What Is WAN and How Does It Function?
What is a WAN, and why is it significant compared to other types of computer networks, such as Local Area Networks (LANs) or Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs)? A wide-area network (WAN) is a system that connects multiple LANs or other networks, allowing them to communicate with one another. Without WANs, telecommuting, creating unified networks for organizations with multiple locations, and many online activities would be impossible.
A WAN connection typically relies on SD-WAN and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) technologies. Instead of constructing these connections independently, organizations generally opt to lease lines from service providers. In this article, we will go over WAN in great detail. But, before we go any further, let’s go over the topics we’ll be covering in this article:
Table of Content (TOC)
- What is WAN?
- Common examples of a WAN connection
- How do WAN Connections Function?
- WAN Network Technologies
- Wide Area Network Protocols
- Advantages of Using WAN
- Disadvantages of Using WAN
What is WAN?
A wide-area network (WAN) is a collection of interconnected local-area networks (LANs) or other networks. This network is not bound to a single location and allows communication, information sharing, and other functions between devices all over the world.
You can lease a private WAN infrastructure as a service from a third-party provider such as an internet service provider or cable company. Large businesses frequently use WANs to connect their office networks; each office usually has its LAN, which connects via a WAN. Wide-area networks are the backbone of an enterprise in today’s world. Companies can use WANs for a variety of tasks, such as:
- Use voice and video to communicate.
- Run or host internal applications.
- Access data storage and backup data remotely, etc.
Are you interested in learning about the Local Area Network? If so, read the article on what LAN is.
Best-suited IT & Software courses for you
Learn IT & Software with these high-rated online courses
Common Examples of a WAN Connection
Some of the common examples of a wide area network connection are:
| WAN Connection Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Leased Lines | Dedicated point-to-point connection for consistent and secure data transfer between two locations. |
| Fiber Optic Networks | High-speed connections using fiber optic cables, often used for long-distance communication. |
| DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) | Internet connection over traditional telephone lines, suitable for small offices and homes. |
| Satellite | Provides connectivity in remote areas using satellites; offers slower speeds and higher latency. |
| Cellular Networks (4G/5G) | Wireless WAN connection using mobile network towers, enabling connectivity for mobile devices and remote areas. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | Securely extends a private network over a public network using encrypted connections. |
| MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) | A private network solution directing data based on labels for efficiency and reliability. |
| Internet | Global network connecting millions of private, public, academic, and business networks. (The internet is the world's most extensive WAN) |
How do WAN Connections Function?
WANs are either point-to-point, with a direct connection between two sites, or packet-switched, with data transmitted in packets over shared circuits. Point-to-point WAN service can use either analog dial-up lines or modems to connect the computer to the phone line. Local telephone companies and long-distance carriers are both point-to-point WAN service providers.
Packet-switched network services are typically chosen by organizations with low data volumes or multiple sites for which multiple dedicated lines would be prohibitively expensive.
WAN Network Technologies
In the design of a WAN network, two technologies are used, namely:
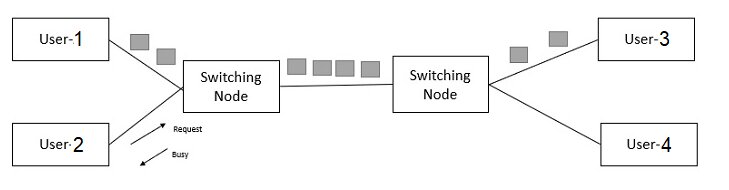
Circuit switching: All messages will take the same path in a circuit-switched network. And resources along that path will be reserved for this connection. As a result, there is no need to keep track of the fragmentation because the entire message is sent as a single unit.
Let’s take a look at the figure for a better understanding:
Assume User 1 wants to use the network; it must ask for the request in order to obtain it, and then User 1 can communicate with User 3. If User 2 attempts to communicate with User 4 during the connection phase, the network will send a busy signal.
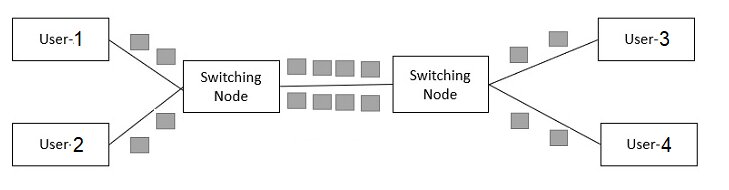
Packet switching: In a packet-switched network, the outgoing link determines the size of the packet, and these packets may take a different path. At the destination, these packets are collected and reassembled.
Now, assume User 1 wants to communicate with User 3 and User 2 wants to communicate with User 4. Then in this type of network, it is possible to do so at the same time.
You can also explore – What is the Difference Between LAN and WAN?
Wide Area Network Protocols
Some of the most common WAN protocols are:
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame Relay | Sends data between LANs or WAN endpoints; defines the physical and data-link layers of telecommunications channels using packet switching. |
| ATM | Asynchronous Transfer Mode encodes data into fixed-sized cells using asynchronous time-division multiplexing. |
| PoS | Packet over SONET converts IP packets into SONET frames, optimizing for lower packet header overhead and high transmission rates. |
| IP Suite | The Internet Protocol suite enables all web devices to connect and communicate with each other simultaneously. |
| MLS | Multiprotocol Label Switching transits traffic using the shortest path based on "labels" rather than network addresses. |
You can also explore – What is Wireless Networking?
Advantages of using Wide Area Network
Some of the advantages of using a wide area network are:
- Covers a broader geographic area.
- It benefits the global market and business.
- IT infrastructure is centralized.
- Increase your privacy.
- Assists global markets and businesses.
- Allows users to share resources and application software.
- Allows you to send messages to anyone else on the network very quickly.
Disadvantages of using Wide Area Network
Some of the disadvantages of using a wide area network are:
- It is very expensive because we must pay each time we transfer data.
- Troubleshooting WAN can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Wide Area Network is insecure and untrustworthy.
- Because it is a public network, it is heavily reliant on a third party.
- The network is difficult to maintain and requires skilled technicians and network administrators.
- It has more security issues than LAN because it uses more technologies and has a wider coverage area.
Conclusion
This article covered WAN in great detail, including various topics, such as what is WAN, its examples, its working, protocols, technologies, and many more.

FAQs
What are some of the most common WAN issues?
Common WAN issues include loss of Internet connectivity, DNS issues, interface issues, router configuration issues, etc.
Is it possible to have a LAN in a WAN?
It is possible, and almost always the case, for LANs to be linked to WANs.
What is one of the most serious problems in WAN?
One of the most serious problems with WAN is a lack of bandwidth.
Why are WANs so popular?
Through a WAN provider, WANs can facilitate communication, information sharing, and much more between devices worldwide.
How are WANs interconnected?
WANs can be linked via the internet, leased lines, or satellite links.
What are the advantages of WAN?
Some of the benefits of WAN include: Improve efficiency Communication is simple. Broad network coverage Distribute information over a large area, etc.
What is the WAN speed?
The WAN can reach speeds of up to 150 Mbps.
What is the world's largest WAN?
The Internet is the world's largest WAN.
How do WAN routers function in a network?
WAN routers connect different networks over vast geographical areas, facilitating data transfer between them. They route data packets to their destination, manage traffic, and ensure efficient communication by using various protocols. These routers can handle connections to multiple WAN technologies, such as MPLS, VPN, and dedicated leased lines, providing seamless connectivity across the network.
What are the common technologies used in WAN connections?
Common technologies employed in WAN connections include MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), leased lines, broadband, point-to-point links, and cellular data networks. These technologies provide various speed, reliability, and capacity levels, allowing organizations to choose the best fit for their connectivity needs.
What role does WAN play in business continuity and disaster recovery?
WAN is crucial in business continuity and disaster recovery by enabling remote data backup and access to critical applications from different locations. In case of a local failure, WAN ensures that teams can still operate from alternate sites, access essential data, and maintain communication. It is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring operational resilience.
How does WAN affect the performance of applications?
WAN can significantly influence application performance due to latency and bandwidth limitations. Information travels longer distances, which can result in delays. Therefore, optimizing WAN connections with techniques like compression, caching, and Quality of Service (QoS) can enhance application responsiveness, especially for latency-sensitive applications like video conferencing.
Why is security important in WAN configurations?
Security is vital in WAN configurations due to the transmission of sensitive data across public or shared networks. Implementing security measures such as encryption, firewalls, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) helps protect data integrity and confidentiality. These safeguards prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
What are the advantages of using a WAN for organizations?
WANs offer organizations several advantages, such as improved communication between geographically dispersed offices, centralized data management, and increased collaboration. Besides all this, WANs enable organizations to streamline operations and enhance overall productivity by connecting multiple sites.

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio