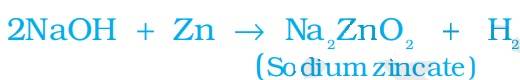What are acids and bases?
An acid contains hydrogen particles and donates protons to other substances and compounds. A base could be an ion or compound, and it accepts the hydrogen particles from acids. Acids could be identified by taste because it's acidic and sour in nature. Even after donating hydrogen ions, the taste of acids remains the same. Acids turn blue litmus red.
Bases are known to turn red litmus blue. Bases are somewhat bitter in taste. The bases which dissolve or disappear in water are known as alkali. When bases react with acids, they form the salt.
- Acids and Bases with metals
- pH level and properties of Acids and Bases
- FAQs on Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases with metals
when acids and bases react with metal, metal replaces the hydrogen from the acids. This chemical reaction can be seen as hydrogen gas. The remaining part of the acids reacts with the metal and produces salts.
Acid +Metal Salt + Hydrogen Gas.
The chemical reaction between acids, bases, and metals can be understood from the following diagrammatic presentation.
The above reaction can also be written as:
It can be seen in the above chemical reaction that hydrogen is produced, but with metals, this case is not possible.
pH level and properties of Acids and Bases
To find the acidity level of any substance, the pH level is used as a parameter. The PH level of a substance is found with the help of a Litmus paper.
- Acids: Acids turn blue litmus red. The acid's acidity level is high. When acids release the hydrogen ion from concentration, the acidity level of acid remains almost the same. The acidity scale ranges from 0 to 14. 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the least acidic substance. The properties of acids are as follows:
- The pH level of all the acids are less than 7
- They are corrosive in nature because of their high acidic properties
- When metals and acids react, they produce hydrogen gas
- Acids can produce electricity and are considered good conductors
- Some examples of acids are Sulphuric acid, Hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, etc
- Bases: Bases turn red litmus blue. The acidity level of bases is generally low. The pH scale of bases is always more than 7 because they are less acidic in nature. The properties of Bases are as follows:
- The Ph level of all bases are more than 7
- When they dissolve in water, they release hydrogen ions
- Examples of bases are sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, etc
Acids and Bases for Class 10
This chapter is good to understand and grasp the context of Acids and bases, and it carries a weightage of 3-4 marks overall. This contains one small objective type question and also three small one-mark questions accounting for the overall marks mentioned above.
Illustrated Examples
Example 1) State the chemical formula of the fluorosulfuric acid.
Answer – The chemical formula of fluorosulfuric acid is HSO3F.
Example 2) State the name of the most dangerous acid.
Answer – The most dangerous acid is Hydrofluoric acid.
Example 3) describe the fatal amount of hydrochloric acid.
Answer – the fatal amount of hydrochloric acid is 33% in 250ml.
Explore exams which ask questions on Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts
Select your preferred stream
FAQs on Acids and Bases
Q. What is the definition of acids by Lewis’s concept?
Q. What is the strongest acid on the earth?
Q. Which acid is considered as only weak acid?
Q. Which acid is the least corrosive?
Q. What is the pH level of Sulphuric acid?
Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test