Top 130 Networking Interview Questions and Answers for 2025
Computer networking is a growing career choice due to the widespread use of computers and the Internet. If you are preparing for a network expert interview, expect technical questions covering various topics. As a networking expert, you must master Routing, Firewall, Operating Systems, Cybersecurity, Linux, Python, Scripting, Network automation, DNS, IoT, Windows Server, etc. Our detailed guide on hardware and networking interview questions and answers covers the most frequently asked questions in the interview.
Networking Interview Questions
Best-suited Networking courses for you
Learn Networking with these high-rated online courses
These networking interview questions will assess your technical skills, experience, and system preferences. Interviewers want to see whether you can easily communicate technical requirements. They will test the technical knowledge necessary to get the job done. This article lists 100+ networking interview questions that are categorized into two main segments –
Networking Interview Questions For Freshers
Let’s start with the basic networking interview questions. This section covers networking interview questions for freshers.
Q1. What is a network?
Ans. A network consists of two or more separate devices linked together so that they can communicate. Networks can be classified according to different criteria, such as scope, type of connection, functional relationship, topology, or function.
- Scope: Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
- Connection type: Wired or wireless.
- Topology: Star, Ring, Bus, or Mesh.
- Function: Client-server or peer-to-peer networks.
Example: The internet is a massive network connecting billions of devices globally.
Explore popular courses on Shiksha Online related to networking:
| Popular Technology Course | Top Networking and Hardware Courses |
| Top Cisco Certifications Courses | Popular Networking Certifications Courses |
Q2. What are the different types of networks?
Ans. Considering the size or span of a network, we can classify them as follows:
- PAN (Personal Area Network) – PAN is made up of devices used by a single person. It has a range of a few meters.
- WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) – It is a PAN network that uses wireless technologies as a medium.
- LAN (Local Area Network) – LAN is a network whose range is limited to a relatively small area, such as a room, a building, an aeroplane, etc.
- WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) – WLAN is a LAN network that uses wireless means of communication. It is a widely used configuration due to its scalability and because it does not require the installation of cables.
- CAN (Campus Area Network) – A network of high-speed devices that connects LANs in a limited geographical area, such as a university campus, a military base, etc.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) - MAN is a high-speed (broadband) network that provides coverage in a larger geographic area than a campus but is still limited.
- WAN (Wide Area Network) – WAN extends over a large geographical area using unusual means of communication, such as satellites, interoceanic cables, fibre optics, etc. Use public media.
- VLAN – It is a type of logical or virtual LAN, mounted on a physical network, to increase security and performance. In special cases, thanks to the 802.11Q protocol (also called QinQ), it is possible to mount virtual networks on WAN networks. It is important not to confuse this implementation with VPN technology.
Read more – What is Networking?
Q3. What is Network Cabling?
Ans. Network cables can connect two computers or computer systems directly. A cable is a cord made up of different conductors that are insulated from each other. A wrap for better strength and flexibility usually protects this cord.
To choose a network cable, several aspects must be taken into account, such as –
- The distance that must be covered with that cable
- The maximum data transmission speed
- The coating of the cable
- The type of network to be created
- The type of braiding, shielding, and/or sheath
Q4. What are the different types of network cables used in networking?
Ans. The different types of cables used in networks are –
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Cable Installation Guides
- Coaxial Cable
- Fibre Optic Cable
- Wireless LANs
Explore these online degree programmes–
Q5. What is a ‘subnet’?
Ans. A ‘subnet’ is a generic term for a section of an extensive network, usually separated by a bridge or a router. It also works for the network’s broadcast domains, manages traffic flow, and helps improve network performance. Uses of the subnet in networking include:
- Relieving network congestion
- Reallocating IP addresses
- Improving network security
Q6. What is DNS?
Ans. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a central part of the internet, providing a way to match names (a website you’re seeking) to numbers (the address for the website). Anything connected to the internet – laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and websites – has an Internet Protocol (IP) address made up of numbers.
Key functions of DNS include:
- Mapping domain names to IP addresses for easier navigation.
- Simplifying user access to websites without remembering numerical IP addresses.
- Ensuring seamless internet browsing.
Example: When you type "www.abc.com" in a browser, DNS finds the corresponding IP address and connects you to the server hosting the website.
You can also explore: What Is An IP Address?
Explore – What is network security?
Q7. Differentiate between ‘forward lookup’ and ‘reverse lookup’ in DNS.
Ans. Following are the major differences between a forward lookup and a reverse lookup in DNS:
| Forward DNS lookup | Reverse DNS lookup |
| Converts a human input or a domain name to an IP address | Converts an IP address into a domain name |
| Has a mapping between hostnames and IP addresses | Has a mapping that relates IP addresses to hostnames |
| Used for a website or other server access | Used for network troubleshooting |
| Utilizes different servers with different IP addresses | Resolves reverse lookup queries where a client requests a hostname by providing an IP address |
| Uses A Records (basic) to identify any IP address for a particular hostname | Uses DNS pointer record to identify a hostname for a given IP address |
Q8. What is Network Topology?
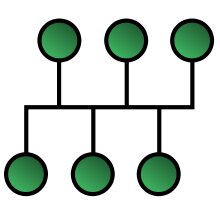
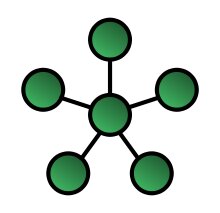
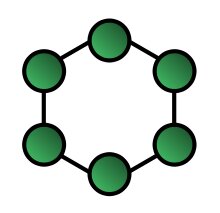
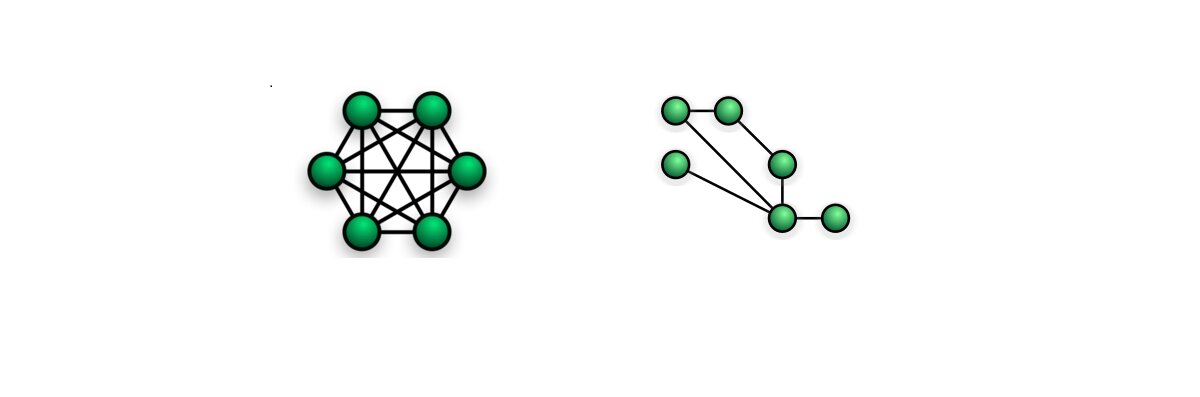
Ans. This is among the important networking interview questions. Network topology is the physical or logical arrangement in which the devices or nodes of a network (e.g. computers, printers, servers, hubs, switches, routers, etc.) are interconnected over a communication medium. It consists of two parts – the physical topology, which is the actual arrangement of the cables (the media), and the logical topology, which defines how the hosts access the media.
Types of network topologies –
Bus – In the bus network topology, each workstation is connected to a main cable called a bus. Therefore, each workstation is directly connected to every other workstation on the network.
Star – In the star network topology, there is a central computer or server to which all workstations are directly connected. Each workstation is indirectly connected to the other through the central computer.
Ring - In the ring network topology, the workstations are connected in a closed-loop configuration. Adjacent workstation pairs are directly connected, and other pairs of workstations are indirectly connected, passing data through one or more intermediate nodes.
Mesh – Mesh network topology has two forms – full and partial mesh. In the full mesh topology, each workstation is directly connected. In the partial mesh topology, some workstations are connected to all the others, and some are connected only to the other nodes with which they exchange more data.
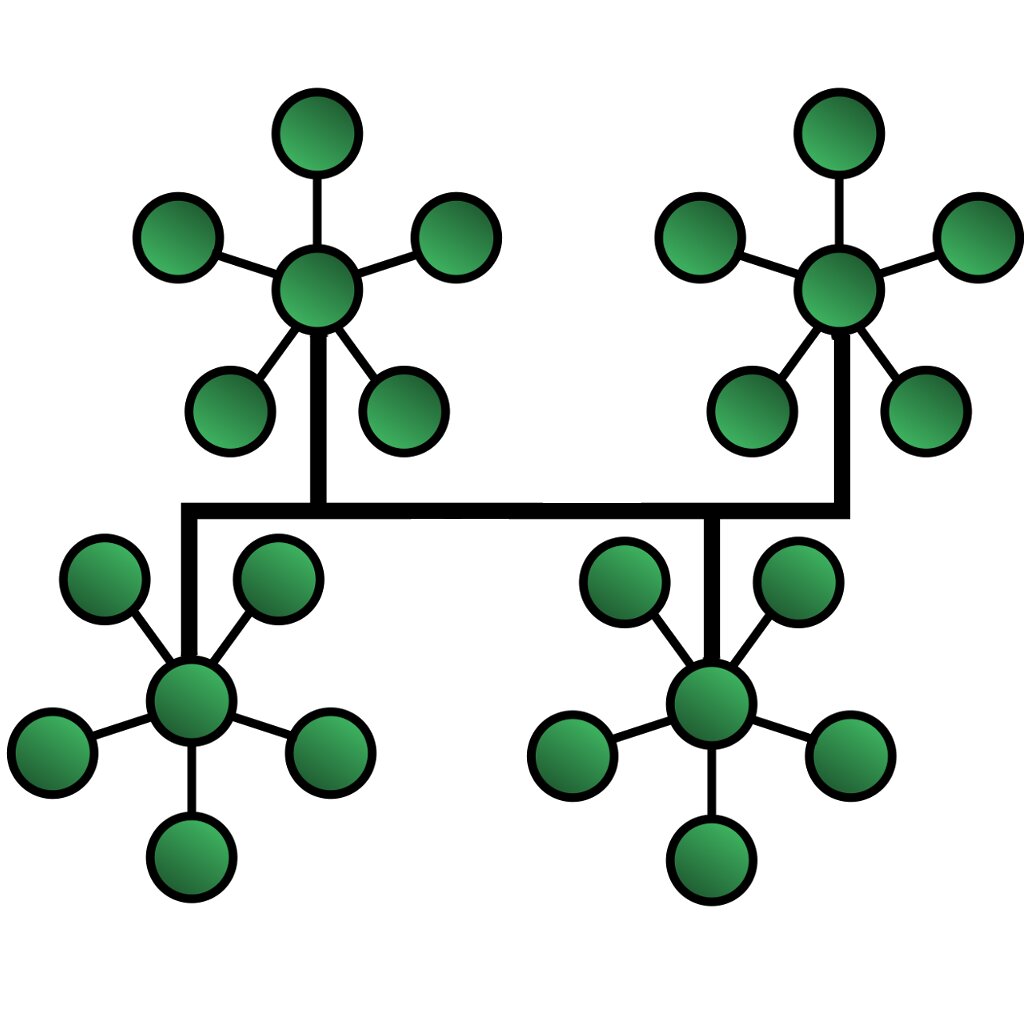
Tree – The tree network topology uses two or more star networks connected. The central computers in star networks are connected to the main bus. Thus, a tree network is a bus network of star networks.
Q9. What are ‘client’ and ‘server’ in a network?
Ans. Clients and servers are separate logical entities that work together over a network to accomplish a task.
A client application is the element of communication that requests a network service, such as accessing a web page, downloading a file, or sending an email.
A server application is the element of communication that responds to customer requests, providing the required service, such as sending the web page, the requested file, or the email.
Computer applications such as email, the World Wide Web, and network printing use the client-server model.
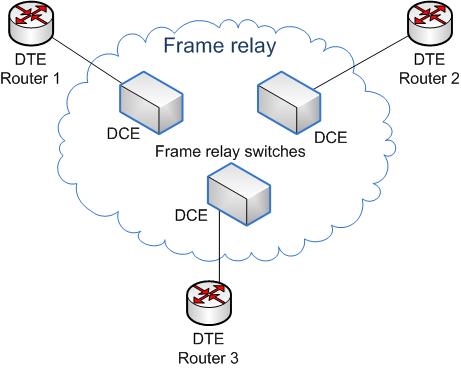
Q10. What is a ‘frame relay’, and which layer does it operate?
Ans. Frame Relay is a data link layer digital packet-switched network protocol technology designed to connect local area networks (LANs) and transfer data over wide area networks (WANs). Frame Relay shares some of the same underlying technology as X.25.
It is based on the older X.25 packet-switching technology designed to transmit analogue data as voice conversations. Unlike X.25, which is designed for analogue signals, Frame Relay is a fast packet technology, meaning the protocol does not attempt to correct errors. It is often used to connect LANs with main backbones, as well as in public-wide area networks and in private network environments with leased T-1 lines. It requires a dedicated connection during the transmission period and is not ideal for voice or video, which require a constant stream of transmissions.
Q11. What are the different features of Frame Relay?
Ans. The different features of Frame Relay are:
- Frame Relay is a connectionless service, which means that every data packet that passes over the network contains address information
- Frame Relay is a service that is provided with a variety of speeds from 56 Kbs to 25 Mbs. Although the speeds most used for the service are currently 56 Kbs and 1,544 Mbs
- The frames are of variable length and go up to 4,096 bytes
- Frame Relay is considered a broadband ISDN service
- It operates at high speed (1,544 Mbps to 44,376 Mbps).
- It operates only on the physical and data link layers. Therefore, it can be easily used on the Internet.
- Its large frame size is 9000 bytes, which allows it to accommodate all local area network frame sizes.
- Frame Relay can only detect errors (at the data link layer). It does not have flow control or error control.
Q12. How does a Frame Relay Work?
Ans. Frame Relay supports the multiplexing of traffic from multiple connections over a shared physical link. It uses hardware components, including router frames, bridges and switches, to pack data into individual frame relay messages. Each connection uses a 10-bit Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) for unique channel addressing. There are two types of connections:
- Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) for persistent connections are intended to be maintained for long periods even if data is not actively transferred.
- Switched Virtual Circuits (SVCs) for temporary connections that last only one session.
Frame Relay then places the data in a variable-size unit called a frame. It leaves any necessary error correction (data retransmission) until the endpoints, speeding up the overall data transmission.
Q13. What is a MAC address?
Ans. A MAC (Media Access Control) address is the unique 48-bit hardware address of a LAN card, usually stored in the network adapter card's ROM.
The MAC address is a unique identifier that manufacturers assign to a network card or device. It is also known as a physical address represented by hexadecimal digits. Each MAC address is unique worldwide and, in theory, is fixed for each device.
Each MAC address includes six pairs of numbers. The first three pairs help to identify the manufacturer, and the next three to the specific model. It is important to remember that a computer may have a variety of hardware to connect to networks; thus, it is common to have a MAC address for Ethernet, one for Wi-Fi, and another for Bluetooth.
Q14. What is ‘beaconing’?
Ans. Beaconing is the process that allows a network to self-repair network problems. This is among the important networking interview questions; you must also prepare for the related terminologies.
Features:
- Used in wireless networks like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
- Helps maintain connectivity and manage devices in a network.
Example: A Wi-Fi router regularly broadcasts beacon frames to indicate it is active and available for devices to connect.
Q15. Differentiate between ‘attenuation’, ‘distortion’, and ‘noise’.
Ans. When a signal travels through a medium, it loses some of its energy due to its resistance. This loss of energy is called attenuation.
When a signal travels through a medium from one point to another, it may change the form or shape of the signal. This is known as distortion.
Noise is unwanted electrical or electromagnetic energy that degrades the quality of signals and data.
Q16. What is an IP address?
Ans. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical unique address of a device in a network. IP is a datagram-oriented connectionless protocol. Therefore, each packet must contain a header with the source IP address, the destination IP address, and other data to be delivered successfully.
There are two types of IPs –
- Private IP Address – A private IP address is a set of numbers assigned to each computer or system connected to a private network. An example of a private IP address is your mobile phone or your home router, which has a default local address.
- Public IP Address – Public IP addresses are global addresses visible to anyone browsing the Internet. A user needs an internet connection to connect to such devices.
Q17. How to find the IP address of a website?
Ans. Finding the IP address of a website or a domain is not a tricky task and involves the following steps –
- Press the “Start” button on your computer
- Type in the program and file browser “cdm”
- Hit “Enter”
- The MS-DOS console will open, where you must type “nslookup google.com”. Instead of “google.com”, you must write the domain name of the page you want to consult
- Next, you will be able to see the IP address
Q18. What is ‘bandwidth’?
Ans. The limited range of frequencies of signals that a line can carry is called the bandwidth. Bandwidth is often confused with Internet speed when the volume of information can be sent over a connection in a measured amount of time, calculated in megabits per second (Mbps).
Logically the bandwidth of our network will be decisive for its quality and speed. The more bandwidth we have, the better since we can transfer data faster.
Q19. What are ‘firewalls’?
Ans. A firewall is a network security system responsible for managing network traffic. It uses a set of security rules to prevent remote access and content filtering. Firewalls protect the systems or networks from viruses, worms, malware, etc. Firewalls are usually of two types –
Physical – A physical firewall or hardware firewall is a physical device that sits between the external network and the server. They analyze incoming traffic and filter out any threats to the device. Widely used in institutions and large companies.
Logical – A logical or software firewall can exist anywhere on the subnet and protects hosts anywhere without rewiring. They only protect the computer on which they are installed, and in many cases, they are integrated into the operating system.
Q20. How does a firewall work?
Ans. This is among the popularly asked networking interview questions. The firewall ‘listens’ for what information packets are trying to leave or enter the computer system. Blocking can be done based on various criteria, such as the IP to which they are destined, the type of port used to send them, or the application of origin.
One of the most complex aspects of using firewalls lies in their configuration, in deciding what types of connections are blocked and which ones are not.
Q21. What are the major types of networks?
Ans. There are two major types of networks:
-
Server-based networks:
- Centralized servers manage data and resources.
- Common in businesses or organizations.
- Example: A corporate email system where the server handles all communication.
-
Peer-to-peer networks:
- Devices share resources directly without a central server.
- Suitable for small networks, such as home setups.
- Example: File sharing between two personal computers.
Q22. What are the important topologies for networks?
Ans. There are three essential topologies: Star, Bus, and Ring.
-
Star Topology:
- Devices connect to a central hub or switch.
- Advantage: Easy to troubleshoot issues.
- Example: Home Wi-Fi network.
-
Bus Topology:
- Devices are connected along a single communication line (bus).
- Advantage: Simple and cost-effective.
- Example: Older Ethernet networks.
-
Ring Topology:
- Devices form a circular chain, with each connected to two others.
- Advantage: Data travels in one direction, reducing collisions.
- Example: Token Ring networks in older systems.
Q23. Differentiate between static IP addressing and dynamic IP addressing.
Ans. A computer (or another device) is permanently configured to use the same IP address in a static IP address. In a dynamic IP address, the IP address can change periodically and is managed by a centralized network service. Here is a detailed comparison -
| Aspect | Static IP Addressing | Dynamic IP Addressing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The device is assigned a fixed IP address manually. | The IP address is automatically assigned by a DHCP server. |
| Changes | The IP address remains constant. | The IP address can change over time. |
| Configuration | Requires manual setup. | Automatically configured. |
| Use Cases | Servers, printers, or devices requiring consistent IPs. | Personal devices like laptops or mobile phones. |
| Advantages | Reliable for services requiring a permanent address. | Easier to manage and scales well in large networks. |
Example: A web server hosting a website typically uses a static IP address, while your smartphone gets a dynamic IP address from your home Wi-Fi.
Q24. What are the different ways to exchange data?
Ans. Following are the different ways to exchange data:
- Simplex
- Half-duplex
- Full-duplex
Q25. What are routers?
Ans. Routers connect two or more network segments. These intelligent network devices store information such as paths, hops, and bottlenecks in their routing tables. They determine the most accurate data transfer paths and operate in Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Network Layer.
The roles of a router include:
- Inter-network communication
- Best path selection
- Packet forwarding
- Packet filtering
Q26. What are the criteria for the best path selection of a router?
Ans. The following parameters define the path selection:
- Longest prefix match
- Minimum AD (administrative distance)
- Lowest metric value
Q27. Explain what is a source route.
Ans. The source route is defined as a sequence of IP addresses used to identify a datagram’s route. You can also involve the source route in the IP datagram header.
Q28. What is the difference between ‘standard’ and ‘extended’ ACL (access control list)?
Ans. Standard ACLs are source-based, whereas extended ACLs are source- and destination-based.
Q29. What is data encapsulation?
Ans. Data encapsulation is breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks before their transmission across the network.
Q30. What is RAS?
Ans. RAS (Remote Access Services) refers to any combination of hardware and software to enable remote access to tools or information that typically reside on a network of IT devices.
Q31. Mention the different network protocols that are supported by Windows RRAS services.
Ans. Following are the three main network protocols supported by Windows RRAS services:
- NetBEUI
- TCP/IP
- IPX
Q32. What are the perquisites to configure a server?
Ans. The perquisites to configure a server are:
- LAN card should be connected
- Root (partition on which window is installed) should be in NTFS format.
- A server should be configured with a static IP address.
Q33. How can you secure a computer network?
Ans. You can achieve a secure computer network in the following ways:
- Install a reliable and updated antivirus program across the network
- Ensure firewalls are set and configured properly
- Monitor firewall performance
- Ensure User authentication
- Update passwords regularly every quarter
- Create a virtual private network (VPN)
Q34. Mention the uses of the Hamming code.
Ans. Following are some of the common applications of using Hemming code:
- Modems
- Satellites
- PlasmaCAM
- Shielding wire
- Embedded Processor
- Computer Memory
- Open connectors
Q35. What are proxy servers, and how do they protect computer networks?
Ans. Proxy servers prevent external users from identifying the IP addresses of an internal network. They make a network virtually invisible to external users, who cannot identify the physical location of a network without knowledge of the correct IP address.
Q36. What are Nodes and Links?
Ans. Nodes – Devices or data points on a more extensive network are known as nodes. They are individual parts of a larger data structure and contain data. They also link other nodes.
Links- A link is the physical and logical network component for interconnecting hosts or nodes in a network. It is a physical communication medium such as a coaxial cable or optical fibre.
Q37. What is SLIP?
Ans. SLIP, or Serial Line Interface Protocol, was developed during the early UNIX days and is used for remote access.
SLIP does not provide error detection as it relies on higher-layer protocols. Therefore, SLIP alone is not successful on an error-prone dial-up connection. However, it is still useful to test the operating system’s response capabilities under load (looking at ping flood statistics).
Interviewers often ask such networking interview questions, and you must prepare for such abbreviations.
Q38. What is TCP/IP?
Ans. TCP/IP is the short form of the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. It is a set of protocol layers designed to facilitate data exchange on heterogeneous networks.
Learn all about Cisco Certifications, their Scope, and Benefits, read – what are Cisco Certifications?
Q39. How many layers does TCP/IP Model have?
Ans. TCP/IP Model has four layers:
| Layer | Description |
| Network Interface | Network Interface is also called a network access layer. It defines how data should be sent physically using the network. |
| Internet | It enables hosts to insert packets into the network and deliver them to the destination on the same or another remote network. |
| Transport | This layer permits devices on the source and destination hosts to converse. It ensures reliability, flow control, and data correction sent over the network. |
| Application | It is the topmost layer of the TCP/IP model. It defines TCP/IP application protocols and how host programs interface with transport layer services to use the network. |
Q40. Explain the different layers in the OSI model?
Ans. It is one of the most commonly asked networking interview questions. The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model consists of seven layers:
| Layer | Description |
| Physical | It is the lowest layer of the OSI Model. It transmits raw unstructured data bits over a communication channel. The Physical layer is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. While receiving data, the Physical layer gets the signal received, converts it into 0s and 1s, and sends them to the Data Link layer. |
| Data Link | The directly connected nodes perform node-to-node data transfer at this layer, where data is packaged into frames. This layer also corrects errors that occur at the Physical layer. The data Link Layer is divided into two sub-layers :
|
| Network | The Network layer transmits data from one host to another in different networks. It receives frames from the data link layer and delivers them to their intended destinations based on the addresses inside the frame. It also takes care of packet routing. |
| Transport | The transport layer manages the delivery and error-checking of data packets. It ensures the end-to-end delivery of the complete message. |
| Session | This layer creates communication channels, called sessions, between devices. It opens sessions, ensures they remain open while data is being transferred, and closes them when communication ends. It is also responsible for authentication and reconnections. |
| Presentation | This layer extracts data from the application layer and manipulates it per the required format to transmit over the network. |
| Application | At the Application layer, both the end-user and the application layer interact directly with the software application. This layer acts as a window for the application services to access the network and display the received information to the user. |
Q41. Which layer of the OSI model does a gateway work in?
Ans. Transport layer.
Q42. Explain why the standard OSI model is known as 802.xx.
Ans. The OSI model was introduced in February 1980. In 802.XX, ‘80’ is named for the year 1980, and ‘2’ is named for the month of February.
Q43. What common software problems lead to network defects?
Ans. It can be any or a combination of:
- Application conflicts
- Client-server problems
- Configuration error
- Protocol mismatch
- Security issues
- User policy & rights issues
This question is among the basic networking interview questions, and you must prepare for such questions.
Q44. Why is encryption on a network necessary?
Ans. Encryption changes data from its original readable to unreadable format, thus ensuring network security. The user must use a secret key or password to decrypt the data.
Encryption is useful for communications and in any case where you want to protect sensitive information. Thus, encrypting the information in disks, folders or even individual files is possible to prevent unauthorized access. Then, in addition to protecting users’ privacy, data encryption prevents other types of attacks, such as identity theft or bank fraud, and provides a protection mechanism against the theft or loss of devices with sensitive information.
Q45. What are the types of errors?
Ans. There are two categories of errors –
- Single-bit error – one-bit error per data unit
- Burst error – Two or more bits of errors per data unit
Q46. What is a client-server model?
Ans. The client-server model or architecture is a communication framework for network processes. This framework is distributed among service requestors, clients, and service providers. It offers them transparent access to applications, data, computing services or any other resource of the workgroup and/or across the organization on multiple platforms.
Client-Server Functions
- User interface management
- Management of shared peripherals
- Capture and validation of input data
- Generation of queries and reports on databases
- Control of concurrent access to shared databases
- Create communications links with other local or wide area networks
Q47. What is TELNET?
Ans. TELNET is a client-service protocol on the internet or local area network, allowing a user to log on to a remote device and have access to it. This is among the most commonly asked networking interview questions. Technically, it is a bidirectional interactive text-oriented communication facility which uses a virtual terminal connection.
Q48. What is RIP?
Ans. In networking, RIP is an abbreviation for Routing Information Protocol. It is a simple protocol that exchanges information between the routers.
Q49. What is half-duplex?
Ans. It is the mode of communication between two devices. Here the data flows bi-directionally but simultaneously. A perfect example of a half-duplex is a walkie-talkie.
Q50. What is a full-duplex?
Ans. It is a mode of communication between two devices, and the data flow is bi-directional, too, but the flow is simultaneous. One of the examples of a full-duplex is a telephone.
Q51. What is netstat?
Ans. Netstat is a command-line utility program that provides information about a connection’s current Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) settings.
Q52. What is a peer-peer process?
Ans. The processes on each machine that communicate at a given layer are called the peer-peer process.
Q53. What is anonymous FTP?
Ans. With the help of an anonymous FTP, users can be granted access to files in public servers. Users can log in as anonymous guests, thus the name.
Q54. What is NAT?
Ans. Network Address Translation is a protocol that allows a network device, usually a firewall, to assign a public address to a computer/s inside a private network.
Q55. Mention a few examples of private network addresses.
Ans. Few examples of private network addresses are:
10.0.0.0 with a subnet cover of 255.0.0.0172.16.0.0 with subnet cover of 255.240.0.0192.168.0.0 with subnet cover of 255.255.0.0.
Q56. Can you tell me the main elements of a protocol?
Ans. There are three main elements of a protocol –
- Syntax: It refers to the structure or format of the data and their order of presentation.
- Semantics: It specifies the meaning of each section of bits.
- Timing: Timing refers to two characteristics: the timing and speed of data sending.
Interviewers often ask such common networking interview questions.
Q57. What is NIC?
Ans. NIC is the abbreviation for Network Interface Card. It is a peripheral card with electronic circuitry. It is attached to a PC and connects to a network. NIC has its own MAC address and this identifies a PC on the network.
Q58. What is the difference between Communication and Transmission?
Ans. Transmission – A process of sending and receiving data between source and destination in only one way. It is regarded as the physical movement of data.
Communication – A process of sending and receiving data between source and destination, in both ways.
Q59. Explain NAT in networking.
Ans. Network Address Translation (NAT) is a protocol used to convert the IP address of the computer network into a local network to a single IP address. It takes all your local network devices and provides a single IP address to share a single connection to the internet. NAT is used as a router, computer, and firewall in a local network.
Q60. Explain NOS.
Ans. Short form for Network Operating System. Specialized software that provides connectivity to a computer such that it can communicate with other computers and devices on a network.
Q61. What is IDEA?
Ans. IDEA is the abbreviation for International Data Encryption Algorithm. It is the replacement for the Data Encryption Standard (DES).
Q62. What is ASCII?
Ans. American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Q63. What is Brouter?
Ans. Brouter is a device that functions as both a bridge and a router. It forwards data within the networks and also routes data to individual systems in a network.
Q64. Mention the maximum length of the Thinnet cable.
Ans. The maximum length of the Thinnet cable is 185 meters.
Q65. Name the cable which uses the RJ11 connector?
Ans. Telephone cables use the RJ11 connector.
Q66. How would you differentiate between Firewall and Antivirus?
Ans. Both are security applications used in networking.
A firewall prevents unauthorized access in private networks as intranets. However, it does not protect against viruses, spyware, or adware.
An antivirus is a software that protects a computer from any malicious software, virus, spyware, or adware.
You may consider such networking interview questions to be basic, but such questions are the favourite of interviewers as interviewees often leave behind such networking interview questions while preparing.
Q67. How will you recover data from a Virus-infected system?
Ans. We will install an OS and updated antivirus in a system that is free of any viruses, and then connect the hard drive of the infected system as a secondary drive. The hard drive will then be scanned and cleaned. Data can now be copied into the system.
Q68. What is ipconfig?
Ans. ‘ipconfig’ is an acronym for Internet Protocol Configuration. We use ipconfig on Microsoft Windows to view and configure the network interface. It displays all TCP/IP network summary information available on a network and helps to modify the DHCP protocol and DNS settings.
Q69. What is ifconfig?
Ans. It is an acronym for Interface Configuration and is used on Linux, Mac, and UNIX operating systems. ‘ifconfig’ configures and controls the TCP/IP network interface parameters from Command Line Interface while allowing the user to check the IP addresses of these network interfaces.
Q70. What is the semantic gap?
Ans. Semantic gap is a difference between high-level programming sets in various computer languages and the simple computing instructions used by microprocessors.
Q71. What is the difference between a Domain and a Workgroup?
Ans. This is one of the important networking interview questions that you must prepare for your interview. The main difference between a Domain and a Workgroup is where do the computer networks belong to. If it is a home network, then computers will be a part of a workgroup, and if it’s a workplace network, then the computers will be a part of a domain.
Below are some of the major differences between a Domain and a Workgroup:
| Domain | Workgroup |
| The computers in a domain have a centralized database. | The computers in the workgroup have their own local database. |
| Computers can be on a different local network. | All computers must be on the same local area network. |
| One or more computers are servers for providing access, security permission to all other computers in a network. | All computers are peers and no computer has control over another computer. |
| A domain is used for transferring and sharing sensitive and important data. | It is used for sharing less secure data. |
| Domain has centralized authentication servers which set the rule of authentication. | Each computer has its own authentication rule for every user account. |
| If a user has an account in a domain, then the user can log in to any computer in a domain. | Each computer has a set of user accounts. If the user has an account on that computer, then only the user will be able to access the computer. |
| Changes made in one computer are automatically made to all other computers in a network. | Computer settings need to be changed manually for each computer. |
| It is used by large public and business networks. | A workgroup is better suited for fewer computers. |
| Thousands of computers can be connected. | Only 20 computers connected. |
Q72. What Is NVT?
Ans. NVT stands for Network Virtual Terminal and is a representation of a primary terminal. This virtual terminal helps you to start a telnet session.
Q73. What Is BGP?
Ans. BGP or Border Gateway Protocol is a protocol used to transfer data and information between different host gateways or autonomous systems.
Q74. What is Round Trip Time?
Ans. Round Trip Time or RTT is the time taken to send a message from one end of a network to the other and back.
Q75. What are 127.0.0.1 and localhost?
Ans. Localhost is the standard hostname given to the machine, and it is represented by the IP address 127.0.0.1. Therefore, we can say that 127.0.0.1 and localhost are the same thing.
Q76. Which are the most typical functional units of the client/server applications?
Ans. The most typical functional units of the client/server applications are –
- Presentation logic or user interface (e.g., ATMs)
- Business logic (e.g., Account balance inquiry)
- Data (e.g., Bank account records)
Q77. What are the Triggers?
Ans. Triggers are event-driven specialized procedures and are managed by database management systems. It is capable of performing complex actions and uses procedural language full throttle.
Q78. What is a Gateway?
Ans. A gateway is a hardware device that is connected to two or more networks. It may be a router, firewall, server, or any other similar device and is capable of regulating traffic in the network.
For more information, you can also explore: What is a Gateway in networking?
Q79. Is there a difference between a gateway and a router?
Ans. A gateway sends the data between two dissimilar networks, while a router sends the data between two similar networks.
Q80. What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)? What are the advantages of using a VPN Connection?
Ans. A VPN or Virtual Private Network is an encrypted connection (secure tunnel) built on the internet from a device to a network. It helps in the creation of a protected network between different networks using the internet (public network), ensuring that sensitive data is safely transmitted. This makes it difficult for third parties to gain unauthorized access, track your activities online, or steal data. By using the VPN, a client can connect to the organization’s network remotely.
Some of the advantages of using VPN Connection are:
- Remote Access
- Protected File Sharing
- Anonymity
- Enhanced Security
- Improved Performance
- Anonymity
- Network Scalability
- Prevents Data Throttling
Q81. Explain the different types of VPN.
Ans. There are two types of VPNs:
- Remote Access Virtual Private Network:
A Remote Access VPN securely connects a device (endpoints like laptops, tablets, or smartphones) outside the corporate office. It allows a client to associate with a private network and access every one of its resources and services remotely. The private network and the user connect securely through the Internet. It is a low-cost solution and is helpful for both business and home users.
- Site-to-Site or Router-to-Router Virtual Private Network:
This VPN is mostly used in large organizations with branches in different locations to connect the network of one office to another in different locations. It has two sub-categories:
- Intranet VPN: Intranet VPN allows several offices of the same company to connect using the Site-to-Site VPN type. It is commonly used for connecting remote offices in different geographical locations using shared infrastructure (internet connectivity and servers) with the same accessibility policies as a private WAN (wide area network).
- Extranet VPN: Extranet VPN allows companies to use Site-to-site VPN type to connect to another company's office. It uses shared infrastructure over an intranet, suppliers, customers, partners, etc., and connects them using dedicated connections.
Q82. What is EGP? What are its advantages?
Ans. EGP stands for Exterior Gateway Protocol. It is used to exchange net-reachability information between Internet gateways within the same or different autonomous systems. EGP is the protocol of the routers. It is used to identify the set of networks that you will be able to reach within or via each independent system.
Networking Interview Questions For Experienced Candidates
We are now moving on to the last category of networking interview questions. This section covers interview questions for experienced candidates.
Q83. Explain 10Base-T.
Ans. 10Base-T specifies data transfer rate, i.e., 10Mbps. Here, the term ‘Base’ defines ‘Baseband’ and not ‘Broadband’. T denotes the type of cable, which is a twisted pair.
Q84. Name the user support layers.
Ans. There are three types of user support layers –
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer and
- Application Layer
Q85. What is Piggy Backing?
Ans. It is the process of gaining access to a restricted communications channel by using an already established session by another user. This technique is known to improve the efficiency of the bidirectional protocols.
Q86. What is an asynchronous transmission?
Ans. It is a serial mode of transmission. It is the process of data transmission, where every character is a self-contained unit. Each character in asynchronous transmission has its start and stop bits, along with an uneven interval between them.
Q87. What do you mean by a synchronous transmission?
Ans. Synchronous transmission refers to continuous data streaming in the form of signals, accompanied by regular timing signals. The external clocking mechanism generates these signals and ensure that senders and receivers are in synchrony.
Q88. What are the different types of transmission media?
Ans. Transmission media has two broad types –
- Guided media (wired)
- Unguided media (wireless)
Q89. What is Process Sigma?
Ans. Process Sigma measures the frequency of a task performed without error. It is expressed as a number of standard deviations on a normal distribution.
Q90. What is FMEA?
Ans. Failure Mode Effect and Analysis or FMEA is a qualitative and systematic tool to identify potential failure modes in a system, the reasons, and their effects.
Q91. What is the backbone network?
Ans. It refers to a centralized infrastructure for distributing different routes and data to various networks. Backbone networks connect LANs and WANs and also handle the management of bandwidth and multiple channels.
Q92. What is OSPF?
Ans. OSPF is an abbreviation for Open Shortest Path First. It is a routing protocol that uses a link-state routing (LSR) algorithm to find out the best possible path for data exchange.
Q93. What is the range of addresses in the classes of internet addresses?
Ans. Following are the five different ranges of addresses in the classes of the internet:
- Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
- Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
- Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
- Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- Class E: 240.0.0.0 – 247.255.255.255
Q94. What are Datalink Protocols?
Ans. Datalink protocols are defined as the sets of requirements used to implement the data link layer. There are the following categories of Data Link protocols:
- Synchronous Protocols
- Asynchronous Protocols
- Bit Oriented protocols
- Character Oriented Protocols
Q95. What are the functions of a Network Layer?
Ans. The Network Layer or OSI Layer 3 provides services for exchanging individual sections of data over the network between identified end devices. To perform this end-to-end transport, Layer 3 uses four basic processes:
- Addressing
- Encapsulation
- Routing
- Decapsulation
Q96. Name the access method used in the 1000BaseTX network.
Ans. CSMA/CD access method is used in the 1000BaseTX network.
Q97. Mention the different types of links used to build a computer network.
Ans. Following are the different types of links used to build a computer network:
- Cables
- Wireless Links
- Last-Mile Links
- Leased Lines
Q98. Mention the types of wires used for data transmission in UTP cable.
Ans. There are four types of wires used for data transmission in UTP cable, which are wires 1, 2, 3, and 6. Where wires 1 and 2 are used to transmit the data, while wires 3 and 6 are used to receive the data.
Q99. Can we use RG59 and RG6 cables in a computer network?
Ans. RG59 and RG6 cables are not used in the computer network. These cables are made for the cable TV network.
Q100. What is 10Base2?
Ans. 10Base2 is part of the IEEE 802.3a standard, specifying data transmission speeds of 10Mbps and a total segment length of 185 meters using RG-58 coaxial cable. The 10Base2 standard specifies a physical bus topology and uses BNC connectors with 50-ohm terminators at each end of the cable. One of the physical ends of each segment must be grounded.
Q101. Name the cable used in the 10BaseFL network.
Ans. Fibre optical cable is the cable used in the 10BaseFL network.
Q102. Why is IP protocol deliberated as a connectionless protocol?
Ans. An IP protocol is considered connectionless because it does not build up a connection before sending data to the endpoint.
Q103. How many network segments can be populated in 10Base2?
Ans. 10Base2 networks allow a maximum of five segments with only three of those segments populated. Each of the three populated segments can have a maximum of 30 nodes attached.
Q104. What is the point-to-point protocol?
Ans. A communications protocol is used to connect computers to remote networking services, including Internet service providers.
Q105. What is NIC?
Ans. The NIC stands for the network interface controller. NIC is a device or module that controls and configures the interface of a processor system to a network or other interconnection. There are many different types of interfaces in electronic systems. NICs generally configure, maintain the current state, handle faults, and provide algorithm implementation to transfer data to and from the interface successfully.
Q106. Mention any five applications that use TCP ports.
Ans. Following are the five applications that use TCP port:
- FTP
- POP
- SSH
- SMTP
- Telnet
Q107. What is the 5-4-3 rule? In which architectures do we use the 5-4-3 rule?
Ans. In the 5-4-3 rule, a maximum of five segments in a network are connected with four repeaters. It is used in 10Base2 and 10Base5 Ethernet architectures. In this rule, only three segments can be populated with nodes.
Q108. Name the measurement unit used to measure the transmission speed of Ethernet.
Ans. Mbps is the measurement unit used to measure the transmission speed of Ethernet.
Q109. Name the switching method used to explore the destination Mac address.
Ans. The switching method that is used to explore the destination Mac address is Cut Through.
Q110. Mention the use of DDR on Cisco routers.
Ans. DDR stands for dial-on-demand routing used to generate and close a circuit-switched session. It provides on-demand routing to low-volume and periodic traffic.
Q111. Mention the number of access lists required per interface.
Ans. One access list can be used per interface and per protocol.
Q112. How can the user data be converted from DTE to the WAN Service Form?
Ans. To convert the user data from the DTE to the WAN Service Form, we can use the Modem, CSU/DSU, and TA/NT1.
Q113. Name the types of WAN services obtained by Cisco routers.
Ans. WAN services obtained by Cisco routers are switched services where protocols are used to connect end-to-end devices and Interface front end.
Q114. Name the various technologies involved in building WAN links.
Ans. Various technologies involved in building WAN links are:
- Digital connections – using digital-grade telephone lines
- Analogue connections – using conventional telephone lines
- Switched connections – using different sets of links between the sender and receiver to move data.
Q115. Explain the Sliding Window in Agile.
Ans. The sender and receiver must handle the manageable sequence numbers in the Sliding Window. This abstract concept defines the range of sequence numbers with the concern of sender and receiver.
Q116. What standard colour sequences are used for a straight-through cable?
Ans. Standard colour sequences used for a straight-through cable are Orange/white, orange, green/white, green, blue/white, blue, brown/white, and brown.
Q117. What is a Network Interface Card?
Ans. Network Interface Card is a connecting device used to interlink computers with the network. These cards are of two types: Internal network cards and External network cards.
Q118. What is SMTP?
Ans. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a protocol used to move all internal mail across different networks. It works with a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) and provides the mail transmission on the TCP/IP protocol stack.
Q119. Explain the role of the IEEE in computer networking.
Ans. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an organization comprising engineers who manage standards for electrical and electronic devices. It involves networking devices, cablings, network interfaces, and connectors.
Q120. What are the advantages of PAN?
Ans. PAN has a number of advantages, including:
1. PAN does not require extra space as it does not need cables and wires.
2. It is used in TV and AC rooms, offices, conferences and meetings.
3. It provides multiple device connectivity at the same time.
4. It has an affordable cost.
Q121. What are the disadvantages of PAN?
Ans. PAN has the following disadvantages:
1. It can only be operated in a lesser range of areas.
2. It is used for personal areas.
3. It has a slow rate of transfer.
4. It also causes interference with radio signals.
Q122. What are the examples of WPAN?
Ans. Wireless keyboards, smartphones, TV remotes, wireless printers, BlueTooth, firewire, ZigBee, Wireless USB, and Wibree are some of the examples of WPAN.
Q123. Name the layers of the TCP IP protocol suite that are involved in a link-layer switch.
Ans. In TCP IP protocol, a link-layer switch is involved with the data-link and physical layers.
Q124. What is MAU?
Ans. A Multistation Access Unit(MAU) is a device used to connect multiple network stations in star topology in the form of a ring, which is also known as a token ring network.
Q125. Mention the maximum number of networks and hosts used in classes A, B, and C networks.
Ans. The maximum number of networks and hosts used in class A, B, and C networks are:
- Class A: 126 networks, 16,777,214 hosts.
- Class B: 16,384 networks, 65,534 hosts.
- Class C: 2,097,152 networks, 254 hosts.
Q126. Differentiate between a ‘bit rate’ and a ‘baud rate’.
Ans. A bit rate is the number of bits transmitted during one second, whereas, baud rate refers to the number of signal units per second that are required to represent those bits.
Baud rate = bit rate / N, where N is the no. of bits represented by each signal shift.
Q127. What is Project 802?
Ans. IEEE started a project to set standards to enable intercommunication between equipment from various manufacturers.
Q128. What is ICMP?
Ans. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network layer protocol of the TCP/IP suite used by hosts and gateways to send notifications of datagram problems back to the sender.
Q129. What are the differences between TCP and UDP?
Ans. This is one of the important networking interview questions. The differences between TCP and UDP are:
For more information, you can also explore: TCP vs UDP: What’s the Difference?
| TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
| Connection-oriented protocol. | Datagram-oriented protocol. It is a connectionless protocol. |
| TCP is more reliable as it guarantees the delivery of data to the destination router. | UDP is less reliable as the delivery of data to the destination cannot be guaranteed |
| TCP offers extensive error-checking mechanisms. | UDP provides only the basic error-checking mechanism. |
| Slower transmission. | Faster transmission. |
| Heavyweight. | Lightweight. |
| Packets order can be preserved or can be rearranged. | Packets order is not fixed as all packets are independent of each other. |
| Does not support Broadcasting. | Supports Broadcasting |
| The header size is 20 bytes. | The header size is 8 bytes. |
| HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and SMTP use TCP. | Protocols like DNS, RIP, SNMP, RTP, TFTP, and NIP use UDP. |
Q130. Explain the DHCP Protocol.
Ans. DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is a standardized network protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It is used to auto-configure devices on IP networks enabling them to use the TCP and UDP-based protocols. The DHCP servers automatically assign IP addresses to the network devices, reducing the errors caused by the manual allocation of IP addresses. DHCP is commonly used in networks ranging in size from small home networks to campus networks.
We hope these networking interview questions will help you to crack your next hardware and networking interview.
All the best!