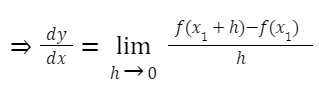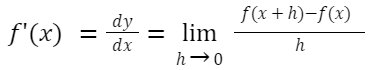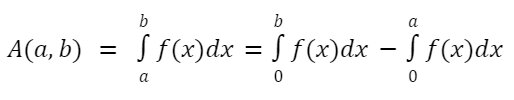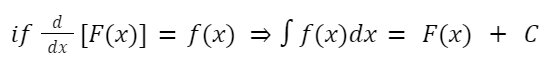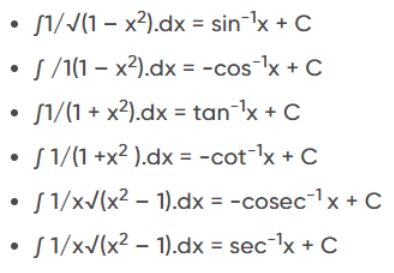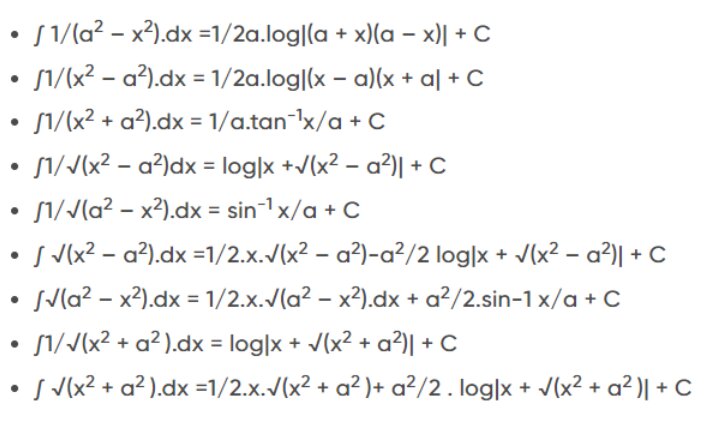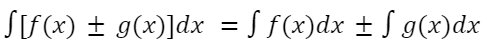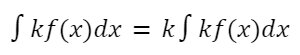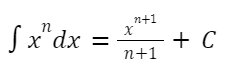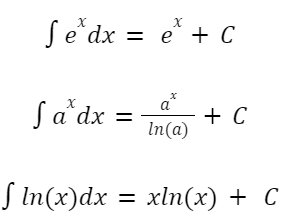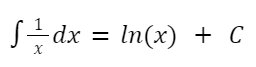Differential Calculus for Data Science
Differentiation is the process of finding the derivative of a function. The derivative of a function measures the rate of change of a function. In this article, we will discuss differentiation, its formula, rules for differentiation, and later in the blog we will also discuss about integration.
In data science and machine learning, calculus is used to find the instantaneous rate of change or the summation of infinitely many small factors to optimize machine learning algorithms. The direct implication of calculus can be directly seen in the Gradient Descent (we use derivatives to find the best parameter that minimizes the cost function) and AUC-ROC (we use integration to find the area between the curves).
This article will briefly discuss differentiation in calculus, and at the end of the article, we will also share some important integration formulas.
So, without further delay, let’s dive deep into learning about differentiation in calculus.
Best-suited Data Science Basics courses for you
Learn Data Science Basics with these high-rated online courses
What is Differentiation
Differentiation is the process of finding the derivative of a function. The derivative of a function measures the rate of change of a function, i.e., it finds the instantaneous rate of change of one variable (dependent variable or function) with respect to another variable (independent variables). It is defined as the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The derivative can be used to analyze the behavior of a function and understand how it changes over time.
Notation: Let f(x) is any function, then the derivative of f(x) with respect to x is given by: f’(x) or df/dx.
Example: The velocity of a moving car is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time, i.e.
v(t) = ds/dt, where
v(t) = velocity at any time t
s = displacement
t = time
Geometrically, the derivative of y = f(x) at any point P(a,b) equals the slope of a tangent to the curve, i.e., the slope of the tangent to curve y = f(x) at point (a, b) is
slope = change in Y/ change in X = (dy/dx)(a, b)
Now, let see the mathematical definition of differentiation or the formula for differentiation
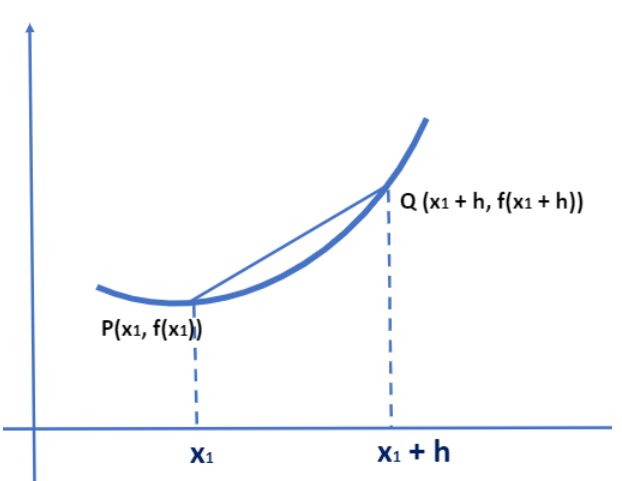
Let y = f(x) be any function and P (x1, f(x1)) be any point on f(x), and we know the derivative of f(x) and any point P equals to the slope of a tangent to the curve. Now, to find the tangent, let’s consider another point: h units away from P, i.e., Q (x1+h, f(x1+h)), and then we will find the slope of the secant line PQ.
Slope of secant line PQ = f(x1 + h) – f(x1) / ((x1 + h) – x1)
= f(x1 + h) – f(x1) / h
Now, if h -> 0, the slope of secant line PQ should be a good approximate for slope of the tangent line.
=> slope of tangent line = slope of secant line as h -> 0
Now, it’s time for the formal definition of derivative.
Definition
Let f(x) be any function, the derivative function of f at x is given by:
If the above limit exists, f is said to be differentiable at x; otherwise f is non-differentiable at x.
Example: Find the derivative of function f(x) = 2x^2 – 16x + 35, using the definition of the derivative.
Answer:
Differentiation Formulas of Elementary Functions
- Constant Function: d/dx [k] = 0, where k is a constant
- Expotential Function:
- d/dx [ax] = ax log a
- d/dx [e(ax)] = ae(ax)
- Logarithmic Function:
- d/dx [loga x] = 1/ (x ln a)
- d/dx [ln x] = 1/x
- Trignometric Function
- d/dx [sin x] = cos x
- d/dx [cos x] = -sin x
- d/dx [tan x] = sec2 x
- d/dx [sec x] = sec x tan x
- d/dx [cosec x] = -cosec x cot x
- d/dx [cot x] = -cosec2 x
Rules for Differentiation
Let f(x), g(x) and h(x) are three differentiable function such that:
Power Rule
d/dx [ xn] = nx(n-1),
where n is any fraction of integer
Example: Find the derivative of f(x) = x5.
Answer: f(x) = x5 => f’(x) = 5x(5-1) = 5x4
=> f’(x) = 5x4
Sum and Difference Rule
h(x) = f(x) + g(x) => h’(x) = f’(x) + g’(x)
h(x) = f(x) – g(x) => h’(x) = f’(x) – g’(x)
Example: Find the derivative of f(x) = x2 – 2x + 1
Answer: f(x) = x2 – 2x + 1
=> f’(x) = [x2]’ – [2x] + [1]’
=> f’(x) = [2x(2-1)] – [2(1)x(1-1)] + [0]
=> f’(x) = 2x – 2 + 0
=> f’(x) = 2x – 2
Product Rule
h(x) = f(x)g(x)=> h’(x) = f’(x)g(x) + f(x)g’(x)
Example: Find the derivative of f(x) = (x+1)sinx
Answer: f’(x) = [d/dx(x+1)]sinx + (x+1)[d/dx(sinx)]
=> f’(x) = [d/dx(x) + d/dx(1)] sinx + (x+1)[cosx]
=> f’(x) = [1+0]sinx + (x+1)cosx
=>f’(x) = sinx + (x+1)cosx
Quotient Rule
h(x) = f(x)/g(x) => h’(x) = [ f’(x)g(x) – f(x)g’(x)] / (g’(x))2
Example: Find the derivative of f(x) = sinx / cosx
Answer: f(x) = sinx / cosx
=> f’(x) = [d/dx (sin x)] cos x – sin x[d/dx(cos x)] / [d/dx(cos x)] 2
=> f’(x) = (cos x)cos x – sin x(-sin x) / (-sin x) 2
=> f’(x) = cos^2x + sin 2 x / sin 2 x
=>f’(x) = 1/sin 2 x [since, sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1]
=> f’(x) = cosec2x [since, cosecx = 1/sinx]
Chain Rule
[ f(g(x))]’ = f’(g(x))g’(x)
Example Find the derivative of sin(x + 1).
Answer: Consider h(x) = sin(x+1)
here, f(x) = sin x, and g(x) = x+1
=> f’(x) = cos x and g’(x) = 1
Now, substituting the value of f’(x), g(x), and g’(x) in chain rule, we get:
=> h’(x) = f’(g(x))g’(x)
=> h’(x) = cos(x+1)(1)
=> h’(x) = cos(x+1)
Integral Calculus
Definition
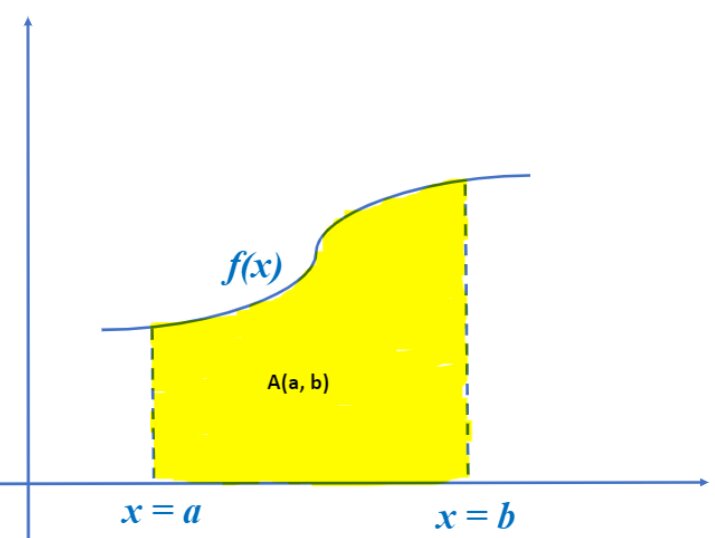
Integration or anti derivative in calculus is used to find the area under the curve. The area under any function f(x) between x = a, and x = b is given by:
Note:
Integration Formulas of Elementary Functions
Trigonometric Integration Formula
Inverse Trigonometric Function
Advanced Formulas of Integration
Integration Rule
Sum and Difference Rule
Constant Multiplication Rule
Power Rule
Exponent Rule
Reciprocal Rule
Application of Integraion in Data Science and Machine Learning
- To find the Area under the curve in the evaluation metric AUC-ROC.
- To find the Probability Density Function.
- To find the mean, and variance of a continuous random variable.
Conclusion
Differentiation and integration are the key concept of calculus, that is widely used in data science and machine learning. In this article, we have briefly discussed how to differentiate and integrate functions.
Hope you will like the article.
Top Trending Article
Top Online Python Compiler | How to Check if a Python String is Palindrome | Feature Selection Technique | Conditional Statement in Python | How to Find Armstrong Number in Python | Data Types in Python | How to Find Second Occurrence of Sub-String in Python String | For Loop in Python |Prime Number | Inheritance in Python | Validating Password using Python Regex | Python List |Market Basket Analysis in Python | Python Dictionary | Python While Loop | Python Split Function | Rock Paper Scissor Game in Python | Python String | How to Generate Random Number in Python | Python Program to Check Leap Year | Slicing in Python
Interview Questions
Data Science Interview Questions | Machine Learning Interview Questions | Statistics Interview Question | Coding Interview Questions | SQL Interview Questions | SQL Query Interview Questions | Data Engineering Interview Questions | Data Structure Interview Questions | Database Interview Questions | Data Modeling Interview Questions | Deep Learning Interview Questions |