To learn about electric charge Class 12, we need to be aware of the fact that when breaking down any matter into smaller parts, it follows a universal order. Matter breaks into compounds, compounds break into molecules, molecules break into atoms, and atoms break into subatomic particles. Electron, Proton, and Neutron.
These particles at the subatomic level have some intrinsic properties, including space, mass, and charge.
Electric charge, too, is an intrinsic property. What this means is that all subatomic particles, by virtue of their existence, have electric charges.
We also need to know that there are two types of electric charge: positive and negative. A proton carries a positive charge, while an electron carries a negative charge. In Class 12 Physics, we learn that positive and negative charges differ based on their direction or polarity of charge.
As you go ahead, you will find out that electric charge is the foundation of electromagnetism, an important topic for CBSE boards and other competitive exams. Even the study of stationary electric charges, known as electrostatics, helps us understand how charges in the presence of electric field lines or magnetic fields exert forces. So being clear with the electric charge Class 12 notes is quite necessary.
What You'll Learn with our Electric Charge Physics Notes
- Gain a deeper explanation of the NCERT definition of electric charge with practical examples. By the end of this guide, you will be able to explain how and why electric charge is an intrinsic property and describe its two types clearly.
- Understand and readily apply the three main properties of electric charge, which are additivity, conservation, and quantisation, to confidently solve JEE mains-level questions.
- What is an Electric Charge?
- Is Electric Charge Scalar or Vector?
- Types of Electric Charge
- Three Properties of Electric Charge
- Methods of Charging Class 12
- JEE Mains Practice Problems for Electric Charge
- What Type of Questions Should You Expect on Electric Charge Class 12?
- Complete Study Material for Class 12
- Frequently Asked Questions on Electric Charge Class 12
What is an Electric Charge?
An electric charge is the intrinsic property of elementary particles that causes matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
NCERT's class 12 physics book discusses how electricity was termed after the Greek word, elektron that meant amber. It also describes a historical explanation of the electric charge term below.
"It was concluded, after many careful studies by different scientists, that there were only two kinds of an entry, which are called the electric charge....
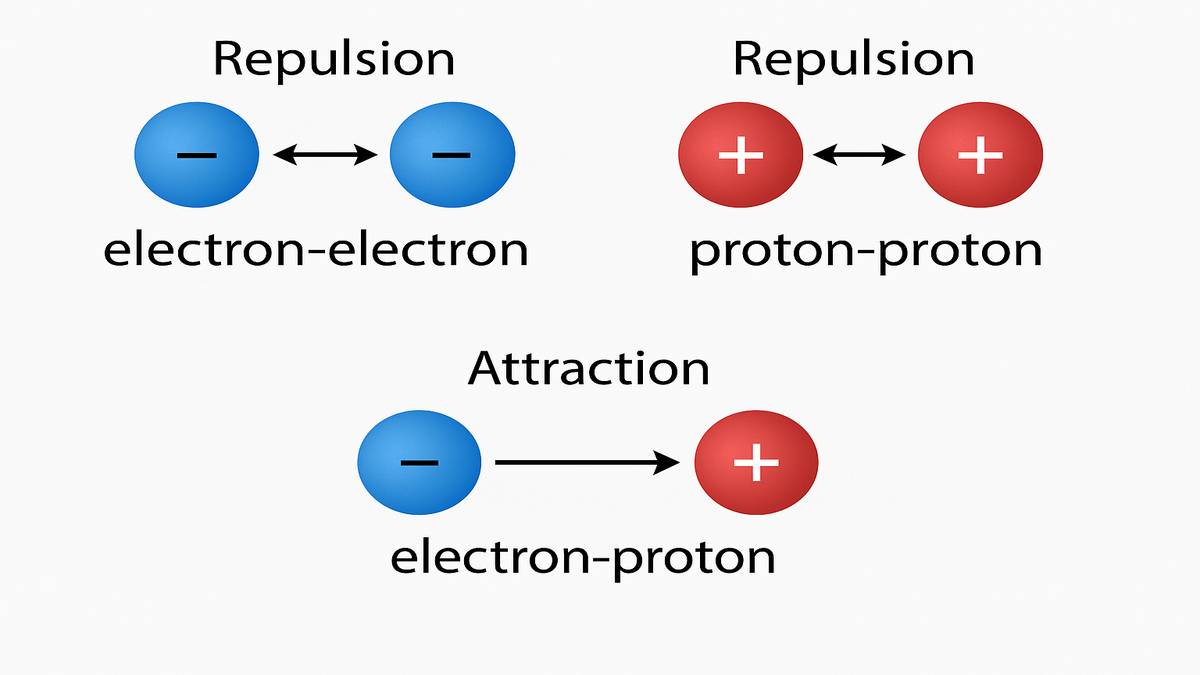
...There are two kinds of electrification, and we find that (i) like charges repel and (ii) unlike charges attract each other."
In the above explanation, we understand that an entry can be an entity or a type of electric charge, which can be either positive or negative.
Some basic principles of electric charge Class 12 you should know.
- Electric charge can neither be created nor destroyed.
- There are only two types of electric charges: positive and negative.
- The net amount of electric charge in any object will be an integral multiple of the free electrons present in the object.
The basic formula for electric charge in physics is
Where ,
is an integer
Q is the total electric charge
- We can also measure electric charge in terms of electric current. It's the rate at which the charge flows through a conductor in a given time. The formula for electric current is:
-
= Electric current (in Ampere)
-
= Time (in seconds)
- The SI unit of electric charge is Coulomb (C). Microcoulomb (μC) and nanocoulomb (nC) are also widely used as units of charge. You may also go back to brush up on units and measurement.
Is Electric Charge Scalar or Vector?
Electric charge is a scalar quantity. It only depicts its nature through signs. And it does not tell us a physical direction as a vector would. So, only the magnitude is enough to specify the electric charge. Neither does it need to obey vector addition laws, ie, the triangle law or parallelogram law.
All you need to know about electric charge in Class 12 is that it follows the basic algebraic operations, such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
For example, the net charge in an isolated system is always the sum of all individual charges. It does not matter if the charges have any direction.
Types of Electric Charge
As mentioned above, there are two types of electric charge: positive and negative.
- Protons have a positive charge. But, the positive Charge is a result of the absence of free electrons in conductors. We denote that by the "+" sign.
- Electrons have a negative charge. The net negative charge means the conductor or the object has excess electrons. We use the "-" sign.
If there is an equal amount of positive and negative amount of charges, they cancel each other out, and the object remains neutral.
Like charges repel each other, and opposite charges attract each other. This aspect of electric charge is called the polarity of charges.
Three Properties of Electric Charge
There are three basic properties of electric charge in Class 12 Physics.
Additivity of Electric Charge
When there are 'n' number of charges present in an isolated system, the net charge in an isolated system is the algebraic sum of all the individual charges present in the system. Mathematically:
But, whenever there is a continuous charge distribution, we use integration for the net charge:
Where, is the small element of charge present.
Quantisation of Electric Charges
Electric charge always exists as an integral multiple of the quantum unit (the smallest possible unit) of charge. This is equivalent to the charge of an electron. The basic formula for electric charge that we saw earlier is this.
Where:
-
= total charge
-
-
= integer ( )
Conservation of Electric Charge
Two descriptions explain the conservation of charge.
- Electric charge can be only transferred from one object to another, but charge cannot be either created or destroyed.
- The above statement gives another description: the net charge in an isolated system is always the same.
The conservation of charges holds for all the processes and situations of electrostatics, whether dynamic or static.
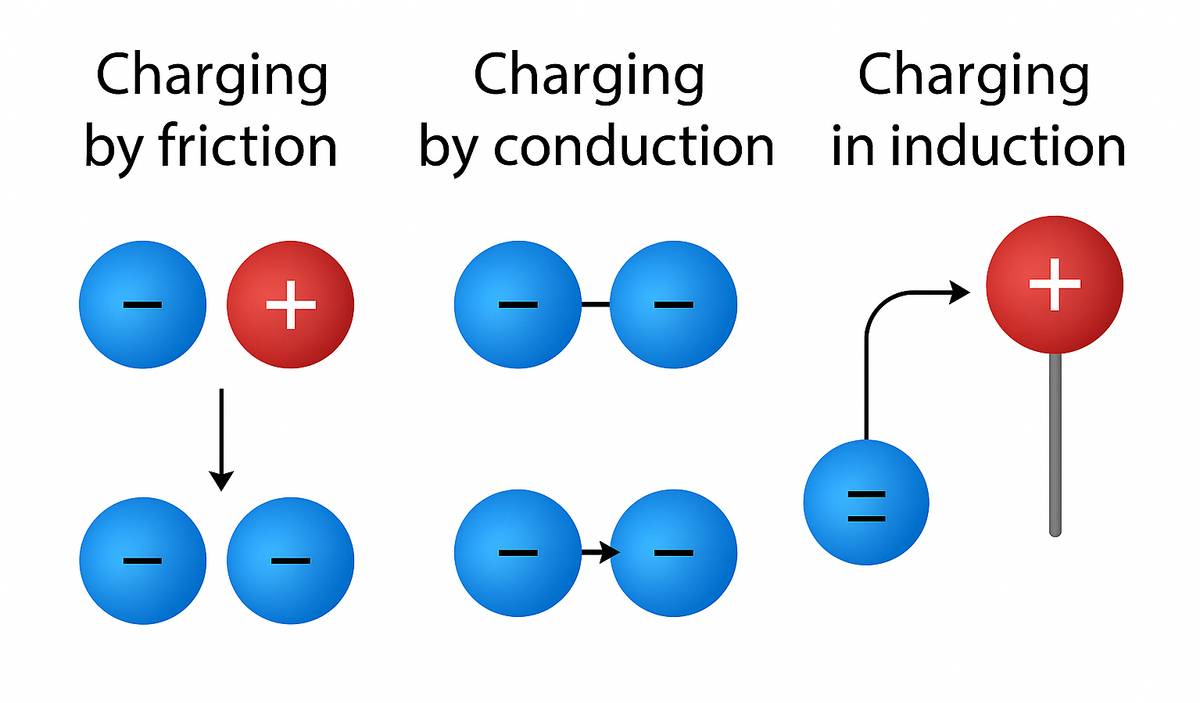
Methods of Charging Class 12
The process of transferring electric charge to a body (either by extracting a free electron or by adding free electrons) is called charging. So, the object becomes positively or negatively charged.
There are three methods of charging.
- Charging by friction
- Charging by conduction
- Charging by induction
Charge by Friction
When we rub two objects together, there is a transfer of free electrons from one object to another. The friction while rubbing causes electrons present in the outermost shell to break free and transfer to another body.
That's why the net negative charge in one body will be equal to the net positive charge on the other body involved in the process.
Charge by Conduction
When an uncharged object comes in proximity to and touches any charged object, it shares the total electric charge present in the system. When these two charged bodies in touch are separated, both objects share the total charge individually. This means the uncharged body is also charged. One of these bodies will discharge, and the other will be charged, to achieve stability.
Charging by Induction
The method of charging an uncharged body (conducting) when it is only near but not in touch causes electrons to displace due to electrostatic repulsion. This causes polarisation of total charges in the conductor; positive charges are collected in one corner, and negative charges are collected in another corner. By connecting one corner to earth, the net positive charge on the other end goes to earth. Only another end charge remains in the body. This process of charging is called charging by induction.
JEE Mains Practice Problems for Electric Charge
Below are JEE-type practice problems available below.
What Type of Questions Should You Expect on Electric Charge Class 12?
In the electric charge Class 12 topic, you could expect questions that test you on the following.
- Basic conceptual principles and properties, ranging from the conservation of charges, quantisation, and the types. For applied questions on these concepts, you will have to remember the main electric charge formula, Q = ne.
- Secondly, you should definitely look into finding the net electric field from different sources of charge.
Complete Study Material for Class 12
Frequently Asked Questions on Electric Charge Class 12
Commonly asked questions
Why do conductors have a positive charge, a lack of free electrons, not as excess number of protons?
This is an interesting question! Even though a proton has a positive charge, the net positive charge in a conducting material is always due to the removal of free electrons.
This happens due to the availability of only free electrons in all conductors. Since protons are present in the nucleus, they can not roam freely in the conductor, as electrons travel freely in the conductor due to their presence in the outer shell.
Why is an electric charge a scalar quantity?
When two or more individual charges are present in a system, the total charge will be an algebraic sum of all individual charges and not the vector sum. Therefore, an electric charge is considered as a scalar quantity.
How is the body mass affected when charging?
You should know that electrons have a definite mass. The mass of a body increases a little when it gains electrons. The body mass can also slightly decrease if the body loses electrons during charging.
Physics Electric Charge and Field Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter