What is Charles Law?
Jacques Charles was a French founder, scientist, mathematician, and balloonist. Charles Law is all about the volume of the ideal gas at a consistent pressure and is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. Charles Law, also referred to as the law of volumes, provides information on how gas increases when the temperature rises.
If we use V1 and T1, they stand for the initial volume and gas temperature, and V2 and T2 as the final volume and temperature. The mathematical relationship of the Law of Charles becomes:
Equation IS = V2 / T2 can be V1 X T2 = V2 X T1.
Charles's Law is a unique theory law on gas. This law applies to gases that keep under constant pressure, but the temperature and volume are constantly changing. We can understand that, notably, the density of the gas is inversely proportional to the temperature in the Kelvin units, when it is at a constant mass and pressure.
What are the real-life examples of Charles's Law?
A hot air balloon, the human lungs, pool floats, a ping-pong ball with rackets, tyres, helium balloons, delicious bakery products like bread and cakes are some real-life examples of Charles's Law.
Explore exams which ask questions on Chemistry States of Matter
Select your preferred stream
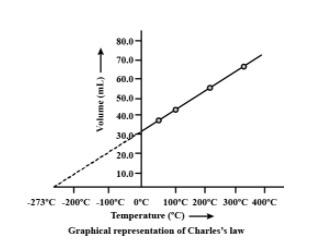
How do you explain Charles Law with the help of graphical representation?
The connection between the volume and the gas temperature can be constructed by graph plotting.
A straight line has been obtained. Here we are using a unit of temperature in Kelvin, for graphical presentation in Celsius units.
Illustrated Examples
1. Which law is the following formula?
V1/T1=V2/T2
Answer: Charles Law
2. A metal container of gas has a volume of 1500mL at 300C. What volume will the gas occupy at 00C if the pressure remains constant?
Answer: By Charles Law, we can say:
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
We have to convert the given temperatures to Kelvin.
300C+273=303K
00C+273=273K
We have to use these temperatures and the initial volume and then we can solve for the final volume of the gas.
The equation will be 1500mL / 303K=V2 / 273K
Then, The equation will be V2=(1500mL) X (273K) / 303K
Hence, the final volume will be after calculation, V2= 1351.48 which approximately = (1351mL)
FAQs on Charles Law
Q: What does Charles Law give its mathematical equation?
Q: What, in a simple concept, is Charles Law?
Charle’s law equation is as below:
V∝T
Here, V stands for the volume of the gas and T means temperature.
Q: Why does pressure have importance in Charles Law?
Q: In Charles Law, what are those constants?
Q: Why is the law of Charles significant?
News & Updates
Chemistry States of Matter Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test