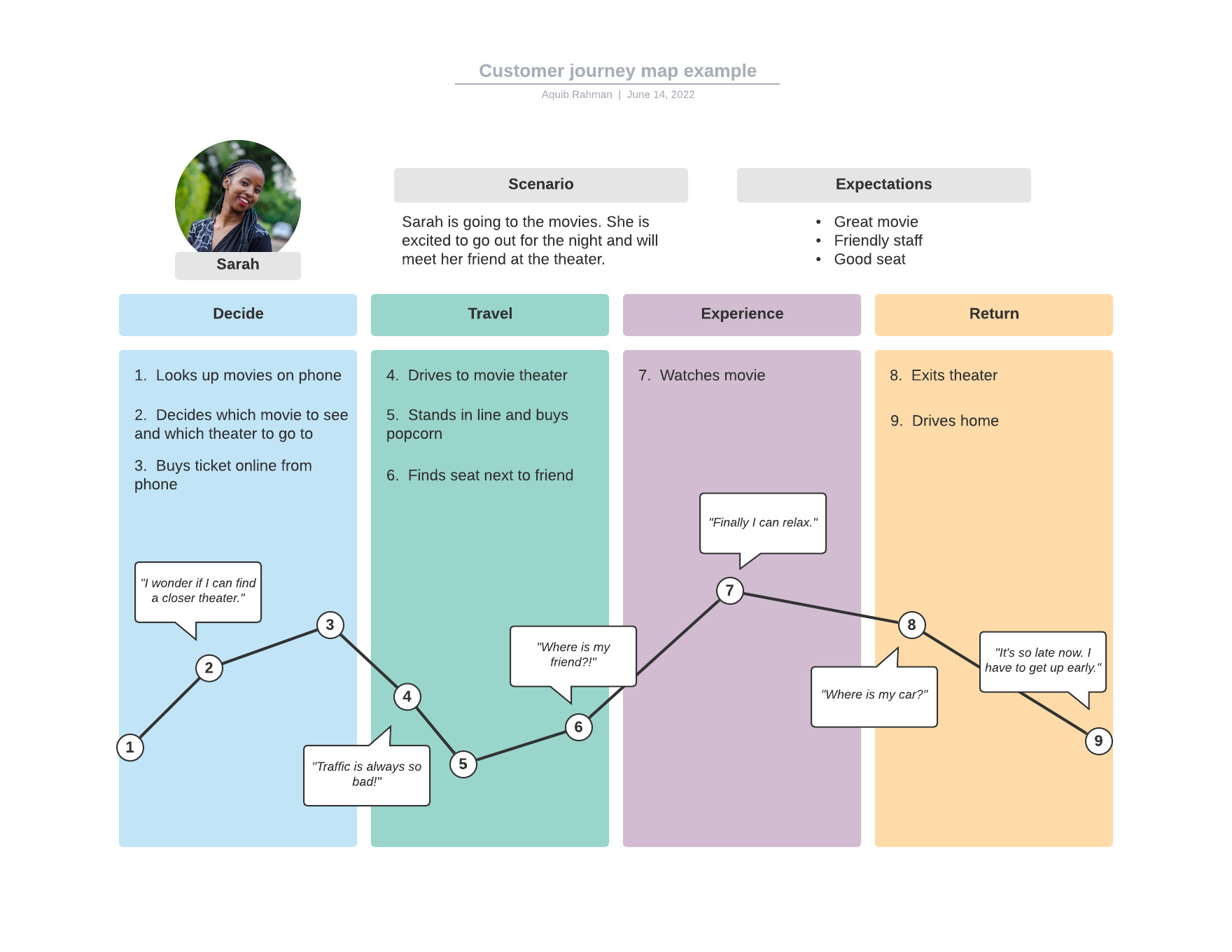
Example of a Customer Journey Map
Here is what a basic customer journey map looks like across different touchpoints. You can check out the Lucidchart tool that offers a free plan to map customer experiences and journeys.
In this example, you can see that the customer Sarah is going out to watch a movie in the theatre. She is expecting that it will be great as well as looking for good hospitality in the movie theatre.
You can see that the first phase is that she is looking at a list of movies on her phone. She then checks out the nearest movie theatre that is playing a film that she wants to watch with her friend. After finalising, she buys a ticket. The customer journey does not end there.
Now, when she is driving to the movie theatre, she faces road traffic, which can be considered a bottleneck.
While her expectations or basic touchpoints are met, there are other behaviours to keep a track of. She is late after watching the movie. That means she has to get up early. But there could be other touchpoints too, that you can find out and chart them in different pointers from 1 to 9 above.
Best-suited Digital Marketing courses for you
Learn Digital Marketing with these high-rated online courses
Importance of a Customer Journey Map
Overall, a customer journey map helps in improving and nurturing long-term customer relationships. Let’s look into why creating one is so important.
To Personalise Communication
Customer journey mapping helps in personalising communication. According to Startup Bonsai, 80% of customers are more likely to buy from a brand that offers a tailored experience. 42% of customers feel frustrated by impersonal content (Adobe).
To Stay Ahead of the Customer
With a customer journey map, you can filter out the preferences of your target audiences beforehand. You don’t have to send a message to your prospect and later find out that they do not prefer it. That may, in fact, damage the reputation of your brand. A customer journey map helps you avoid such major pitfalls when growing your business.
You may further refer to our blog on Voice of the Customer.
To Compete In Your Industry
According to CXPA, 67% of customer experience professionals use customer journey mapping globally. Such efforts help in obtaining a newer target audience as well, especially when you are expanding your business. Apart from that, you can utilise new opportunities by investing in newer strategies for a single or more digital channel (s) that help you attract your new target audience.
Types of Customer Journey Maps
Some common customer journey maps you can use are
Current State Customer Journey Map
In this type of customer journey map, the focus is on the ‘current’ interaction of customers with a brand. Based on objective customer data, it outlines what the customers think or feel at the present moment so that marketing departments and sales teams can together improve how they perceive the brand.
Future State Customer Journey Map
This map predicts how the customer will interact with the brand. Unlike the current state customer journey map that is focused on data, this map focuses on interpreting the values and desires of the customer.
Day-in-the-Life Customer Journey Map
A little close to current state maps, these go a step ahead to understand how the customer behaves in other online channels apart from interacting with the brand.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
Here is a breakdown of how you can create a customer journey map using the elements mentioned above.
Plan and List Objectives
It is ideal that you define the key objectives of the customer and your business. By doing so, you can determine how mapping the customer journey will help you achieve short- or long-term goals. In short, a dedicated list of objectives helps you learn about different touchpoints that will positively affect the brand perception of customers.
Conduct Research For the Right Buyer Persona
Focus on identifying who is the right customer for your product or service. You can do this by looking into who has currently interacted with your brand.
You can send questionnaires with basic questions such as ‘How did you first interact with the website?’, ‘Why did you decide to purchase or not purchase our product/service?’, etc. This can be done by sending surveys to your email subscribers.
Another way to know your buyer persona is to use digital marketing tools.
Google Analytics helps you analyse data relating to user engagement and behaviour on your website. You can track metrics such as sessions, goal completions, etc.
You may also consider using important survey data such as Net Promoter Score and Customer Effort Score to know about the customer directly.
Determine the Customer Touchpoints Relevant To You
There can be multiple touchpoints for different customers, and they vary according to your industry and target audience. But you can follow the 5A’s customer path, as described by Philip Kotler above. Based on that
- See where the customers are facing obstacles and how your business can solve those
- Look into factors that motivate the customer
Identify Bottlenecks and Update Your Customer Journey Map
Once you have an idea of how you can work on the touchpoints, you can focus on creating a current or future state customer map.
Then you can utilise different marketing efforts based on the given customer data. Just know that all elements in the modern marketing mix revolve around the customer. Businesses use inbound marketing tactics and marketing automation platforms to connect with the right audience at the right time.
If your business goals change, or you happen to see that the marketing efforts need to cover different touchpoints, update the map accordingly.
When to create a Customer Journey Map?
Customer journey maps are dependent on the business goal. They are created during the initial research phase when the objectives are clearly defined.
Also, know that customer journey maps are not always chronological as the sales funnel, from awareness to conversion. The reason is that customers want to have their own time in making a purchase. They may not respond to communication through email marketing or social media marketing immediately. They also may not buy after going through the different stages in the sales funnel. Instead, they can advocate to their peers about the product who make the purchase.
So to map the customer journey in a non-linear manner, you have to consider different approaches than a linear one that takes the customer gradually through the sales funnel. For example, you can focus on retargeting, which involves sending relevant communication when the customer abandons their cart.
Parting Thoughts
So this was all about a customer journey map. Hope that you are able to create it and make your marketing efforts more customer-focused to improve your ROI.
Here are some related courses you may want to take if you are planning on learning mapping the journey of customers.
- Marketing Foundations: Customer Decision Journey on LinkedIn Learning
- Product Development: Customer Journey Mapping with Miro on Coursera

Aquib is a seasoned wordsmith, having penned countless blogs for Indian and international brands. These days, he's all about digital marketing and core management subjects - not to mention his unwavering commitment ... Read Full Bio