What are Alcohols?
Alcohols are organic compounds formed by a covalent bond of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups with the carbon atom. They get connected in an alkyl group.
Example – ethyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, etc. When there are two carbons, alcohol is called Ethanol. The general formula for alcohol is CnH2n+1OH.
Alcohols are commonly occurring organic compounds containing carbon. Most of the alcohols are colourless liquids or solid at room temperature.
Types of alcohol
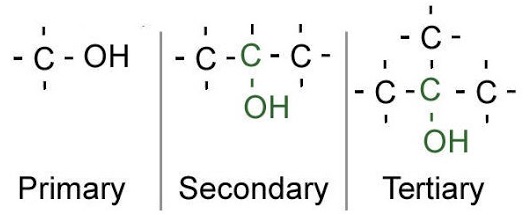
Alcohols are characterized by the number of carbon atoms that bond with the atom containing the hydroxyl functional group. Alcohols fall under three types, namely- Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary alcohols-
FAQS regarding Types of Alcohols
Q. What type of alcohol is methanol?
A. Methanol also called methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, or wood spirit is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a colourless liquid, highly flammable with air, and completely miscible in water.
Procedure to name alcohols is –
Find the longest and most continuous sequence of hydroxyl carbon atoms
Start numbering from the end of the chain and assign the lowest possible number to the -OH group attached to the carbon
Replace the ending -e with the suffix -ol
Suffixes such as -dilo and -trilo are put if there is the presence of multiple alcohols
A. Some of the uses are –
People consume it in the form of beverages because of the presence of 30-40% of Ethanol in it
When alcohol gets heated in the air, it can be used as a transportation fuel or blended with petrol
It behaves as a solvent when dissolved in liquids
Its use as an antiseptic agent is also becoming popular with time
A. Few properties of alcohol are –
Since they are hydrogen, carbon compounds are strongly polar
They have a high boiling point and are highly soluble in water too
They absorb many radiations
They are colourless at room temperature
Some highly branched and complex alcohols are solid at room temperature
A. Ethanol, when mixed with other ingredients, is called Denatured alcohol. It kills germs and is highly flammable. The usage of this type of alcohol is mostly in hand sanitisers and cleaning products. Similar to Ethanol, even Denatured alcohol is unsafe.
News & Updates
Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test