Knowing nav Tag in HTML
Have you ever wondered how websites organize their menus and links for easy navigation? The HTML <nav> tag is the key for this, which is specifically designed to define navigation sections. It not only enhances the semantic structure and accessibility of web pages but also plays a key role in SEO and user experience by clearly marking the primary navigational areas of a site. Let us understand more!





Best-suited Web Development courses for you
Learn Web Development with these high-rated online courses
What is a nav Tag in HTML?
The HTML <nav> tag is a semantic element introduced in HTML5, specifically designed to define a section of a webpage that contains navigation links to other pages or to different parts of the same page. It plays a crucial role in web development. The <nav> tag gives semantic meaning to the enclosed content, indicating that it's a navigation section. It can improve a site's SEO because search engines prefer well-structured and semantically meaningful content.
Let's first check out a video on the same.
Source: Code Range

Basic Syntax of nav Tag in HTML
<nav>
<!-- Navigation links go here -->
<a href="page1.html">Page 1</a>
<a href="page2.html">Page 2</a>
<!-- More links can be added as needed -->
</nav>
This tag is specifically meant for major navigation blocks, like the primary menu of a website. It helps with the semantic organization of the webpage, making it more accessible and understandable both for users and search engines.
Usage of HTML nav Tag with Examples
Let's see some examples showing the uses of the nav tag.
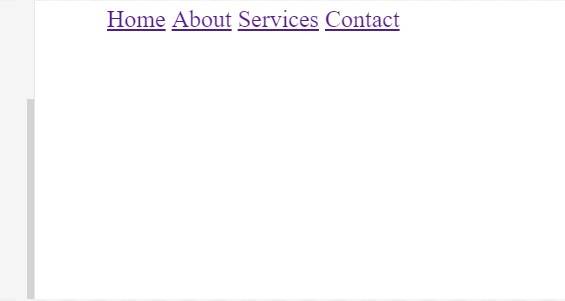
Example 1: Basic Horizontal Navigation Bar
Problem Statement: Create a simple horizontal navigation bar for a website.
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Horizontal Navigation Bar</title> <!-- Styling for horizontal navigation --> <style> nav ul { list-style-type: none; } nav ul li { display: inline; margin-right: 20px; } </style></head><body> <!-- Navigation section --> <nav> <ul> <!-- Navigation links --> <li><a href="#">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#">About</a></li> <li><a href="#">Services</a></li> <li><a href="#">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav></body></html>
Output
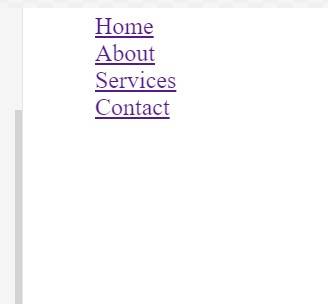
Example 2: Vertical Navigation Sidebar
Problem Statement: Create a vertical navigation sidebar.
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Vertical Navigation Sidebar</title> <!-- Styling for vertical navigation --> <style> nav ul { list-style-type: none; } nav ul li { margin-bottom: 10px; } </style></head><body> <!-- Sidebar navigation section --> <nav> <ul> <!-- Sidebar links --> <li><a href="#">Dashboard</a></li> <li><a href="#">Profile</a></li> <li><a href="#">Messages</a></li> <li><a href="#">Settings</a></li> </ul> </nav></body></html>
Output
Example 3: Breadcrumb Navigation
Problem Statement: Implement breadcrumb navigation for a website.
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Breadcrumb Navigation</title> <!-- Styling for breadcrumb navigation --> <style> nav { margin-bottom: 20px; } .breadcrumb { list-style-type: none; } .breadcrumb li { display: inline; } .breadcrumb li::after { content: " > "; } .breadcrumb li:last-child::after { content: ""; } </style></head><body> <!-- Breadcrumb navigation section --> <nav> <ul class="breadcrumb"> <!-- Breadcrumb links --> <li><a href="#">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#">Category</a></li> <li>Product</li> </ul> </nav></body></html>
Output
Example 4: Navigation with Dropdown Menus
Problem Statement: Create a navigation bar with dropdown menus for subcategories.
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Navigation with Dropdowns</title> <!-- Styling for navigation with dropdown menus --> <style> nav ul { list-style-type: none; } nav ul li { display: inline-block; position: relative; } nav ul li ul { display: none; position: absolute; list-style-type: none; } nav ul li:hover ul { display: block; } </style></head><body> <!-- Navigation section with dropdowns --> <nav> <ul> <!-- Main navigation item with dropdown --> <li><a href="#">Services</a> <ul> <!-- Dropdown links --> <li><a href="#">Web Design</a></li> <li><a href="#">Hosting</a></li> </ul> </li> <li><a href="#">Products</a> <ul> <li><a href="#">New Arrivals</a></li> <li><a href="#">Most Popular</a></li> </ul> </li> </ul> </nav></body></html>
Output
Example 5: Responsive Navigation Bar
Problem Statement: Create a responsive navigation bar that adapts to different screen sizes.
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Responsive Navigation Bar</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <!-- Styling for responsive navigation --> <style> nav ul { list-style-type: none; } nav ul li { display: inline-block; } /* Responsive design for smaller screens */ @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { nav ul li { display: block; } } </style></head><body> <!-- Responsive navigation section --> <nav> <ul> <!-- Responsive navigation links --> <li><a href="#">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#">About</a></li> <li><a href="#">Services</a></li> <li><a href="#">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav></body></html>
Output




Key Takeaways
-
The HTML <nav> tag provides a semantic way to define navigation sections, enhancing the structure and readability of web content.
-
It improves accessibility, allowing screen readers and assistive technologies to identify navigation areas for better user navigation.
-
Using <nav> helps in search engine optimization (SEO) as it clearly defines navigation links, which are important for site crawling.
-
<nav> makes designing user-friendly and organized navigation menus easier, which is crucial for a positive user experience.
FAQs
What is the purpose of the nav tag in HTML?
The nav tag is a semantic HTML element used to define a section of a page that links to other pages or to parts within the page: a section with navigation links. It is intended to help with the document's structure and provide a semantic meaning to web navigation areas.
How does the nav tag improve accessibility in web design?
Using the nav tag improves accessibility as it allows screen readers and other assistive technologies to identify the navigation sections of a web page. This helps users with disabilities easily find and navigate through the main sections of a page.
Can you have multiple nav tags on a single HTML page?
Yes, it's perfectly acceptable to have multiple nav tags on a single page. However, it's recommended to use them for major navigation blocks. For example, you might have one for the primary site navigation and another for a sidebar or footer navigation.
What is the difference between the nav tag and other linking elements like div?
The key difference is semantic meaning. While both nav and div can be used to group elements, nav is specifically meant for navigation links. This semantic distinction helps with search engine optimization and accessibility, as it provides more context about the purpose of the content within the tag.
Should all links on a webpage be placed inside a nav tag?
No, not all links need to be inside a nav tag. The nav tag should be reserved for major block of navigation links. If the links are not a major part of the page's navigation, such as links within an article's content, they should not be placed inside a nav tag.