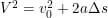- What is Kinetic Energy?
- Kinetic Energy: Formula
- Types of Kinetic Energy
- Derivation of Kinetic Energy
- Kinetic Energy Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Kinetic Energy
What is Kinetic Energy?
Force is required to make an object move or accelerate, and for every work, there should be work associated with it. When work is done, an external force releases the object’s energy to accelerate it, and the object moves at a constant speed. The energy that is transferred in the object is known as Kinetic energy. In other words, kinetic energy can be described as the object’s energy while in motion.
Kinetic Energy: Formula
The formula for kinetic energy shows the relationship between the mass of the body and the velocity of the body. It can be expressed as under:
K.E. = ½ mv2
Here,
- KE is the kinetic energy
- m denotes the mass of the body
- v denotes the velocity of the body
Types of Kinetic Energy
There are five types of Kinetic energy, which are listed below:
- Radiant energy
- Thermal energy
- Sound energy
- Electrical energy
- Mechanical energy
Derivation of Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy can be derived in a couple of ways, but algebra is considered the best way to fully understand the formula.
By using the work-energy theorem and the second law of Newton, the following equation will be formed:
- ΔK = W = FΔs = maΔs
After integrating it in kinematic equations, we will get:
On combining both the equations, we get
As we discussed above, the kinetic energy is held by virtue of its motion, and it will be zero when it is at rest position. So, we can say that:
- KE = ½ mv2
The derivation of kinetic energy can be calculated using the calculus method by using the work-energy theorem and the second law of Newton. In the calculus method, we just assume the acceleration of the object. After rearranging the work-energy theorem to get the function of the differential terms, we will get the final formula of kinetic energy as we did in the algebra method.
Kinetic Energy Illustrated Examples
Example 1) Write the types of Kinetic Energy.
Answer – There are five types of Kinetic energy, which are listed below:
- Radiant energy
- Thermal energy
- Sound energy
- Electrical energy
- Mechanical energy
Example 2) Write two examples of thermal and sound energy.
Answer – Hot springs and heated swimming pools are examples of thermal energy. On the other hand, the tuning fork and the beating drums are examples of sound energy.
Example 3) Write the meaning of Electrical energy.
Answer – Electrical energy can be defined as the combination of positive and negative charge-free electrons.
FAQs on Kinetic Energy
Q: The potential energy function for a particle executing linear simple harmonic motion is given by V(x) =kx^2/2, where k is the force constant of the oscillator. For k = 0.5 N m^-1, the graph of V(x) versus x is shown in Fig. 6.12. Show that a particle of total energy 1 J moving under this potential must ‘turn back’ when it reaches x = ± 2 m.
A:
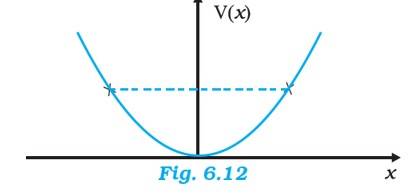
Given, particle energy , E = 1 J,
- Force constant, k = 0.5 N/m
- Kinetic energy, KE = 1/2mv2
- From the equation, total energy, E = KE +PE,
- we get 1 = (1/2)mv2 + (1/2) kx2 when it turns back, v becomes 0
- 1 = (1/2) X 0.5 X x2 , x = ± 2
Q: What do you mean by Kinetic Energy?
A: Kinetic energy can be described as the energy held by the object by its motion.
Q: What is the formula of Kinetic Energy? A: The formula of Kinetic energy is K.E. = ½ mv2
A: The formula of Kinetic energy is K.E. = ½ mv2
Q: What is the derived unit of kinetic energy?
A: The derived unit of Kinetic energy is Joules (J).
Q: What factors affect the kinetic energy?
A: The two factors that affect the kinetic energy of a moving object are mass and the speed of the object.
Q: What is m in the formula of Kinetic energy?
A: The m in the Kinetic energy is the mass of the body or an object.
Physics Work, Energy and Power Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test