What is the Zero Trust Model?
With cloud computing, remote workforces, and mobile devices becoming more prevalent, traditional security models can no longer protect sensitive data and information. This is where the Zero Trust model comes in. It is a security architecture that assumes no user, device, or network is inherently trusted and continuously verifies every user and device attempting to access resources.
In this article, we will explore the Zero Trust model in great detail. But, before moving ahead, let's explore the topics we will cover in this article. ,
Table of Contents (TOC)
- What Is the Zero Trust Model?
- How Does Zero Trust Enhance Security in Modern Organizations
- What Are the Three Principles of Zero Trust?
- Why Is Identity Verification Crucial in a Zero Trust Approach?
- How Can Zero Trust Be Implemented in a Multicloud Environment?
- What Are the Challenges in Adopting Zero Trust?
- How Does Zero Trust Differ from Traditional Security Models?
What Is the Zero Trust Model?
The Zero Trust model is a security concept where no one is trusted by default. Even if they are inside the network, verification is required from everyone trying to access resources.
Best-suited Networking courses for you
Learn Networking with these high-rated online courses
How Does Zero Trust Enhance Security in Modern Organizations?
Zero Trust enhances security by continuously verifying every user and device through various methods, such as multi-factor authentication, device posture checks, and identity and access management controls. Doing so reduces the chance of unauthorized access and limits the spread of data breach within a network.
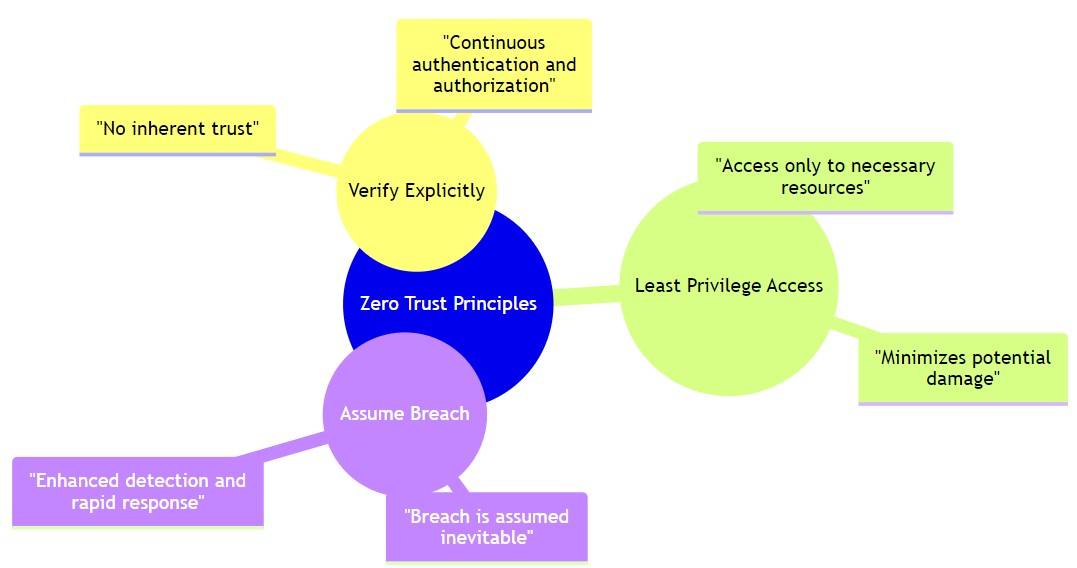
What Are the Three Principles of Zero Trust?
The three principles of Zero Trust are:
- Verify: Never trust; always verify. All users and devices must be authenticated and authorized before being granted network access.
- Least Privilege: Users should only have access to the resources they need to do their job and nothing more. Doing so reduces the attack surface and limits the damage that can be done in case of a breach.
- Assume Breach: Assume that a breach has occurred or will occur at some point. It means monitoring all network activity and implementing real-time measures to detect and respond to suspicious behaviour.
Why Is Identity Verification Crucial in a Zero Trust Approach?
Identity verification is crucial in a zero trust approach because it helps to ensure that only authorized users and network devices can access sensitive data or critical systems.
In a zero trust model, every user, device, and application is treated as a potential threat until proven otherwise. By verifying the identity of users and devices before granting access, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
How Can Zero Trust Be Implemented in a Multicloud Environment?
In a multicloud environment, Zero Trust can be enforced by:
- Implementing consistent security policies across all cloud platforms by using a cloud security solution.
- Using centralized identity management to manage user access to resources across multiple cloud platforms from a single point of control.
- Implementing micro-segmentation (dividing a network into smaller segments to isolate resources and control access) to isolate resources and control access.
What Are the Challenges in Adopting Zero Trust?
Here are the main challenges in adopting Zero Trust:
- Adopting Zero Trust requires significant changes to existing infrastructure, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Organizations must continuously monitor and verify access requests, which can be resource-intensive.
- Strict verification processes may create additional steps for users to access resources, which in turn will hamper user experience.
- Adopting Zero Trust requires a cultural shift within an organization to ensure buy-in from all stakeholders.
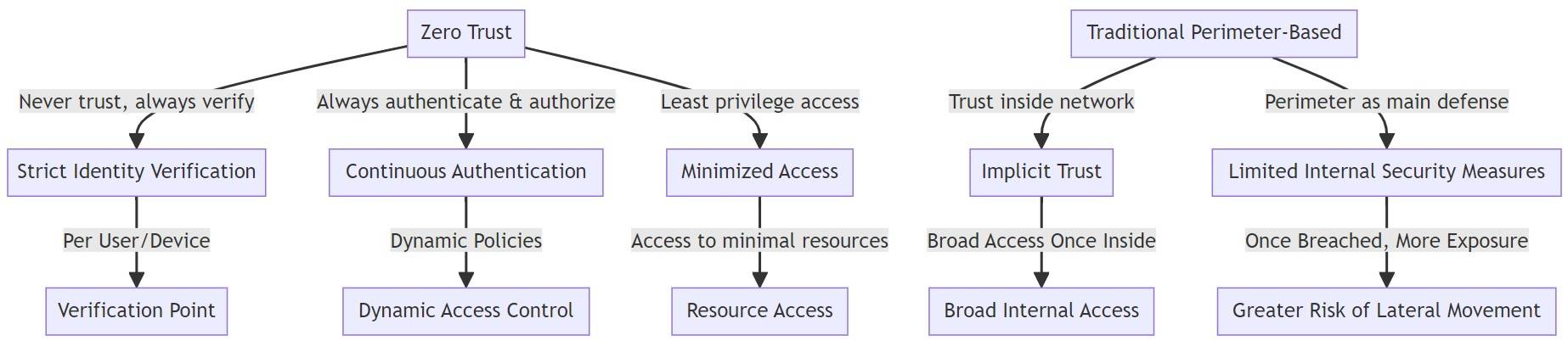
How Does Zero Trust Differ from Traditional Security Models?
Zero Trust differs from traditional security models by assuming no user, device, or network is inherently trusted. Traditional models relied on a perimeter-based approach, where users inside the network were trusted.
Must Explore Articles:





FAQs Related to Zero Trust
What Role Does Zero Trust Play in Remote Work Security?
Zero Trust secures data and resources in remote work by ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access corporate resources, regardless of their location. It helps mitigate the risks associated with remote access.
How Are Devices Managed Under a Zero Trust Architecture?
In a zero trust architecture, devices are managed by:
- Continuously assessing their security posture
- Enforcing compliance with security policies,
- Granting access to network resources based on the device's verified security status.
This approach assumes that all devices, users, and traffic are potentially hostile and implements strict security controls to prevent unauthorized access to network resources.
What Are the Future Trends in Zero Trust Security?
Here are some of the future trends in Zero Trust Security:
- Increased adoption of cloud-based security solutions
- Integration with emerging technologies like 5G and IoT
- Use of advanced analytics and machine learning for continuous monitoring and threat detection
- More automation in security checks
- Integration of artificial intelligence to detect threats

Anshuman Singh is an accomplished content writer with over three years of experience specializing in cybersecurity, cloud computing, networking, and software testing. Known for his clear, concise, and informative wr... Read Full Bio