Difference Between LAN, MAN and WAN
The main difference between LAN, MAN and WAN lies in the geographical area they cover. LAN covers a small geographical area, like a building; MAN covers a larger area, such as a city; and WAN covers the largest area, such as a country or the whole world.
When it comes to the difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN in terms of data transfer rate, LAN has the highest transfer rate among the three. It can transfer data at a speed of up to 10 Gbps. In comparison, MANs offer a transfer rate that falls between LANs and WANs. On the other hand, WANs have the slowest transfer rate and can only transfer data at a speed of up to 1 Gbps.
Best-suited Networking courses for you
Learn Networking with these high-rated online courses
Table of Contents (TOC)
- Difference Between LAN, MAN, and WAN
- What is a LAN Network?
- What is a MAN Network?
- What is a WAN Network?
- How Do LAN, MAN, and WAN Differ in Terms of Geographic Coverage?
- Which Technologies Are Used in LAN, MAN, and WAN?
- What Are the Speed and Latency Differences Among LAN, MAN, and WAN?
-
How do the Costs of Setting Up and Maintaining LAN, MAN, and WAN Compare?
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies of LAN, MAN, and WAN
Difference Between LAN, MAN, and WAN
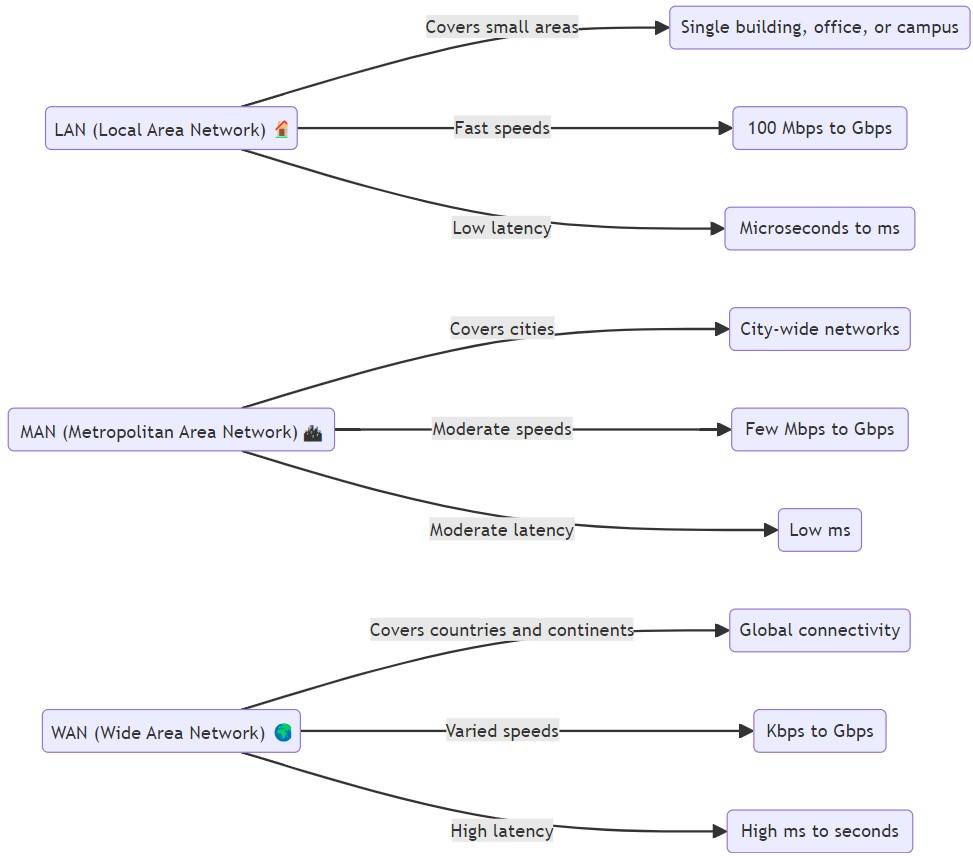
For better clarity, let's comprehend the difference between these three network types (LAN vs MAN vs WAN) in a tabular format.
| Benchmark | LAN (Local Area Network) | MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area Covered | Covers a small geographical area, such as a single building, office, or campus. | Covers a city or a large metropolitan area, connecting multiple LANs. | Covers vast geographical areas like cities, countries, or continents. |
| Typical Speed | 100 Mbps to multiple Gbps, depending on setup and hardware. | A few Mbps to multiple Gbps, depending on the provider and technology. | Can range from Kbps to multiple Gbps, depending on infrastructure and use. |
| Latency | Very low (microseconds to milliseconds). | Low latency (few milliseconds to tens of milliseconds). | High latency (tens to hundreds of milliseconds), especially over long distances. |
| Ownership | Typically owned and managed by a single organization. | Owned by an organization or service provider. | Managed by multiple service providers, often with shared infrastructure. |
| Transmission Media | Ethernet cables, Wi-Fi, fiber optics. | Fiber optic cables, copper wires, and wireless links. | Leased lines, satellite links, submarine cables, public internet. |
| Common Technologies | Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth. | Ethernet, FDDI, ATM, SONET/SDH. | PPP, Frame Relay, MPLS, ATM, Internet protocols (TCP/IP). |
| Security | Relatively secure with physical protections, firewalls, and VPNs. | Similar to LAN but includes additional measures like leased lines. | Heavy reliance on encryption, VPNs, firewalls, and access controls. |
| Fault Tolerance | Redundancy achieved using STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), LACP, and backup links. | Redundant links and load balancing for reliability. | Highly redundant with backup routes, load balancing, and protocols like BGP. |
| Scalability | Limited to a small area, suitable for a limited number of devices. | Moderate scalability, connecting multiple LANs. | Highly scalable to connect vast areas and a large number of networks. |
| Cost | Relatively low installation and maintenance costs. | Higher than LAN due to larger area coverage and additional equipment. | Highest cost, influenced by bandwidth, distance, and provider fees. |
| Examples | Office networks, school labs, home networks. | City-wide networks, university campuses, large regional offices. | The internet, multinational corporate networks, military communications. |
| Primary Use | Interconnecting devices in a small area to share resources and data. | Interconnecting LANs within a metropolitan area. | Interconnecting LANs, MANs, and remote networks across the globe. |
Must Read Articles:


What is a LAN Network?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a type of computer network that connects devices in a localized area, such as a home, office, or school. It allows sharing of resources, such as printers and files, and enables communication between devices.
An example of a LAN is a group of computers connected to an office. The advantages of LAN networks include faster communication, resource sharing, and increased security. Disadvantages include limited range and scalability.
What is a MAN Network?
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a type of computer network that covers a larger geographical area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. It typically spans a metropolitan area or a city.
An example of a MAN is a network connecting multiple office buildings within a city. Some advantages of MANs include high-speed data transfer, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. A disadvantage is that it requires a significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance.
What is a WAN Network?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects devices located in different geographical locations. It spans a large area, usually a country or even the entire world. The Internet is an example of a WAN network.
The advantages of a WAN network include the ability to connect remote locations and share resources, such as files and applications. Disadvantages can include lower speeds, higher costs, and potential security risks.
For more information about WAN networks, you can refer to the What Is WAN and How Does It Function article.
How Do LAN, MAN, and WAN Differ in Terms of Geographic Coverage?
LANs are the smallest of the three and are typically confined to a single building or campus. They connect devices within a small area, such as a home or office.
MANs cover a larger area than LANs but not as large as WANs. They are typically used to connect networks within a city or metropolitan area.
WANs are the largest of the three and connect networks located in different geographical areas. They can span cities, states, or even countries.
For example, a LAN could connect the devices within a single home or office, a MAN could connect the devices within a university campus, and a WAN could connect the devices of a multinational corporation across different countries.
Which Technologies Are Used in LAN, MAN, and WAN?
The technologies used in LAN, MAN, and WAN depend on their size and requirements. LANs use Ethernet for high-speed data exchange in small areas. Various types of network devices, such as switches, routers, and hubs, are used to manage data flow and connectivity.
MANs use SONET and DWDM technologies to transmit large amounts of data over larger areas such as cities. These technologies facilitate high-speed data transfer and help connect multiple LANs in a metropolitan area.
WANs use various technologies to achieve long-distance communication, such as leased lines for dedicated bandwidth, Frame Relay and ATM for cost-effective scaling, and MPLS for efficient traffic management across widespread geographical locations.
What Are the Speed and Latency Differences Among LAN, MAN, and WAN?
Here are the speed and latency differences when comparing LAN, Man, and WAN:
| Network Type | Speed | Latency | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAN (Local Area Network) | 100 Mbps to multiple Gbps (high-speed wired technologies like Ethernet or Wi-Fi) | Very low latency, usually a few milliseconds or microseconds | Home or office network |
| MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | A few Mbps to multiple Gbps (fibre optic cables or wireless point-to-point links) | Higher than LAN, but still low, ranging from a few milliseconds to tens of milliseconds | University campus network |
| WAN (Wide Area Network) | A few Kbps to multiple Gbps (leased lines, satellite links, or public Internet) | Highest latency, ranging from tens of milliseconds to hundreds of milliseconds or even seconds | Multinational corporation's global network |
How do the Costs of Setting Up and Maintaining LAN, MAN, and WAN Compare?
The costs of setting up and maintaining LAN, MAN, and WAN networks vary greatly based on factors such as scale, technology, and infrastructure requirements.
Local Area Network (LAN) Costs
- Setup Costs: Setting up a LAN is generally the least expensive. Costs typically involve purchasing networking equipment like routers, switches, cables, and any necessary hardware like computers and printers.
- Maintenance Costs: Maintenance is relatively low. Many organizations can manage LANs in-house, with ongoing expenses primarily related to occasional equipment upgrades or troubleshooting.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Costs
- Setup Costs: Establishing a MAN is more expensive than a LAN due to the need for advanced infrastructure to connect multiple LANs across a metropolitan area. It may involve leasing lines or deploying fibre optic cables.
- Maintenance Costs: Ongoing maintenance can also be higher, as it often requires specialized knowledge and potentially third-party service providers to manage and maintain the network infrastructure.
Wide Area Network (WAN) Costs
- Setup Costs: WANs incur the highest initial setup costs. They require extensive networking equipment and infrastructure to cover large geographical areas. Costs can involve leasing telecommunications lines or utilizing satellite connections, which can be particularly expensive.
- Maintenance Costs: WAN maintenance is also costly, often involving dedicated IT personnel or managed service providers to oversee the network. Besides, bandwidth costs to cover large distances can be relatively high compared to LANs and MANs.
Real-World Applications & Case Studies of LAN, MAN, and WAN
Here are some of the real-world applications of each of these networks:
LAN
- In the healthcare industry, medical devices and computers are connected within a limited area to create a network that enables real-time patient vital signs monitoring.
- In the retail industry, it connects point-of-sale (POS) terminals, barcode scanners, and inventory management systems within a finite area to enable real-time inventory levels and sales data tracking.
MAN
- In the education sector, it connects different university campuses across a city to share resources and facilitate collaboration between students and faculty.
- In the manufacturing industry, it connects different production facilities across a metropolitan area to enable real-time monitoring and control of production processes and inventory levels.
WAN
- In the financial industry, it connects bank branches and ATMs across vast geographical areas to enable secure and reliable financial transactions.
- In the transportation industry, it connects different logistics company locations spread over long distances to enable real-time shipment tracking and optimize delivery routes.
Conclusion
LANs are the most cost-effective option for small environments, while MANs are a more expensive alternative for urban connectivity. WANs represent the highest costs, appropriate for organizations needing extensive coverage across vast regions.
If you are interested in learning more about computer networks and their type, take on certifications like Networking Essentials, Certificate in Computer Hardware and Networking, or you can also opt for degree programs such as Online BCA from prestigious universities or colleges like Amity Online or Online Manipal.
Must Read Articles:




FAQs
What is the main difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN?
LAN (Local Area Network) connects devices in a small area, like a home or office. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) spans a city or large campus, connecting multiple LANs. WAN (Wide Area Network) covers broader geographical areas, often connecting multiple MANs and LANs, like the Internet. Each serves different networking needs based on scale and distance.
How Do LAN, MAN, and WAN Manage Data Security and Fault Tolerance?
Data Security:
- LAN: Physical security, firewalls, IDS/IPS, VPNs, user authentication, and data encryption.
- MAN: Similar to LANs, plus dedicated leased lines or secure wireless links.
- WAN: Encryption (IPsec, SSL/TLS), VPNs, firewalls, IDS/IPS, access control, and user authentication. It relies on secure protocols over public networks.
Fault Tolerance:
- LAN: Redundant components (switches, routers, links), protocols like STP and LACP for automatic rerouting.
- MAN: Redundant links, alternative paths, load balancing.
- WAN: Multiple service providers, redundant links, load balancing, failover mechanisms, dynamic routing (BGP), backup links (satellite, cellular).
What are the typical uses of LAN?
LANs are commonly used in homes, schools, and businesses to connect computers, printers, and other devices within a limited area. They facilitate resource sharing, such as internet access and file sharing, and enable communication through local servers. LANs are essential for efficient operations in small to medium-sized environments.
How do security measures differ among LAN, MAN, and WAN?
Security measures differ significantly among LANs, MANs, and WANs due to their distinct scales and usage. In a LAN, security is often managed through firewalls, antivirus software, and secure passwords. Since the network is smaller and localized, monitoring and controlling access are more straightforward.
For MANs, the larger scope requires stronger encryption and more robust policies to protect data travelling over greater distances. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are often used for secure connections.
WANs, being the largest, face diverse security challenges. They commonly implement complex security protocols, including end-to-end encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular audits to protect sensitive information across vast geographical areas.
How does a MAN differ in speed from a WAN?
MANs typically offer higher speeds than WANs due to their limited geographical coverage, which allows for faster data transmission. While WANs can experience latency and slower speeds due to long-distance connections and various transmission mediums, MANs provide a more stable and quicker network experience within a metropolitan area.
What are the advantages of using WAN?
WANs provide extensive connectivity over large distances, enabling organizations to connect multiple branches and remote locations. They support global communication and data sharing, making them essential for multinational companies. WANs also facilitate cloud services and remote access, enhancing collaboration and operational efficiency across diverse geographical areas.
Can LAN, MAN, and WAN Networks Interconnect?
Yes, LAN, MAN, and WAN networks can interconnect with each other through:
- LAN-to-WAN: Routers/gateways connect LAN to the WAN service provider's network (Internet, leased lines).
- LAN-to-MAN: Routers/switches connect LAN to MAN, enabling communication between devices within the respective networks.
- MAN-to-WAN: High-speed links/routers connect MAN to WAN, allowing access to remote locations/resources.
- LAN-to-LAN, MAN-to-MAN, WAN-to-WAN: Routers/gateways interconnect networks of the same type across different locations.
Why Are WANs Particularly Beneficial for Large Organizations?
WANs are particularly beneficial for large organizations as they:
- Connect geographically distributed locations across cities/countries.
- Enable secure remote access and teleworking for employees/partners.
- Facilitate centralized data storage, processing, and resource sharing.
- Scalable and flexible to accommodate growth/changes.
- Promote collaboration and integration across different sites.
- Support business continuity and disaster recovery strategies.
- Reduce operational costs through centralization and remote management.
What are some of the emerging networking technologies that have the potential to shape the future of LAN, MAN, and WAN?
Several emerging networking technologies have the potential to shape the future of LAN, MAN, and WAN. Some of those technologies are Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), the Internet of Things (IoT), Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs), and 5G Networks.
Is LAN more speedy than MAN?
When comparing data transmission speeds, Local Area Networks (LAN) are generally faster than Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). LANs utilize private network addresses for enhanced connectivity and often rely on wired connections, which reduces errors and improves data security during exchanges of information and services.
Can LANs be connected to WANs?
Yes. LANs can be connected to WANs through routers or gateways. This connection allows devices on a local network to access resources and services available on a wider network, such as the Internet. This integration is crucial for businesses that require both local and remote connectivity for their operations.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio