
Skimming, scanning, and previewing are powerful reading techniques for IELTS that help you navigate passages efficiently, save time, and focus on what’s important—whether you’re quickly grasping the main idea, locating specific details, or understanding the text's structure. Previewing is a technique that can help you quickly assess a passage and identify its structure and key ideas. By previewing the text before you dive into reading it in detail, you can manage your time more effectively and answer questions with more confidence.
What is Previewing in IELTS Reading?
Previewing is the process of quickly scanning a passage to get a general idea of what it's about before reading it in full. It's like flipping through a book's chapters to understand the main points without reading every word. Often, previewing is also referred to as surveying, as it involves surveying the content to form a basic understanding of the passage’s structure and topics. By doing so, you can identify key areas that might contain important details for answering questions.
Predict your IELTS, TOEFL, and PTE in just 4 steps!
How Does Previewing Help?
The key benefit of previewing is that it saves time. By quickly scanning the title, headings, subheadings, and any highlighted or bolded text, you get an overview of the main topics without getting bogged down in details. This gives you a roadmap of the passage, helping you focus on the most important parts when answering questions. Since previewing helps you understand the structure of the text, it also helps with anticipating the type of information you will be looking for, making it easier to tackle questions efficiently.
How to Preview Effectively for IELTS Reading Success
To preview effectively, follow these steps:
- Read the title: This gives you a general sense of the topic.
- Scan the headings and subheadings: They act like signposts, helping you understand the structure of the text and the main themes.
- Glance at any visuals: Diagrams, charts, and images often summarize key ideas and can provide insights into the passage.
- Look for bolded or underlined words: These often highlight important concepts or keywords.
- Check the first sentence of each paragraph: These often introduce the main idea or topic of the paragraph.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to quickly gather a sense of what the passage is about without getting lost in details.
Previewing vs. Skimming vs. Scanning
Skimming focuses on quickly getting the general idea or overall sense of the passage, including reading the first and last sentences of paragraphs in detail and quickly browsing the content to understand its flow.
Scanning involves looking for specific information within the text, such as dates, names, or key facts, without reading the entire passage. This technique is typically used when you're answering detail-based questions like "True/False/Not Given" or "Multiple Choice," where you need to locate particular pieces of information quickly.
Previewing, on the other hand, emphasizes structural awareness. It helps you understand how the passage is organized and what key ideas each section will likely cover, which prepares you for more focused reading. Previewing is more about understanding the framework of the text rather than the specific content or the gist of the details.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping the title and headings: These are your first clues about the passage.
- Overlooking visuals: Charts, graphs, and images often summarize information and give you a head start.
- Getting stuck on the details: Remember, previewing is about getting the big picture, not about focusing on the small details just yet.
- Not reviewing the paragraph structure: Don’t ignore the first sentence of each paragraph. It often summarizes the main point of that section.
IELTS Reading Previewing Practice
Start with short articles or blog posts. Set a timer for two minutes and survey the text. Gradually move to longer passages. The more you practice, the sharper your previewing skills will become.
Task: Practice previewing the following short passage and answer the questions
The Concept of Role Theory
Role Set
A Any individual in any situation occupies a role in relation to other people. The particular individual with whom one is concerned in the analysis of any situation is usually given the name of focal person. He has the focal role and can be regarded as sitting in the middle of a group of people, with whom he interacts in some way in that situation. This group of people is called his role set. For instance, in the family situation, an individual’s role set might be shown as in Figure 6.
The role set should include all those with whom the individual has more than trivial interactions.
Role definition
B The definition of any individual’s role in any situation will be a combination of the role expectations that the members of the role set have of the focal role. These expectations are often occupationally denned, sometimes even legally so. The role definitions of lawyers and doctors are fairly clearly defined both in legal and in cultural terms. The role definitions of, say, a film star or bank manager, are also fairly clearly defined in cultural terms, too clearly perhaps.
C Individuals often find it hard to escape from the role that cultural traditions have defined for them. Not only with doctors or lawyers is the required role behaviour so constrained that if you are in that role for long it eventually becomes part of you, part of your personality. Hence, there is some likelihood that all accountants will be alike or that all blondes are similar - they are forced that way by the expectations of their role.
D It is often important that you make it clear what your particular role is at a given time. The means of doing this are called, rather obviously, role signs. The simplest of role signs is a uniform. The number of stripes on your arm or pips on your shoulder is a very precise role definition which allows you to do certain very prescribed things in certain situations. Imagine yourself questioning a stranger on a dark street at midnight without wearing the role signs of a policeman!
In social circumstances, dress has often been used as a role sign to indicate the nature and degree of formality of any gathering and occasionally the social status of people present. The current trend towards blurring these role signs in dress is probably democratic, but it also makes some people very insecure. Without role signs, who is to know who has what role?
E Place is another role sign. Managers often behave very differently outside the office and in it, even to the same person. They use a change of location to indicate a change in role from, say, boss to friend. Indeed, if you wish to change your roles you must find some outward sign that you are doing so or you won’t be permitted to change - the subordinate will continue to hear you as his boss no matter how hard you try to be his friend. In very significant cases of role change, e.g. from a soldier in the ranks to officer, from bachelor to married man, the change of role has to have a very obvious sign, hence rituals. It is interesting to observe, for instance, some decline in the emphasis given to marriage rituals. This could be taken as an indication that there is no longer such a big change in role from single to married person, and therefore no need for a public change in sign.
In organisations, office signs and furniture are often used as role signs. These and other perquisites of status are often frowned upon, but they may serve a purpose as a kind of uniform in a democratic society; roles without signs often lead to confused or differing expectations of the role of the focal person.
Role ambiguity
F Role ambiguity results when there is some uncertainty in the minds, either of the focal person or of the members of his role set, as to precisely what his role is at any given time. One of the crucial expectations that shape the role definition is that of the individual, the focal person himself. If his occupation of the role is unclear, or if it differs from that of the others in the role set, there will be a degree of role ambiguity. Is this bad? Not necessarily, for the ability to shape one’s own role is one of the freedoms that many people desire, but the ambiguity may lead to role stress which will be discussed later on. The virtue of j ob descriptions is that they lessen this role ambiguity. Unfortunately, job descriptions are seldom complete role definitions, except at the lower end of the scale. At middle and higher management levels, they are often a list of formal jobs and duties that say little about the more subtle and informal expectations of the role. The result is therefore to give the individual an uncomfortable feeling that there are things left unsaid, i. e. to heighten the sense of role ambiguity.
G Looking at role ambiguity from the other side, from the point of view of the members of the role set, lack of clarity in the role of the focal person can cause insecurity, lack of confidence, irritation and even anger among members of his role set. One list of the roles of a manager identified the following: executive, planner, policy maker, expert, controller of rewards and punishments, counsellor, friend, teacher. If it is not clear, through role signs of one sort or another, which role is currently the operational one, the other party may not react in the appropriate way — we may, in fact, hear quite another message if the focal person speaks to us, for example, as a teacher and we hear her as an executive.
IELTS Reading Previewing Exercises
Instruction: Read the passage title and the subheadings, then answer the following multiple-choice questions.
Questions 1-6
1. How is the passage structured?
(A) It is a single continuous discussion without headings.
(B) It is divided into several sections with subheadings.
(C) It presents only definitions without explanations.
(D) It contains only bullet points and lists.
2. What additional element is included in the passage besides text?
(A) A photograph of people in different roles
(B) A table comparing role definitions
(C) A diagram labeled "Figure 6"
(D) A timeline of role theory development
3. What does the title The Concept of Role Theory suggest about the passage?
(A) It will explain how roles function in society and workplaces.
(B) It will describe the history of role-playing games.
(C) It will focus only on the psychological effects of different roles.
(D) It will analyze the roles of actors in the film industry.
4. Which of the following words appears in a special format in the passage?
(A) "Ambiguity" (bolded)
(B) "Focal person" (italicized)
(C) "Hierarchy" (underlined)
(D) "Manager" (capitalized in all letters)
5. Based on the subheadings (e.g., Role Set, Role Definition, Role Ambiguity), what can you predict about the passage?
(A) It will focus on legal definitions of roles in business.
(B) It will explain different aspects of how roles are defined and understood.
(C) It will criticize the idea of role theory in psychology.
(D) It will compare role theory to other learning methods.
6. Which section is most likely to discuss difficulties or confusion related to roles?
(A) Role Set
(B) Role Definition
(C) Role Ambiguity
(D) Role Success
7. Based on the first two sentences of the passage, what can you predict about its focus?
"Any individual in any situation occupies a role in relation to other people. The particular individual with whom one is concerned in the analysis of any situation is usually given the name of focal person."
(A) The passage will explain different types of social roles and how they interact.
(B) The passage will discuss leadership styles in organizations.
(C) The passage will focus on the history of human behavior studies.
(D) The passage will compare cultural differences in social roles.
Answers for Questions 1-7
1. Answer: (C) Three main parts
Explanation: The passage is divided into three main sections with the headings Role Set, Role Definition, and Role Ambiguity. These indicate distinct parts of the discussion on role theory.
2. Answer: (A) Yes, a diagram labeled "Figure 6"
Explanation: The passage mentions Figure 6, which is described as a diagram illustrating the concept of a role set in a family situation.
3. Answer: (A) The passage will explain different types of social roles and how they interact.
Explanation: The first two sentences introduce the concept of roles in relation to others, suggesting that the passage will explore various roles and how they function in social settings.
4. Answer: (A) The Concept of Role Theory suggests a discussion about roles in social and professional contexts.
Explanation: The title includes Role Theory, which implies a theoretical explanation of roles in different settings, likely touching on their definitions, functions, and complexities.
5. Answer: (C) Italicized words, such as "focal person".
Explanation: The passage contains italicized words to emphasize key terms, such as focal person, which is a central concept in the text.
6. Answer: (A) The passage explains roles, their definitions, and challenges.
Explanation: The subheadings Role Set, Role Definition, and Role Ambiguity indicate a structured discussion on how roles are defined, how they function, and the problems associated with them.
7. Answer: (D) "Role Ambiguity" discusses challenges related to unclear roles.
Explanation: The section titled Role Ambiguity focuses on uncertainty and confusion regarding roles, which can cause stress and difficulty in communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is previewing different from skimming?
Previewing is a reading technique that focuses on understanding the structure and framework of a passage, such as identifying headings, subheadings, visuals, and key formatting. Unlike skimming, it emphasizes how the text is organized rather than its overall gist or content.
Why is previewing useful for the IELTS reading test?
Previewing helps you quickly grasp the layout and structure of the passage, making it easier to locate specific information or understand the passage's flow during detailed reading.
When should I use previewing during the IELTS reading test?
Use previewing at the start of a passage to get an overview before diving into skimming or scanning for answers.
What are the key elements to look for while previewing a passage?
Focus on the title, headings, subheadings, bolded or italicized words, visuals (diagrams, charts, or images), and any highlighted or numbered lists.
How can previewing improve time management during the test?
By previewing first, you save time by knowing where specific information is likely to be in the passage, reducing the need to read every line or search aimlessly.
Comments
(1289)
3 months ago
T
9 months ago
R
9 months ago
R
a year ago
M
a year ago
R
a year ago
Hello Mustafijur. If you are looking for assistance with applying to universities abroad. Get in touch with our Shiksha Study Abroad Counsellors and book a counselling session absolutely free, Click Here
a year ago
R
a year ago



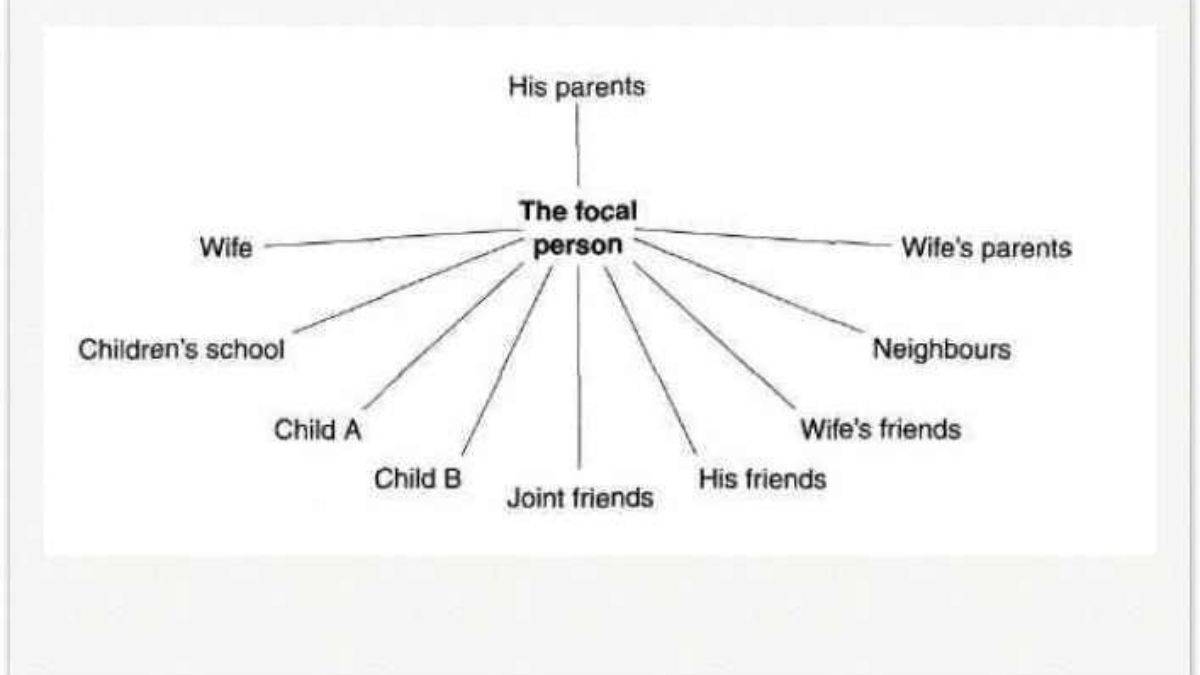 Figure 6
Figure 6